Part:BBa_K3989011
plant immune elicitor elf18 fused with ClyA for OMV display
In this construct, outer membrane-associated protein ClyA (Part:BBa_K811000) is used to display the plant immune elicitor elf18 (Part:BBa_K3989023) to the surface of bacterial outermembrane vesicles (OMVs) to trigger plant immune responses. To make elf18 better recognized by plant immune receptor FLS2, we put mutiple linkers and a 3×FLAG tag between ClyA and elf18 to minimize the steric hindrance.
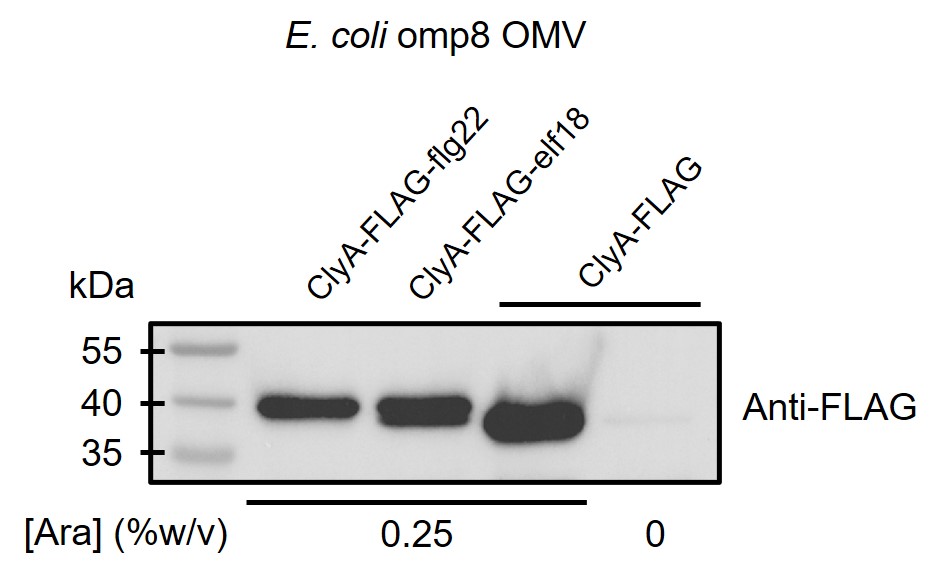
By doing western blot using anti-FLAG antibody, we proved that ClyA-elicitor fusion proteins indeed exist in OMVs (Figure 1).
Figure 1. ClyA protein with or without elicitor fused exists in outer membrane vesicles of E. coli omp8 strain.
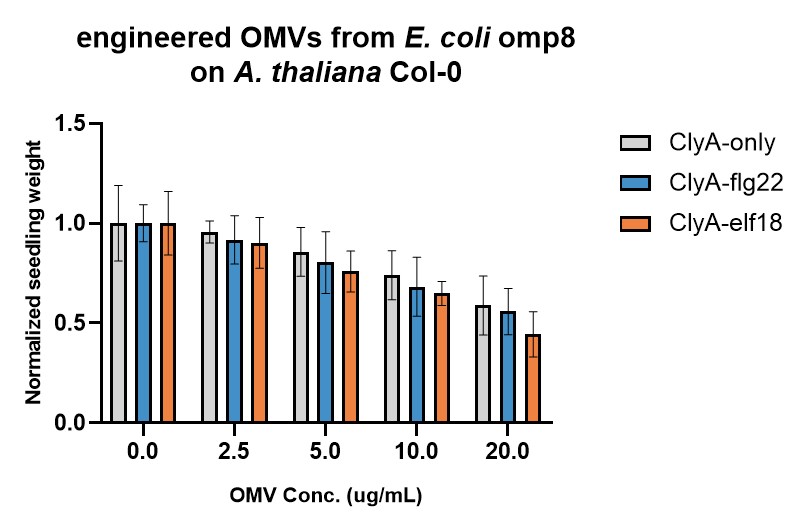
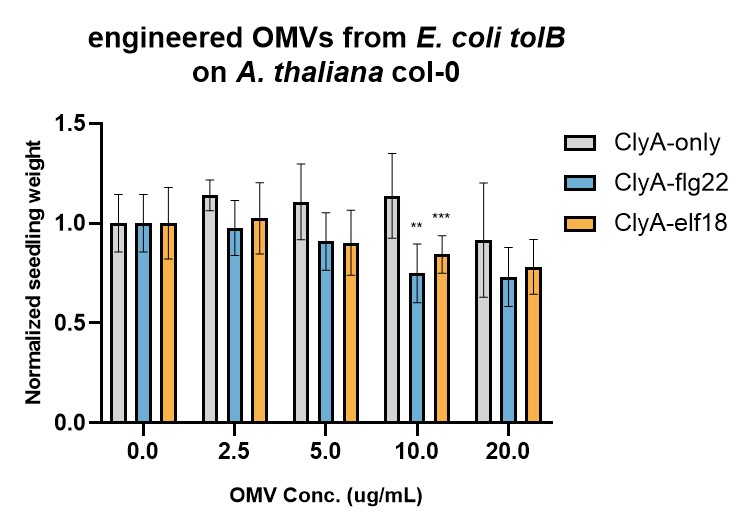
The immunogenicities of engineered OMVs were first tested by Seedling Growth Inhibition (SGI) assay (Figure 2 & 3). In SGI assay, A. thaliana Col-0 seedlings were treated by immune elicitors (OMVs in our case) for 7-10 days, and lower seedling weight indicates that higher immune response is triggered (due to the trade-off between immunity and growth). Two E. coli strains were used, omp8 (Figure 2) and tolB (Figure 3), which can produce high and low immunogenic OMVs, respectively. For both strains, ClyA-flg22 and ClyA-elf18 OMVs seem to trigger stronger immune responses than OMVs containing only ClyA. However, the enhancement effect is more significant for tolB OMVs than omp8 OMVs. The reason might be that natural omp8 OMVs can already trigger strong immune responses, obscuring the additional immune responses triggered by flg22 or elf18.
Figure 2. Evaluation of engineered E. coli omp8 OMVs' immunogenicities by SGI assay.
Figure 3. Evaluation of engineered E. coli tolB OMVs' immunogenicities by SGI assay.
ROS (reactive oxygen species) burst assay was also used to test the immunogenicities of engineered OMVs (Figure 4), which shows how the leaf discs of A. thaliana Col-0 respond to OMV treatments within one to two hours. Both omp8 (Figure 4A, B) and tolB (Figure 4C, D) strains were used to produce OMVs, and both time-course ROS production curve (Figure 4A, C) and total ROS production (Figure 4B, D) are shown. Our results show that only ClyA-elf18 (Part:BBa_K3989011) OMVs, but not Cly-flg22 OMVs, can trigger significantly higher ROS production than ClyA-only OMVs, which is different from SGI assay where both constructs show enhancement effects.
Figure 4. Evaluation of engineered OMVs' immunogenicities by ROS burst assay.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
| None |