Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1789000"
(→Experimental Validation) |
(→Experimental Validation) |
||
| Line 20: | Line 20: | ||
==Experimental Validation== | ==Experimental Validation== | ||
| − | This part is validated through | + | This part is validated through four ways: Enzyme cutting, PCR, Sequence, and functional testing |
===PCR=== | ===PCR=== | ||
| Line 41: | Line 41: | ||
The result of the agarose electrophoresis was shown on the picture above. | The result of the agarose electrophoresis was shown on the picture above. | ||
| + | ===Enzyme cutting=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Methods''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | After the assembly ,the plasmid was transferred into the Competent ''E. coli'' DH5α). After culturing overnight in LB,we minipreped the plasmid for cutting. | ||
| + | The preparation of the plasmid was performed with TIANprep Mini Plasmid Kit from ''TIANGEN''. The cutting procedure was performed with EcoRI and XbaI restriction endonuclease bought from ''TAKARA''. | ||
| + | |||
| + | The plasmid was cutted in a 20μL system at 37 ℃ for 2 hours. | ||
| + | The Electrophoresis was performed on a 1% Agarose glu. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Results''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:NUDT-GFP2-cut.jpg|150px|]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | The result of the agarose electrophoresis was shown on the picture above. | ||
===Functional Test=== | ===Functional Test=== | ||
Revision as of 13:07, 18 September 2015
IaaM
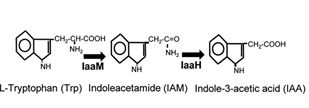
This part is the coding sequence of tryptophan-2-mono-oxygenase.
Usage and Biology
Indole-3-acetic acid (IAA), also known as auxin, is a plant hormone, which can promote growth and protect the soil from erosion. IAA can be synthesized through IAM pathway, originated from Pseudomonas savastanoi. Two important enzymes are contained in this pathway, AKA IaaM and IaaH.
IaaM is the tryptophan-2-mono-oxygenase. This enzyme catalyzes the oxidative carboxylation of L-tryptophan to indole-3-acetamide. IaaH is the indoleacetimide hydrolase. This enzyme catalyses the hydrolysis of indoleacetamide to indoleacetate and ammonia. This pathway is relevantly easy to be expressed in prokaryotic cells, and its substrate (Trp) can be synthesized by host cells.
Sequence and Features
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 402
Illegal BamHI site found at 1347 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 109
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Experimental Validation
This part is validated through four ways: Enzyme cutting, PCR, Sequence, and functional testing
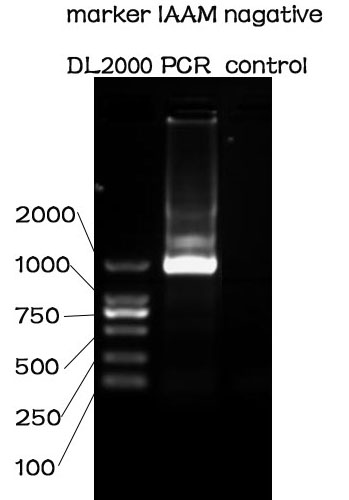
PCR
Methods
The PCR is performed with Premix EX Taq by Takara.
F-Prime: 5'-GAACCTCTTACGTGCCCGATCAA-3'
R-Prime: 5'-CGCCGCAGCCGAACGAC-3'
The PCR protocol is selected based on the Users Manuel. The Electrophoresis was performed on a 1% Agarose glu.
Results
The result of the agarose electrophoresis was shown on the picture above.
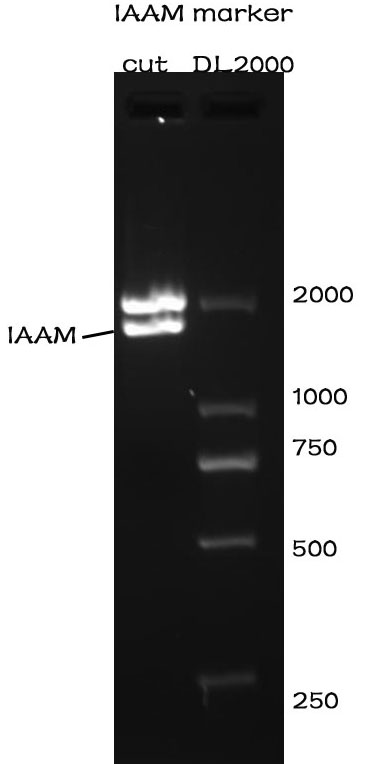
Enzyme cutting
Methods
After the assembly ,the plasmid was transferred into the Competent E. coli DH5α). After culturing overnight in LB,we minipreped the plasmid for cutting. The preparation of the plasmid was performed with TIANprep Mini Plasmid Kit from TIANGEN. The cutting procedure was performed with EcoRI and XbaI restriction endonuclease bought from TAKARA.
The plasmid was cutted in a 20μL system at 37 ℃ for 2 hours. The Electrophoresis was performed on a 1% Agarose glu.
Results
The result of the agarose electrophoresis was shown on the picture above.
Functional Test
This part is tested together with the part BBa_K1789001, in the device BBa_K1789022.
The result shows that this part can work as expected to generate IAA together with IAAH.