Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1499253"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
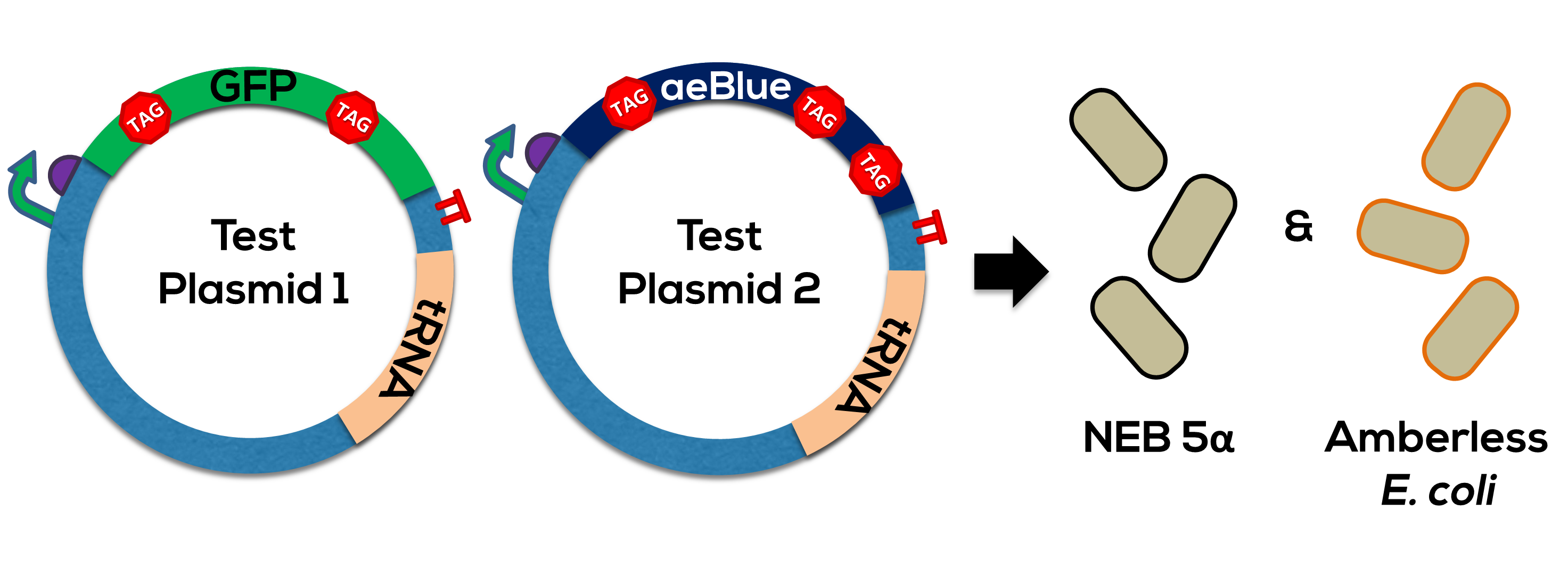
The design of the protein coding region of this part was based off Team Uppsala's 2012 chromoproteins kit, specifically [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K864401 BBa_K864401]. Please see this parts page for the biology of this protein. The supP tRNA is from Stanford-Brown-Spelman's 2014 Amberless toolkit, or [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1499251 BBa_K1499251]. Together, this generator was used to test the orthogonality of the UAG->Leucine coding (Figure 1). | The design of the protein coding region of this part was based off Team Uppsala's 2012 chromoproteins kit, specifically [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K864401 BBa_K864401]. Please see this parts page for the biology of this protein. The supP tRNA is from Stanford-Brown-Spelman's 2014 Amberless toolkit, or [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1499251 BBa_K1499251]. Together, this generator was used to test the orthogonality of the UAG->Leucine coding (Figure 1). | ||
| − | [[SBS_AmberlessOverview2.png|700px|thumb|center|<b>Figure 1.</b> We transformed DH5-alpha and amberless cells with test plasmids, in this case the aeBlue reporter gene with stop codons and the supP tRNA, in order to establish a proof-of-concept for orthogonality using Codon Security.]] | + | [[Image:SBS_AmberlessOverview2.png|700px|thumb|center|<b>Figure 1.</b> We transformed DH5-alpha and amberless cells with test plasmids, in this case the aeBlue reporter gene with stop codons and the supP tRNA, in order to establish a proof-of-concept for orthogonality using Codon Security.]] |
We have observed that this generator works in amberless ''E. coli'', but not DH5-alpha. Because of the toxicity of the tRNA, the part will be difficult to transform into any strain of bacterium that contains genes with the amber stop codon. | We have observed that this generator works in amberless ''E. coli'', but not DH5-alpha. Because of the toxicity of the tRNA, the part will be difficult to transform into any strain of bacterium that contains genes with the amber stop codon. | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
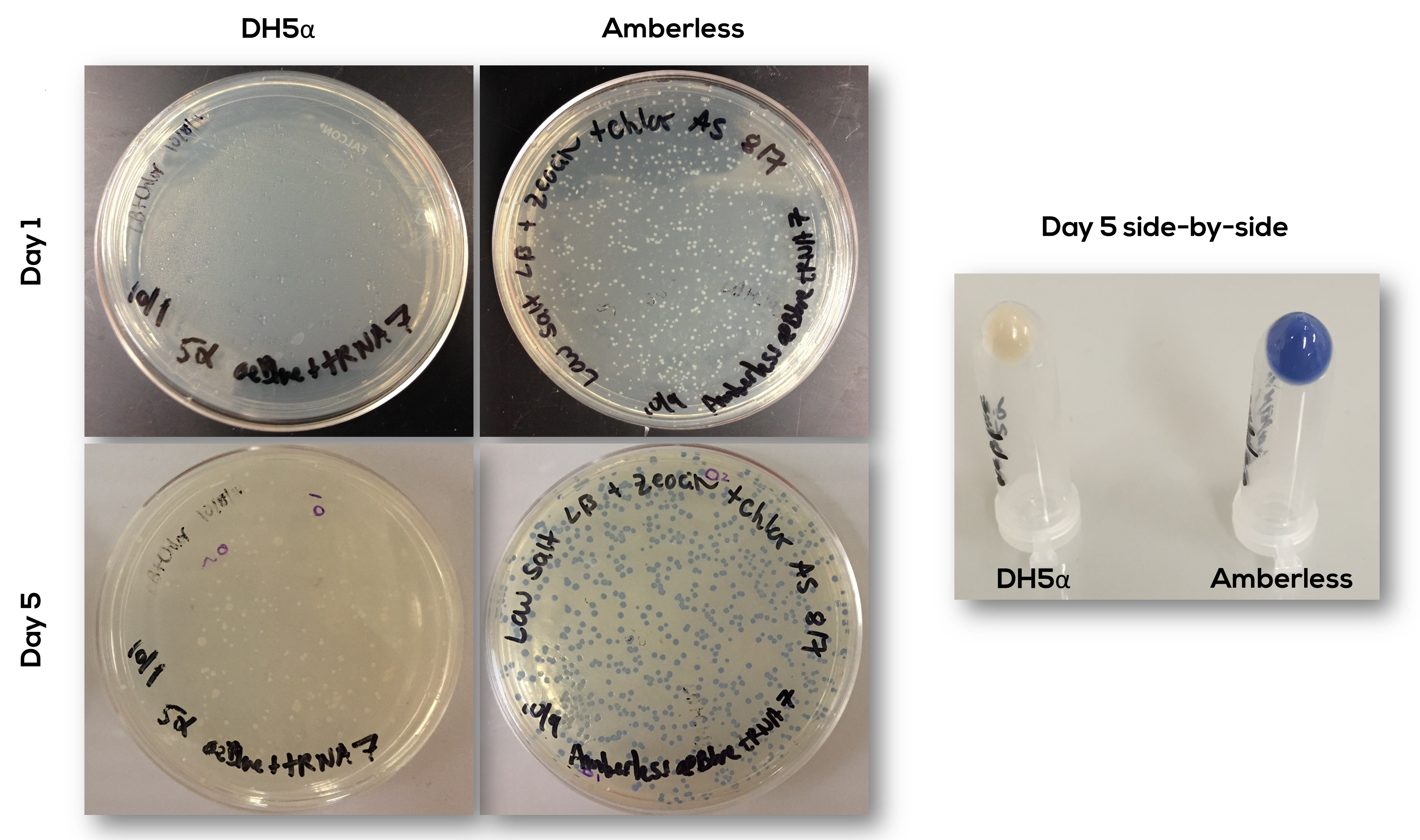
The part has been confirmed to work as expected (Figure 3). | The part has been confirmed to work as expected (Figure 3). | ||
| − | [[SBS_AmberlessResults_Plates.png|600px|thumb|center|<b>Figure 3.</b> Plates after transforming (at Day 0) DH5-alpha and Amberless cells with aeBlue-3S+tRNA. At Day 1, after overnight incubation at 37C, there are no DH5-alpha colonies, but there are over 200 Amberless colonies. At Day 5, 4 days of room temperature incubation, Amberless colonies express the aeBlue protein and colonies appear in DH5-alpha plate, although possibly because of degradation of Chlor antibiotic. Side-by-side comparison of cell pellets shows that only Amberless strongly express the blue protein.]] | + | [[Image:SBS_AmberlessResults_Plates.png|600px|thumb|center|<b>Figure 3.</b> Plates after transforming (at Day 0) DH5-alpha and Amberless cells with aeBlue-3S+tRNA. At Day 1, after overnight incubation at 37C, there are no DH5-alpha colonies, but there are over 200 Amberless colonies. At Day 5, 4 days of room temperature incubation, Amberless colonies express the aeBlue protein and colonies appear in DH5-alpha plate, although possibly because of degradation of Chlor antibiotic. Side-by-side comparison of cell pellets shows that only Amberless strongly express the blue protein.]] |
<!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
Revision as of 16:01, 2 November 2014
aeBlue generator with 3 UAG stops + supP tRNA
This part encodes uvsE, a putative UV damage endonuclease found in D. radiodurans that protects cells from radiation-induced DNA damage.
Usage and Biology
The design of the protein coding region of this part was based off Team Uppsala's 2012 chromoproteins kit, specifically BBa_K864401. Please see this parts page for the biology of this protein. The supP tRNA is from Stanford-Brown-Spelman's 2014 Amberless toolkit, or BBa_K1499251. Together, this generator was used to test the orthogonality of the UAG->Leucine coding (Figure 1).
We have observed that this generator works in amberless E. coli, but not DH5-alpha. Because of the toxicity of the tRNA, the part will be difficult to transform into any strain of bacterium that contains genes with the amber stop codon.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Characterization
Verification of Part
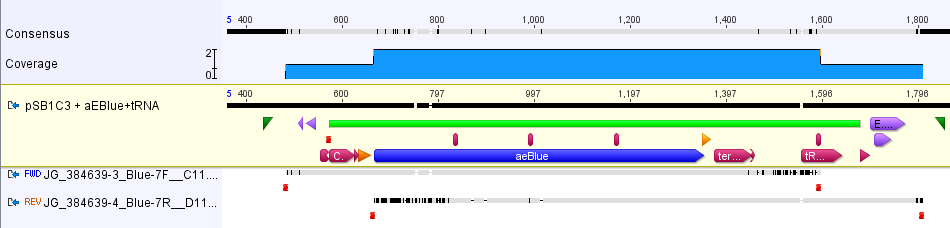
The part was sequence verified in the pSB1C3 backbone before submission to the registry. Two reads, forward and reverse, were obtained using VF2 and VR (Figure 2).
Results
The part has been confirmed to work as expected (Figure 3).