Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1825000"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1825000 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1825000 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This is the coding region of a small antifreeze protein. It works by binding to the ice crystals as they form inside the cell, and by doing so prevents the ice crystals from enlarging and penetrating the cell membrane. | + | This is the coding region of a small antifreeze protein. The antifreeze protein used in this project is normally produced by an insect, the Spruce Budworm, ''Choristoneura fumiferana''. It works by binding to the ice crystals as they form inside the cell, and by doing so prevents the ice crystals from enlarging and penetrating the cell membrane. Through Uniprot we found the amino acid sequence of the protein, where it had the entry name Q9GTP0. We then converted the sequence of amino acids into DNA codons. This DNA sequence were then codon optimized for expression in Physcomitrella patens. Lastly, we sent the DNA sequence to IDT where the gene was synthesized. |
| + | |||
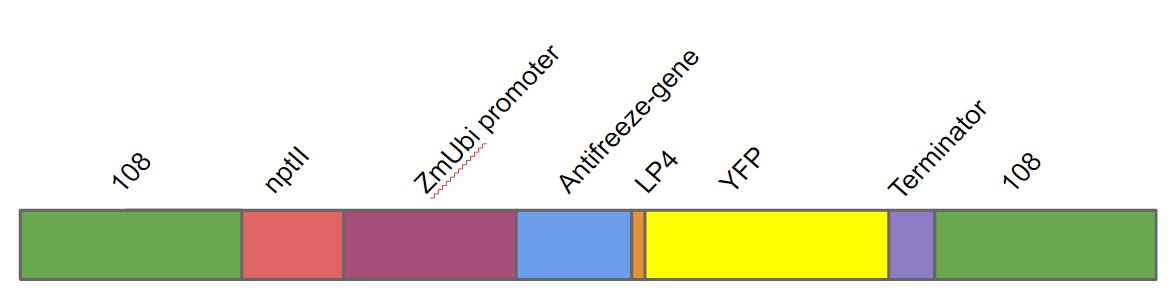
| + | We transformed this gene into ''Physcomitrella patens'' as a part of a larger DNA construct. This DNA construct contained in the following order. A homologous region to the 108 locus on the moss genome, a nptII-resistance cassette, the Zea mays ubiquitin promoter driving the antifreeze protein (AFP) linked to yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) with the LP4 linker sequence, terminator and lastly another 108 region. | ||
| + | [[File:AFP construct.jpg]] | ||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
| Line 17: | Line 19: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1825000 parameters</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1825000 parameters</partinfo> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| + | [[File:Example.jpg]] | ||
Revision as of 13:54, 12 September 2015
UNIK antifreeze protein
This is the coding region of a small antifreeze protein. The antifreeze protein used in this project is normally produced by an insect, the Spruce Budworm, Choristoneura fumiferana. It works by binding to the ice crystals as they form inside the cell, and by doing so prevents the ice crystals from enlarging and penetrating the cell membrane. Through Uniprot we found the amino acid sequence of the protein, where it had the entry name Q9GTP0. We then converted the sequence of amino acids into DNA codons. This DNA sequence were then codon optimized for expression in Physcomitrella patens. Lastly, we sent the DNA sequence to IDT where the gene was synthesized.
We transformed this gene into Physcomitrella patens as a part of a larger DNA construct. This DNA construct contained in the following order. A homologous region to the 108 locus on the moss genome, a nptII-resistance cassette, the Zea mays ubiquitin promoter driving the antifreeze protein (AFP) linked to yellow fluorescent protein (YFP) with the LP4 linker sequence, terminator and lastly another 108 region.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 242
Illegal BglII site found at 296 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]