Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1499203"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1499203 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1499203 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | This part generates the serine deaminase, SdaB ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K847080 BBa_K847080]), which confers basicity resistance with strong promoter/RBS pair ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23038 BBa_BBa_J23038]), terminator ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0010 BBa_B0010]), | + | This part generates the serine deaminase, SdaB ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K847080 BBa_K847080]), which confers basicity resistance with strong promoter/RBS pair ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J23038 BBa_BBa_J23038]), terminator ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_B0010 BBa_B0010]). However, this part will not work without the supP tRNA submitted by Stanford-Brown-Spelman 2014 ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1499251 BBa_K1499251]). |
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
Serine catabolism creates buffers in the cytoplasm to help counter the effects of the high pH. This enzyme will break down serine to confer resistance to higher pH. Please refer to Stanford-Brown 2012 iGEM's page on this enzyme's part, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K847080 BBa_K847080]. | Serine catabolism creates buffers in the cytoplasm to help counter the effects of the high pH. This enzyme will break down serine to confer resistance to higher pH. Please refer to Stanford-Brown 2012 iGEM's page on this enzyme's part, [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K847080 BBa_K847080]. | ||
| − | This part is to be used in the Stanford-Brown-Spelman 2014 iGEM amberless system to confer resistance to higher pH | + | This part is to be used in the Stanford-Brown-Spelman 2014 iGEM amberless system with the supP tRNA to confer resistance to higher pH. The stop codons inhibit the expression of the complete product, except in amberless cells, that do not have the UAG release factors. |
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| Line 18: | Line 18: | ||
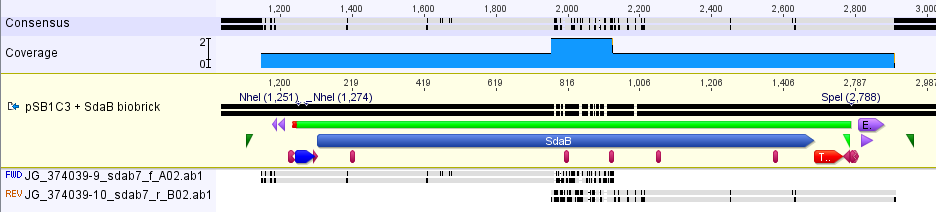
The part was sequence verified in the pSB1C3 backbone before submission to the registry. Two reads, forward and reverse, were obtained using VF2 and VR (Figure 1). | The part was sequence verified in the pSB1C3 backbone before submission to the registry. Two reads, forward and reverse, were obtained using VF2 and VR (Figure 1). | ||
| − | [[Image:SBS_SdaBsequence.png|750px|thumb|center|<b>Figure 1.</b> This part was sequence verified. The silent mutations seen at the beginning of the coding region are from codon optimization that was not inputted into the reference sequence.]] | + | [[Image:SBS_SdaBsequence.png|750px|thumb|center|<b>Figure 1.</b> This part was sequence verified. The silent mutations seen at the beginning of the coding region are from codon optimization that was not inputted into the reference sequence. There were three minor mutations that we do not expect to modify the function of the protein (hydrophobic to hydrophobic)]] |
===Results=== | ===Results=== | ||
Latest revision as of 22:09, 2 November 2014
SdaB protein generator without tRNA + 5 amber stops
This part generates the serine deaminase, SdaB (BBa_K847080), which confers basicity resistance with strong promoter/RBS pair (BBa_BBa_J23038), terminator (BBa_B0010). However, this part will not work without the supP tRNA submitted by Stanford-Brown-Spelman 2014 (BBa_K1499251).
Usage and Biology
Serine catabolism creates buffers in the cytoplasm to help counter the effects of the high pH. This enzyme will break down serine to confer resistance to higher pH. Please refer to Stanford-Brown 2012 iGEM's page on this enzyme's part, BBa_K847080.
This part is to be used in the Stanford-Brown-Spelman 2014 iGEM amberless system with the supP tRNA to confer resistance to higher pH. The stop codons inhibit the expression of the complete product, except in amberless cells, that do not have the UAG release factors.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 6
Illegal NheI site found at 29 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 226
Illegal AgeI site found at 549 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 520
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 667
Characterization
Verification of Part
The part was sequence verified in the pSB1C3 backbone before submission to the registry. Two reads, forward and reverse, were obtained using VF2 and VR (Figure 1).
Results
This part was not investigated, but it could be verified using a basicity resistance assay.
