Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1688012"
Kandidaten (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1688012 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1688012 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | <partinfo>BBa_K1688012 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | |
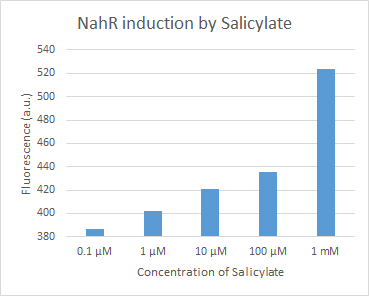
BBa_J61051, NahR with nahR and sal promoters (Pr and Psal), codes for the inducible repressor NahR, which suppresses Psal in the absence of salicylate. This biobrick makes it possible to regulate the expression of the red fluorescent protein dTomato. | BBa_J61051, NahR with nahR and sal promoters (Pr and Psal), codes for the inducible repressor NahR, which suppresses Psal in the absence of salicylate. This biobrick makes it possible to regulate the expression of the red fluorescent protein dTomato. | ||
| − | [[File:uppsala_nahrinduction | + | [[File:uppsala_nahrinduction-dTomato.png]] |
| − | Figure 1. dTomato expressed in ''E. coli'' DH5-alpha. NahR/Psal induction test | + | Figure 1. dTomato expressed in ''E. coli'' DH5-alpha. NahR/Psal induction test in LB medium. Concentration of salicylate from left to right: 0,1 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM, 100 μM and 1 mM. |
| − | + | [[File:uppsala_nahrinductionplate123s-dTomato.png]] | |
| + | |||
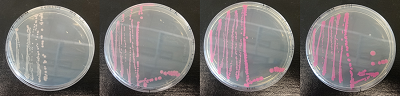
| + | Figure 2. dTomato expressed in ''E. coli'' DH5-alpha. NahR/Psal induction test on agar plate. Concentration of salicylate from left to right: 0,1 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM, 100 μM and 1 mM. | ||
== Usage and Biology== | == Usage and Biology== | ||
Revision as of 20:20, 18 September 2015
dTomato (inc RBS, NahR/Psal promoter system)
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 786
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 77
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 618 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
BBa_J61051, NahR with nahR and sal promoters (Pr and Psal), codes for the inducible repressor NahR, which suppresses Psal in the absence of salicylate. This biobrick makes it possible to regulate the expression of the red fluorescent protein dTomato.
Figure 1. dTomato expressed in E. coli DH5-alpha. NahR/Psal induction test in LB medium. Concentration of salicylate from left to right: 0,1 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM, 100 μM and 1 mM.
Figure 2. dTomato expressed in E. coli DH5-alpha. NahR/Psal induction test on agar plate. Concentration of salicylate from left to right: 0,1 μM, 1 μM, 10 μM, 100 μM and 1 mM.
Usage and Biology
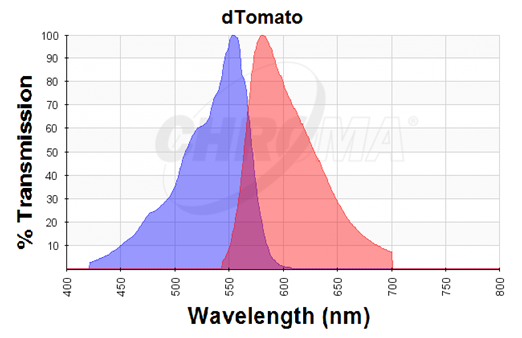
The dTomato protein is a fluorescent protein dimer, created by direct evolution of the wild-type DsRed, from Discosoma sp. (Shaner et al, - Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein, 2004). The dTomato protein is a fluorescent dimer protein that emits orange-red light when it is excited by green-yellow light. It is preferable to use – especially in self-made fluorometry tests – because the excitation wavelengths and the emission wavelengths don't overlap as much as in other fluorescent proteins. The dTomato excitation peak is at 554 nm and 50% of it is at 510 nm. Also, its emission peak is at 581 nm and its 50% emission at 629 nm (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Excitation (blue curve) and emission (red curve) spectra for the dTomato fluorescent protein (the graph is designed with the following tool: https://www.chroma.com/spectra-viewer)
References
Nathan C Shaner, Robert E Campbell, Paul A Steinbach, Ben N G Giepmans, Amy E Palmer & Roger Y Tsien. “Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein”, 2004