Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1825008"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1825008 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1825008 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This part codes for Stilbene synthase, the last enzyme in the resveratrol pathway, similarly to BBa_K1033002. However, this sequence is different and was available at the time our project started. | + | This part codes for Stilbene synthase, the last enzyme in the resveratrol pathway, similarly to BBa_K1033002. However, this sequence is different and was available at the time our project started. Thus we used it for our experiments. |
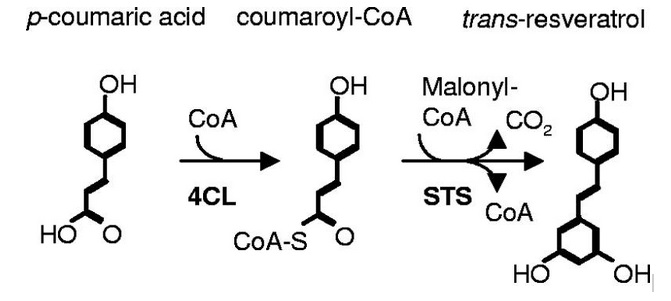
| + | Resveratrol is a phenolic compound found in grapes (''Vitis vinifera'') that is believed to have wide range of health benefits in mammals. Resveratrol exists as both cis- and trans-isomers, but only the trans-isomer has been found in grapes. Resveratrol is produced with intermediates from the phenylpropanoid pathway and is derived from p-coumaric acid which is an intermediate in lignin production. The two key enzymes are Coenzyme A (CoA) ligase (4CL) and stilbene synthase (STS). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:STS.jpg|700px|thumb|left|Resveratrol pathway]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | We have used this gene as a part of larger DNA construct that we have transformed into moss ''Physcomitrella patens''. ''P. patens'' has been shown to produce enzymes similar to 4CL. These enzymes from the Pp4CL family (''P. patens'') have been shown to have similar function as enzymes from the 4CL family of higher plants. This means that ''P. Patens'' only lack the production of STS to produce resveratrol. | ||
| + | |||
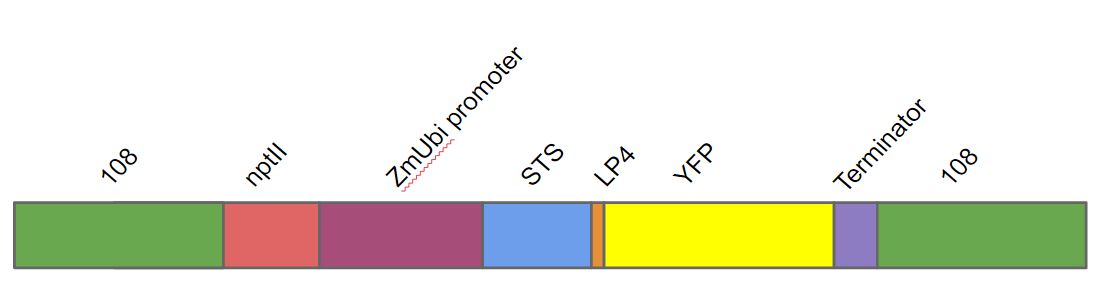
| + | The DNA construct we made contained in the following order. A homologous region to the 108 locus on the moss genome (to ensure stable integration into ''P. patens'' genome), a nptII-resistance cassette, the Zea mays ubiquitin promoter driving the stilbene synthase gene (STS) linked to yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) with the LP4 linker sequence, terminator and lastly another 108 region. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:STS construct.JPG|700px|thumb|left|Gene construct with STS gene]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | A few days after transforming this gene construct into ''P. patens'' protoplasts we observed YFP expression in several moss protoplasts. This confirms that our transformation was successful and highly suggests that the STS enzyme is expressed. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
Revision as of 07:48, 13 September 2015
Stilbene synthase
This part codes for Stilbene synthase, the last enzyme in the resveratrol pathway, similarly to BBa_K1033002. However, this sequence is different and was available at the time our project started. Thus we used it for our experiments. Resveratrol is a phenolic compound found in grapes (Vitis vinifera) that is believed to have wide range of health benefits in mammals. Resveratrol exists as both cis- and trans-isomers, but only the trans-isomer has been found in grapes. Resveratrol is produced with intermediates from the phenylpropanoid pathway and is derived from p-coumaric acid which is an intermediate in lignin production. The two key enzymes are Coenzyme A (CoA) ligase (4CL) and stilbene synthase (STS).
We have used this gene as a part of larger DNA construct that we have transformed into moss Physcomitrella patens. P. patens has been shown to produce enzymes similar to 4CL. These enzymes from the Pp4CL family (P. patens) have been shown to have similar function as enzymes from the 4CL family of higher plants. This means that P. Patens only lack the production of STS to produce resveratrol.
The DNA construct we made contained in the following order. A homologous region to the 108 locus on the moss genome (to ensure stable integration into P. patens genome), a nptII-resistance cassette, the Zea mays ubiquitin promoter driving the stilbene synthase gene (STS) linked to yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) with the LP4 linker sequence, terminator and lastly another 108 region.
A few days after transforming this gene construct into P. patens protoplasts we observed YFP expression in several moss protoplasts. This confirms that our transformation was successful and highly suggests that the STS enzyme is expressed.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]