Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K404122"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
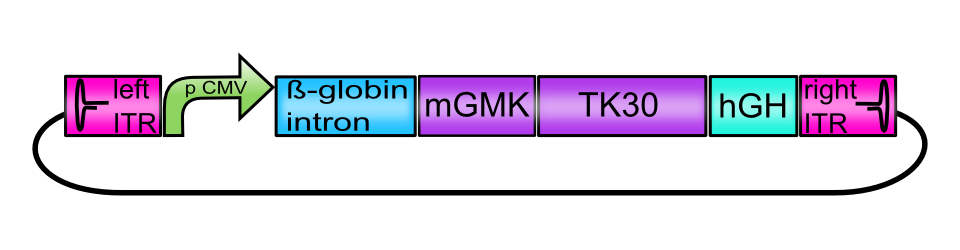
This composite BioBrick serves as an example for the possibilities of our Virus Construction Kit. It has been assembled out of 7 single BioBricks: A promoter, a transcription enhancing sequence, a Gene of Interest that is itself a fusion protein, a polyadenylation sequence required for translation and inverted terminal repeats that are required for replication at either end of the sequence. | This composite BioBrick serves as an example for the possibilities of our Virus Construction Kit. It has been assembled out of 7 single BioBricks: A promoter, a transcription enhancing sequence, a Gene of Interest that is itself a fusion protein, a polyadenylation sequence required for translation and inverted terminal repeats that are required for replication at either end of the sequence. | ||
| + | If cotransfected into helper cell lines together with a plasmid encoding AAV Rep and Cap proteins and a pHelper plasmid encoding adenoviral genes, this BioBrick is being packaged into AAV capsids in single-stranded form and substitutes the AAV genome. | ||
| + | AAV particles containing this Biobrick as a vector sequence are replication-deficient and are therefore considered as biosafety level 1. | ||
[[Image:Freiburg10_Vectorplasmid composite 4.png|thumb|center|480px]]<br> | [[Image:Freiburg10_Vectorplasmid composite 4.png|thumb|center|480px]]<br> | ||
Revision as of 12:56, 27 October 2010
[AAV2]-left-ITR_pCMV_betaglobin_mGMK_TK30_hGH_[AAV2]-right-ITR
This composite BioBrick serves as an example for the possibilities of our Virus Construction Kit. It has been assembled out of 7 single BioBricks: A promoter, a transcription enhancing sequence, a Gene of Interest that is itself a fusion protein, a polyadenylation sequence required for translation and inverted terminal repeats that are required for replication at either end of the sequence. If cotransfected into helper cell lines together with a plasmid encoding AAV Rep and Cap proteins and a pHelper plasmid encoding adenoviral genes, this BioBrick is being packaged into AAV capsids in single-stranded form and substitutes the AAV genome. AAV particles containing this Biobrick as a vector sequence are replication-deficient and are therefore considered as biosafety level 1.
ITRs

The inverted terminal repeat structures can be subdivided into several palindromic motives: A and A’ form a stem loop which encases B and B’ as well as C and C’. Those motives form both arms of the T-shaped structure. The functional motives on the ITR are two regions that bind Rep 68/78, called Rep-binding elements (RBE on the stem and RBE’ on the B arm) and the terminal resolution site (trs) in which the rep proteins introduce single-stranded nicks. The 3’ OH end of the A motive acts as a primer for DNA replication (Im & Muzyczka, 1990) (Lusby, Fife, & Berns, 1980).
CMV promoter
Beta-globin-intron


The beta-globin intron BioBrick consists of a partial chimeric CMV promoter followed by the intron II of the beta-globin gene. The 3´end of the intron is fused to the first 25 bases of human beta globin gene exon 3. The beta globin intron BioBrick is assumed to enhance eukaryotic gene expression (Nott, Meislin, & Moore, 2003). As shown in Figure 9 and Figure 10 the vectorplasmid missing the beta-globin intron showed a negligible difference in mVenus expression compared to viral genomes containing the beta-globin intron. Considering these results and taking into account that a constant volume of viral particles has been used for transduction, the difference between the construct containing and lacking the beta-globin intron is minimal. Since packaging efficiency of the AAV-2 decreases with increasing sizes of the insert (Dong, Fan, & Frizzell, 1996), the iGEM team Freiburg_Bioware suggests using the beta-globin intron in dependence on the size of your transgene.
mGMK_TK30 fusion protein
The thymidine kinase mutant TK30 contains six modified amino acids (Black, Newcomb, Wilson, & Loeb, 1996) created in a first screening showing enhanced affinity for gancivlocir and acyclovir, but reduced specificity for its natural substrate thymidine.
As efficient tumor killing and therefore ganciclovir activation is essential for successful tumor ablation, further improvements were conducted. Overexpression of transgenic thymidine kinase leads to accumulation of non-toxic intermediates, which cannot be phosphorylated sufficiently by endogenous guanylate kinase, the second enzyme in the salvage pathway of nucleotides.
Overcoming this bottleneck was accomplished by fusing the mouse guanylate kinase (mGMK) to the N-terminus of TK30 mutant creating a fusion protein (mGMK_TK30) with enhanced GCV/ACV sensitivity in vitro and in vivo (Ardiani, Sanchez-Bonilla, & Black, 2010) and improved bystander activity. The effect of non-transfected tumor cell killing upon transfer of toxic metabolites through gap junctional intercellular communication (GJIC) or immune-mediated tumor ablation is essential in suicide gene therapy (Pope, 1997). GCV-triphosphate is mainly transported through the central pore formed between connexin proteins from neighboring cells (Gentry, Im, Boucher, Ruch, & Shewach, 2005), but immune-induced bystander effect seems to be likely as well (Grignet-Debrus, Cool, Baudson, Velu, & Calberg-Bacq, 2000).
hGH
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1319
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 1977
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 2882
Illegal AgeI site found at 3011 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 3413
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 1369