Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1529302:Design"
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
| − | + | ==Design Notes== | |
| − | + | ==Materials and Methods== | |
-Strain<br> | -Strain<br> | ||
All the samples were JM2.300 strain. | All the samples were JM2.300 strain. | ||
| − | + | ===C4HSL-dependent CmR expression Protocol=== | |
<b>1.Construction</b><br> | <b>1.Construction</b><br> | ||
A. Ptet-GFP-Ptet-RhlR (pSB6A1), Prhl(RL)-CmR-LasI(pSB3K3)<br> | A. Ptet-GFP-Ptet-RhlR (pSB6A1), Prhl(RL)-CmR-LasI(pSB3K3)<br> | ||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
| − | + | ===C4HSL-dependent 3OC12HSL production Protocol=== | |
<b>1.Construction</b><br> | <b>1.Construction</b><br> | ||
<i>Sender</i><br> | <i>Sender</i><br> | ||
| Line 74: | Line 74: | ||
| − | + | ==Source== | |
Composite of BBa_K1529300, BBa_K395160, BBa_B0034, BBa_C0078.<br> | Composite of BBa_K1529300, BBa_K395160, BBa_B0034, BBa_C0078.<br> | ||
BBa_K1529300 was derived from oligo DNA. | BBa_K1529300 was derived from oligo DNA. | ||
| − | + | ==References== | |
1.Bo Hu et al. (2010) An Environment-Sensitive Synthetic Microbial Ecosystem. PLoS ONE 5(5): e10619<br> | 1.Bo Hu et al. (2010) An Environment-Sensitive Synthetic Microbial Ecosystem. PLoS ONE 5(5): e10619<br> | ||
2.Jennifer M. Henke et al. (2004) Bacterial social engagements. TRENDS in Cell Biology 14: 11<br> | 2.Jennifer M. Henke et al. (2004) Bacterial social engagements. TRENDS in Cell Biology 14: 11<br> | ||
3.Gabriella Pessi et al. (2000) Transcriptional Control of the Hydrogen Cyanide Biosynthetic Genes hcnABC by the Anaerobic Regulator ANR and the Quorum-Sensing Regulators LasR and RhlR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Journal of Bacteriology 182(24): 6940–6949<br> | 3.Gabriella Pessi et al. (2000) Transcriptional Control of the Hydrogen Cyanide Biosynthetic Genes hcnABC by the Anaerobic Regulator ANR and the Quorum-Sensing Regulators LasR and RhlR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Journal of Bacteriology 182(24): 6940–6949<br> | ||
4.Kendall M. Gray et al. (1994) Interchangeability and specificity of components from the quorum-sensing regulatory systems of Vibrio fischeri and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Bacteriology 176(10): 3076–3080<br> | 4.Kendall M. Gray et al. (1994) Interchangeability and specificity of components from the quorum-sensing regulatory systems of Vibrio fischeri and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Bacteriology 176(10): 3076–3080<br> | ||
Latest revision as of 13:40, 23 October 2014
Prhl(RL)-CmR-LasI
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1429
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 991
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Design Notes
Materials and Methods
-Strain
All the samples were JM2.300 strain.
C4HSL-dependent CmR expression Protocol
1.Construction
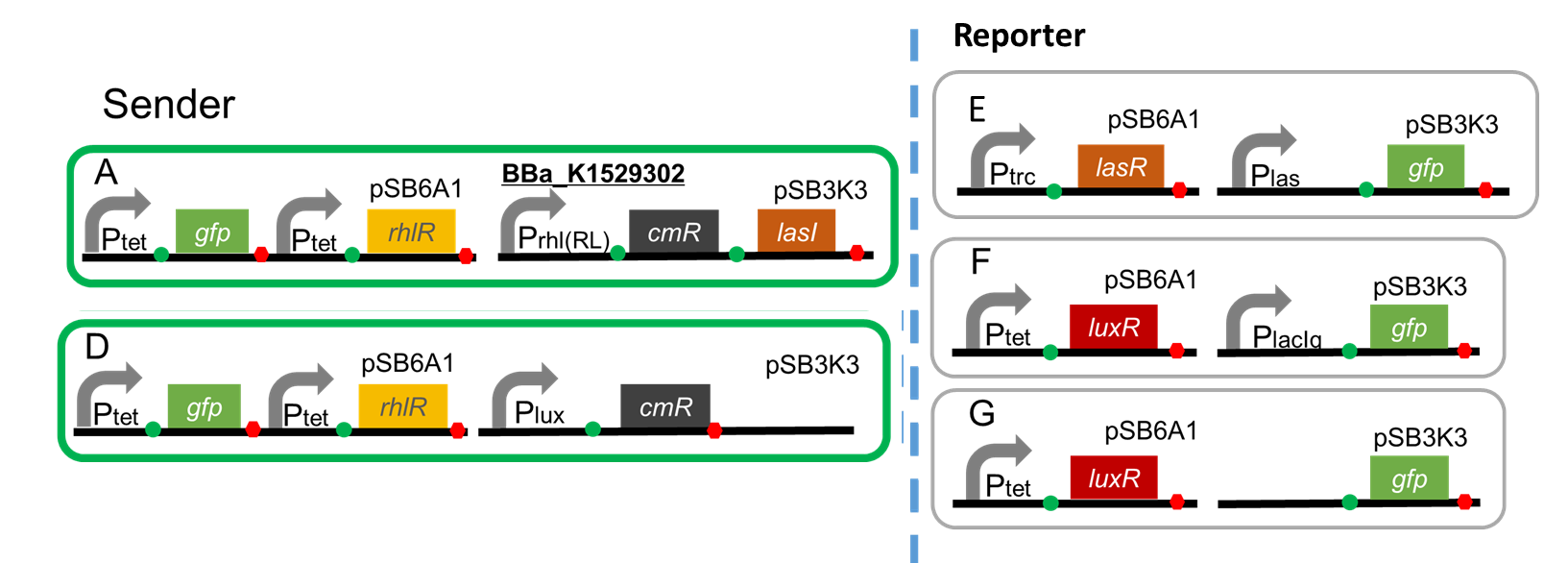
A. Ptet-GFP-Ptet-RhlR (pSB6A1), Prhl(RL)-CmR-LasI(pSB3K3)
B. Ptet-GFP-Ptet-RhlR (pSB6A1), PlacIq-CmR (pSB3K3)…Positive control
C. Ptet-GFP-Ptet-RhlR (pSB6A1), promoter less CmR (pSB3K3)… Negative control
2.Assay protocol
1. Prepare overnight cultures for the sender cells in 3 mL LB medium, containing ampicillin (50 microg / mL) and kanamycin (30 microg / mL) at 37°C for 12h.
2. Make a 1:100 dilution in 3 mL of fresh LB containing antibiotic and grow the cells at 37°C until the observed OD590 reaches 0.5.(→fresh culture)
3. Add 30 microL of suspension in the following medium.
1) 3 mL of LB containing Amp and Kan + 30 microL C4HSL (final concentration is 5 microM)
2) 3 mL of LB containing Amp and Kan + 30 microL DMSO
3) 3 mL of LB containing Amp, Kan and Cm (final concentration is 100 microg/mL) + 30 microL C4HSL (final concentration is 500 microM)
4) 3 mL of LB containing Amp, Kan and Cm (final concentration of Cm is 100 microg/mL) + 30 microL DMSO
4. Grow the samples of sender cells at 37°C for more than 8 hours.
5. Measure optical density every hour. (If the optical density is over 1.0, dilute the cell medium to 1/10.)
C4HSL-dependent 3OC12HSL production Protocol
1.Construction
Sender
A. Ptet-GFP-Ptet-RhlR (pSB6A1), Prhl(RL)-CmR-LasI (pSB3K3)
D. Ptet-GFP-Ptet-RhlR (pSB6A1), Plux-CmR (pSB3K3)
Reporter
E. Ptrc-LasR (pSB6A1), Plas-GFP (pSB3K3)
F. Ptet-LuxR (pSB6A1), PlacIq-GFP (pSB3K3)...Positive control
G. Ptet-LuxR (pSB6A1), Promoter-less-GFP (pSB3K3)...Negative control
2.Assay protocol
Prepare the supernatant of the sender cell
1. Prepare overnight cultures for the sender cells in 3 mL LB medium, containing ampicillin (50 microg / mL) and kanamycin (30 microg / mL) at 37°C for 12h.
2. Make a 1:100 dilution in 3 mL of fresh LB containing antibiotic and grow the cells at 37°C until the observed OD590 reaches 0.5.
3. Add 30 microL of the culture containing the cells in the following medium.
a) Add 15 microL of 10 mM C4HSL to 3 mL LB containing Amp and Kan (final concentration is 50 microM)
b) Add 15 microL DMSO to 3 mL of LB containing Amp+Kan
4. Grow the samples of sender cell at 37°C for 8 hours.
5. Measure the optical density every hour. (If the optical density is over 1.0, dilute the cell medium to 1/10.)
6. Centrifuge the sample at 9000x g, 4°C for 1 min. Filter sterilize the supernatant. (Pore size is 0.22 microm.)
7. Use the supernatant in reporter assay.
Reporter Assay
1. Prepare overnight cultures for the Reporter cell (E~G) in 3 mL LB medium, containing ampicillin (50 microg / mL) and kanamycin (30 microg / mL) at 37°C for 12h.
2. Make a 1:100 dilution in 3 mL of fresh LB + antibiotic and grow the cells at 37°C until you reach an 0.5 in OD590 (fresh culture).
3. Add 30 microL of suspension in the following medium.
1) 2.7 mL filtrate of Aa +300 microL LB
2) 2.7 mL filtrate of Ab +300 microL LB
3) 2.7 mL filtrate of Da +300 microL LB
4) 2.7 mL filtrate of Db +300 microL LB
5) 3 mL LB + 5 microM C12HSL 3 microL (Final concentration is 5 nM)
6) 3 mL LB + DMSO 3 microL
4. Grow the samples of Reporter cell in incubator at 37°C for 4 h.
5. Start preparing the flow cytometer 1 h before the end of incubation.
6. After the incubation, take the sample, and centrifuge at 9000x g, 1 min., 4°C.
7. Remove the supernatant by using P1000 pipette.
8. Add 1 mL of filtered PBS (phosphate-buffered saline) and suspend. (The ideal of OD is 0.3.)
9. Dispense all of each suspension into a disposable tube through a cell strainer.
10. Use flow cytometer to measure the fluorescence of GFP. (We used BD FACSCaliburTM Flow Cytometer of Becton, Dickenson and Company.)
Source
Composite of BBa_K1529300, BBa_K395160, BBa_B0034, BBa_C0078.
BBa_K1529300 was derived from oligo DNA.
References
1.Bo Hu et al. (2010) An Environment-Sensitive Synthetic Microbial Ecosystem. PLoS ONE 5(5): e10619
2.Jennifer M. Henke et al. (2004) Bacterial social engagements. TRENDS in Cell Biology 14: 11
3.Gabriella Pessi et al. (2000) Transcriptional Control of the Hydrogen Cyanide Biosynthetic Genes hcnABC by the Anaerobic Regulator ANR and the Quorum-Sensing Regulators LasR and RhlR in Pseudomonas aeruginosa Journal of Bacteriology 182(24): 6940–6949
4.Kendall M. Gray et al. (1994) Interchangeability and specificity of components from the quorum-sensing regulatory systems of Vibrio fischeri and Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Journal of Bacteriology 176(10): 3076–3080