Difference between revisions of "Help:Cell-free chassis/Modelling"
m |
|||
| Line 19: | Line 19: | ||
[[Image:CFS_model_equations.png]] | [[Image:CFS_model_equations.png]] | ||
| + | '''This equation is partially incorrect - will edit it later''' | ||
| − | + | {| class="wikitable" border="1" cellspacing="0" cellpadding="2" style="text-align:left; margin: 1em 1em 1em 0; background: #f9f9f9; border: 1px #aaa solid; border-collapse: collapse;" | |
| − | + | ! Parameter | |
| − | + | ! Description | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |P || protein concentration | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |E || limiting nutrient/substrate ("energy in system") | |
| − | + | |- | |
| − | + | |μ || instantaneous (observed) synthesis rate coefficient | |
| + | |- | ||
| + | |μ<sub>max</sub> || maximal synthesis rate coefficient | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |K<sub>s</sub> || half-saturation coefficient | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |α<sub>1</sub> || energy molecules consumed per synthesis | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |k<sub>1</sub> || rate of synthesis (promoter concentration and strength) | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |n || positive co-operativity coefficient | ||
| + | |} | ||
* mathematical description of the system + parameter info. | * mathematical description of the system + parameter info. | ||
Revision as of 13:26, 25 October 2007
Cell-Free System modelling
Model assumptions
- Simple constitutive gene expression model
- Protein degradation is negligeable (since protease inhibitors are present in the CFS, the rate of proteolytic degradation is minimal)
- Resources are an important limiting factor to be considered in our CFS (such as molecules of ATP or protein-charged tRNAs)
Model description
Although a study of microbial growth rate is undertaken here, this could be altered to feature the system survival/lifetime, as we are dealing with S30 cell extract. The lifetime of the system would be reflected by the rate of change of system energy (d[nutrient]/dt), which here is decreasing, as there is no source of replenishment of nutrient.
A review of literature suggests that multiple models have been developed to describe this feature of the system. The most widely used models are the Monod, Grau, Teisser, Moser and Contois equations.
These equations describe the functional relationship between the microbial growth rate and essential substrate (nutrient) concentration.
It was proposed, and noted from experimental data, that the behaviour of the system can be described as being limited by the energy of the system, and this could be achieved by using the Hill function.
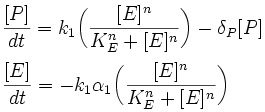 This equation is partially incorrect - will edit it later
This equation is partially incorrect - will edit it later
| Parameter | Description |
|---|---|
| P | protein concentration |
| E | limiting nutrient/substrate ("energy in system") |
| μ | instantaneous (observed) synthesis rate coefficient |
| μmax | maximal synthesis rate coefficient |
| Ks | half-saturation coefficient |
| α1 | energy molecules consumed per synthesis |
| k1 | rate of synthesis (promoter concentration and strength) |
| n | positive co-operativity coefficient |
- mathematical description of the system + parameter info.
- see [http://openwetware.org/wiki/User:Jaroslaw_Karcz/Sandbox]
- link to SBML file
Simulations: typical beahviours
- weak promoter with no degradation (linear production of the output protein) ---> like the pTet data we have
- strong promoter with no degradation (resources are limiting the rate of synthesis as well as the amount of protein to be produced) ---> like the pT7 data we have
