Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K404202"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/5/59/Freiburg10_ViralBrick_motif_His.png | https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/parts/5/59/Freiburg10_ViralBrick_motif_His.png | ||
| + | |||
| + | ===Restriction sites=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | <table border="1" style="float:right; width:480px; height:auto;> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <th><b>Restriction site</b></th> | ||
| + | <th><b>Enzyme</b></th> | ||
| + | <th><b>Recognition sequence</b></th> | ||
| + | <th><b>Activity</b></th> | ||
| + | <th><b>Temp.</b></th> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>upstream 453</td> | ||
| + | <td>[http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productR3132.asp SspI-HF]</td> | ||
| + | <td>[[image:Freiburg10_recognition site SspI-HF.Gif]]</td> | ||
| + | <td>25;100;0;100</td> | ||
| + | <td>37°C</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>downstream 453</td> | ||
| + | <td>[http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productR3138.asp SalI-HF]</td> | ||
| + | <td>[[image:Freiburg10_recognition site SalI-HF.Gif]]</td> | ||
| + | <td>10;100;100;100</td> | ||
| + | <td>37°C</td> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>upstream 587</td> | ||
| + | <td>[http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productR3136.asp BamHI-HF]</td> | ||
| + | <td>[[image:Freiburg10_recognition site BamHI-HF.Gif]]</td> | ||
| + | <td>100;50;10;100</td> | ||
| + | <td>37°C</td> | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | <td>downstream 587</td> | ||
| + | <td>[http://www.neb.com/nebecomm/products/productR3151.asp PvuII-HF]</td> | ||
| + | <td>[[image:Freiburg10_recognition site PvuII-HF.Gif]]</td> | ||
| + | <td>0;25;0;100</td> | ||
| + | <td>37°C | ||
| + | </tr> | ||
| + | <tr> | ||
| + | </table> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Revision as of 14:15, 26 October 2010
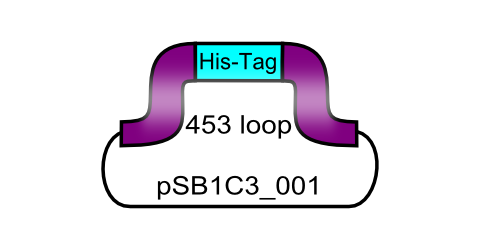
ViralBrick-453-His-Tag
The His-tag motif, ready for insertion into the 453 loop
Usage and Biology
Protein tagging via histidine tags is a widely used method for protein purification: Multiple histidine residues (most commonly: Six) are fused to the end of the targeting protein.
The high binding affinity of histidine towards metal is being exploited for the purification of proteins via the so called “Immobilized Metal Ion Affinity Chromatography“(IMAC): Multiple histidine residues (most commonly: Six) are being fused to the end of the targeting protein. A cell extract containing the recombinant protein is then applied to a column containing immobilized Ni2+-ions. The His-tags complex the Ni2+-ions while other cellular proteins can be washed off the column. The purified proteins can then be eluted with imidazole, which displaces the histidine residues.(Smith, Furman, Ingolia, & Pidgeon, 1988), (Hoffmann & Roeder, 1991)
Since the aim behind engineering therapeutic AAV vectors is a safe administration to human patients, it is important to consider a convenient way of purifying the virus particles. Contamination by cellular proteins could cause toxic side effects or a strong immune response. Koerber et al. have first inserted a His-tag into a surface-exposed loop at amino acid position 587 in the Cap protein and successfully purified recombinant virsuses using IMAC (Koerber et al. 2007). For our Virus Construction Kit, we provide the His-tag motif in the ViralBrick standard, allowing for an easy insertion into the 453 and/or 587 loop .

Restriction sites
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]