Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K731000"
Liyingying (Talk | contribs) |
Liyingying (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 51: | Line 51: | ||
=Characterization by GZ_HFI 2020= | =Characterization by GZ_HFI 2020= | ||
*'''Group:''' GZ_HFI 2020 | *'''Group:''' GZ_HFI 2020 | ||
| − | *Based on this part,we amplified the DNA sequence containing only cyse gene [[Part: | + | *Based on this part,we amplified the DNA sequence containing only cyse gene [[Part:BBa_K3595004]] from <i>E.coli dh5a</i> genome. In order to increase cysteine production, we constructed different cyse mutant genes [[Part:BBa_K3595005]],[[Part:BBa_K3595006]],[[Part:BBa_K3595007]], [[Part:BBa_K3595008]],[[Part:BBa_K3595009]], [[Part:BBa_K35950010]], [[Part:BBa_K3595011]]. By placing these elements downstream of the PTac promoter, we successfully constructed pBR322-KanR-pTac-cysE and pBR322-KanR-pTac-cysE-mutant. |
*In addition, we also established a method for quantitative detection of cysteine, and have completed the functional test of wild-type cysE and different cysE-mutants; | *In addition, we also established a method for quantitative detection of cysteine, and have completed the functional test of wild-type cysE and different cysE-mutants; | ||
==Experimental Setup== | ==Experimental Setup== | ||
| Line 67: | Line 67: | ||
====Cysteine analysis and quantification==== | ====Cysteine analysis and quantification==== | ||
*0.1 ml supernatant of each EcN solution is taken from Deep-well Multiwell Plate and added to 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes respectively. The same operation is repeated as testing standard samples, and then use spectrophotometer with light absorption at 560 nm to test the concentration of cysteine in the solutions. | *0.1 ml supernatant of each EcN solution is taken from Deep-well Multiwell Plate and added to 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes respectively. The same operation is repeated as testing standard samples, and then use spectrophotometer with light absorption at 560 nm to test the concentration of cysteine in the solutions. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Results== | ||
| + | *All of our engineered bacteria have shown great improvement in the ability to produce cysteine, which represents that they can absorb H2S to a larger extent. | ||
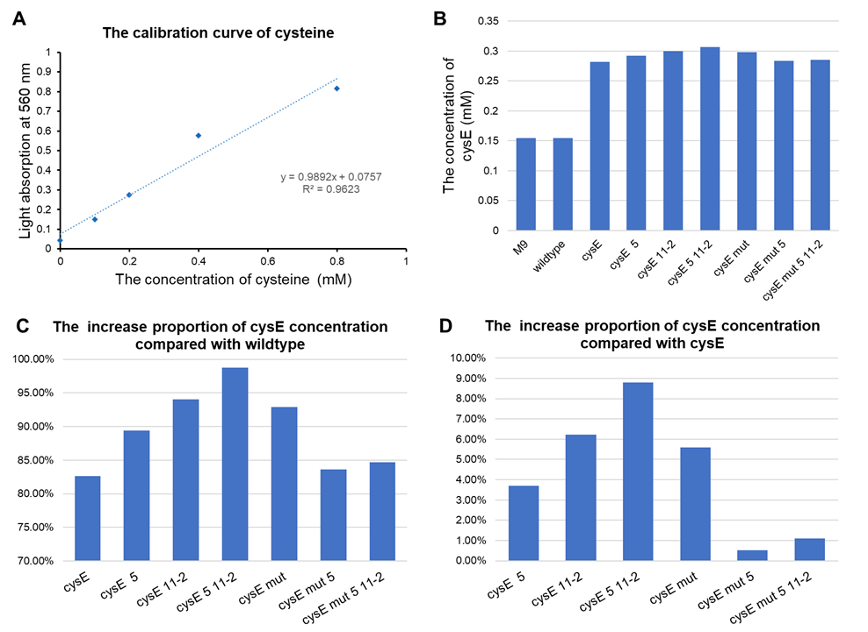
| + | *EcN with plasmid pTYT-cysE-5-11-2 had the best effect, 98.72% batter than EcN wildtype and 8.79% better than overexpression of cysE (pTYT-cysE) | ||
| + | [[File:T--GZ_HFI--H2S.png|600px|thumb|center|Detection results of the effect of the hydrogen sulfide pathway. (A) The calibration line of cysteine. (B) Concentration of cysteine detected in each group. (C) The ratio of increased cysteine concentration in each group compared to wildtype. (D) Cysteine production compared to pTYT-cysE. CysE-mut in the Figure stands for cysE-256. ]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here--> | ||
| + | =Reference= | ||
| + | Kondoh M, et al. L-Cysteine production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2019;103(6):2609-19. | ||
Revision as of 20:51, 27 October 2020
CysE (Serine Acetyltransferase)
CysE is an enzyme involved in cysteine biosynthesis, also known as SAT. It catalyzes the acetylation of serine to give O-acetylserine, a precursor for the biosynthesis of cysteine. Some O-acetylserine is also converted to N-acetylserine, which in turn triggers the assimilation of sulfate through specific genes.
This part has been successfully operated while controlled by araC-pBAD both in pSB1C3 (K731020) and the low copy vector pSB3C5, in which it was characterized.
This part was cloned by the iGEM Trento 2012 team for the creation of an aerobically engineered pathway for the removal of the black crust disfiguring marble stones. Further information about this part and its characterization can be found in the iGEM Trento 2012 wiki.
Usage and Biology
In Escherichia coli conversion of L-serine to L-cysteine is mediated by the action of two enzymes: serine acetyltransferase [1] catalyses the activation of L-serine by acetyl-CoA. Its product, 0-acetyl-L-serine (OAS), is then subsequently converted to L-cysteine by 0-acetyl-L-serine(thio1)lyase.
The synthesis of OAS-(thio1)-lyase and of the enzymes involved in sulphate uptake and reduction is regulated by induction as well as by repression [2].
The expression of cysE (the SAT structural gene), on the other hand, is constitutive whereas the catalytic activity of the gene product, SAT, is sensitive to feedback inhibition by L-cysteine [3].
Please head over to K731020 for documentation on characterization of this Part.
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 698
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterization by GZ_HFI 2020
- Group: GZ_HFI 2020
- Based on this part,we amplified the DNA sequence containing only cyse gene Part:BBa_K3595004 from E.coli dh5a genome. In order to increase cysteine production, we constructed different cyse mutant genes Part:BBa_K3595005,Part:BBa_K3595006,Part:BBa_K3595007, Part:BBa_K3595008,Part:BBa_K3595009, Part:BBa_K35950010, Part:BBa_K3595011. By placing these elements downstream of the PTac promoter, we successfully constructed pBR322-KanR-pTac-cysE and pBR322-KanR-pTac-cysE-mutant.
- In addition, we also established a method for quantitative detection of cysteine, and have completed the functional test of wild-type cysE and different cysE-mutants;
Experimental Setup
Bacteria culture
- Plasmid pBR322-KanR-pTac-cysE and pBR322-KanR-pTac-cysE-mutant was transfered into the Nissle host cell,respestively.
- Single colonies were selected from the experimental LB-agar plate , then inoculated into test-tube tubes with 4000 μL LB liquid medium with 4uL kanamycin for overnight growth at 37 °C and 200 rpm.
- Inoculating 15 uL of culture solution overnight into a 24-well plate containing 3 mL M9 medium for overnight growth at 37 °C and 200 rpm.The media contained 3 ul kanamycin and 1.5 uL 1M IPTG. At the same time, wild-type Nissle was inoculated as negative control, and M9 medium was used as blank control.
- Detecting cysteine concentration in culture medium.
Detection
Determination of Calibration Line
- Centrifuge tubes are added 0.1mM, 0.2mM, 0.4mM, 0.8mM, and 1mM to 1.5 ml standard samples of L-cysteine respectively with 0.1 ml acid ninhydrin reagent and 0.1 ml acetic acid, mixed thoroughly at room temperature.
- The centrifuge tubes are heated in the metal bath with 100 degrees Celsius for 10 minutes, and then rapidly cool in ice.
- Then 0.7 ml 95% ethanol is added in each centrifuge tubes and mixed thoroughly. A reagent blank without cysteine is prepared under the same condition.
- The pipette is used to shift 200 microliter solutions of each mixture to 96-well plates so that solution can be tested by infinite 200Pro spectrophotometer, with light absorption at 560 nm.
Cysteine analysis and quantification
- 0.1 ml supernatant of each EcN solution is taken from Deep-well Multiwell Plate and added to 1.5 ml centrifuge tubes respectively. The same operation is repeated as testing standard samples, and then use spectrophotometer with light absorption at 560 nm to test the concentration of cysteine in the solutions.
Results
- All of our engineered bacteria have shown great improvement in the ability to produce cysteine, which represents that they can absorb H2S to a larger extent.
- EcN with plasmid pTYT-cysE-5-11-2 had the best effect, 98.72% batter than EcN wildtype and 8.79% better than overexpression of cysE (pTYT-cysE)
Reference
Kondoh M, et al. L-Cysteine production by metabolically engineered Corynebacterium glutamicum. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 2019;103(6):2609-19.
