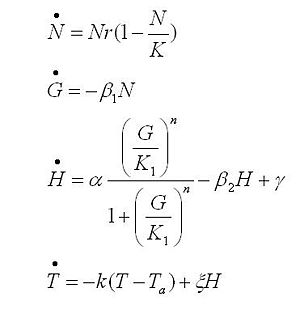Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K141000"
Qiuxinyuan12 (Talk | contribs) |
Qiuxinyuan12 (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 82: | Line 82: | ||
Galactose comsumption and heat effects. | Galactose comsumption and heat effects. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| Line 105: | Line 98: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K141000 parameters</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K141000 parameters</partinfo> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Contribution: NUDT_CHINA 2023== | ||
| + | In our project for iGEM2023, we aims to design a system that can effectively deliver the uncoupling protein UCP1 into adipocytes via PVCs.Herein,one composite part from the registry was used to generate the plasmid for functionality of EGFP-UCP1 Payload Protein in HEK-293T Cells .Remarkably,this part,uncoupling protein UCP1, was submitted by team iGEM08_Valencia.However, we found important information missing on the registry pages of this part. Therefore, we made efforts to provide experimental validation data and our protocol to enable the PVC-based delivery of the UCP1 part into target cells. | ||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <figure class="figure"> | ||
| + | < img src="https://static.igem.wiki/teams/4960/wiki/basic-part/functionality-of-ucp1-based-payload-protein-in-hek-293t-cells.png" class="figure-img img-fluid rounded" height="250px"> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | |||
| + | </html> | ||
| + | Figure 1. Functionality of UCP1-based Payload Protein in HEK-293T Cells. (e, f) Localization Pdp1NTD-EGFP-UCP1 in HEK-293T cells. For wide-field microscopy in e, cells were transfected with pNC088 (PCMV-Pdp1NTD-EGFP-UCP1). For confocal images in f, cells were co-transfected with MTS-mcherry and PNC088. Photos were taken 48 h post transfection, scale bar: 100μm for wide-field microscopy and 10 μm for confocal microscopy. Data are representative images of 3 independent experiments. (g) Charactrization of cellular metabolism in HEK-293T cells transfected with either pNC088 or pcDNA3.1(+). Glucose concentration in the cell culture medium was measured 48 h after transfection; data shows mean±SD, n=3 independent experiments. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | ===Methods=== | ||
| + | To validate the function of Pdp1NTD-3*GGSGG-EGFP-2*GGSGG- UCP1,we transfected HEK-293T cells with pNC088 and observed the cellular localization of the fusion protein 48 hours post-transcription by widefield fluorescent microscopy and live-cell confocal imaging. We also analyzed the glucose consumption of the transfected cells by measuring the glucose levels in the culture medium. This analysis represented the lev | ||
Revision as of 02:21, 12 October 2023
Ucp1
Ucp1 is a gene which encodes for UCP1 protein.
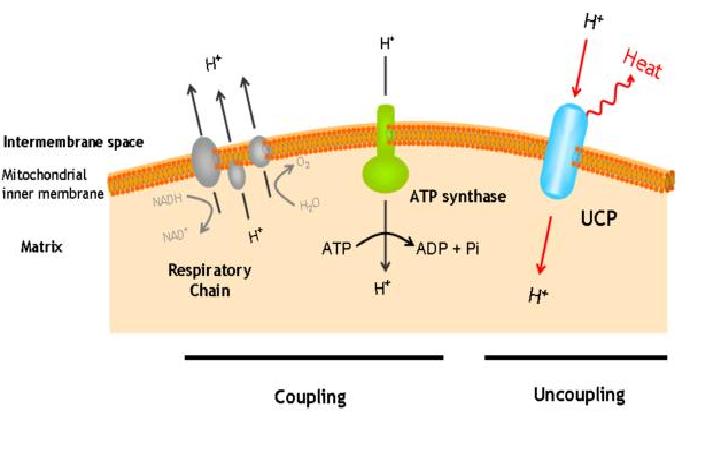
The uncoupling protein UCP1 is a proton carrier characteristic of brown adipose tissue. UCP1 uncouples the respiratory chain of ATP production, converting the metabolic energy in heat.
|
UCP1 is a 33kd protein which is exclusively located in the brown adipocites.
It is an integral protein present in inner mitocondrial membrane.
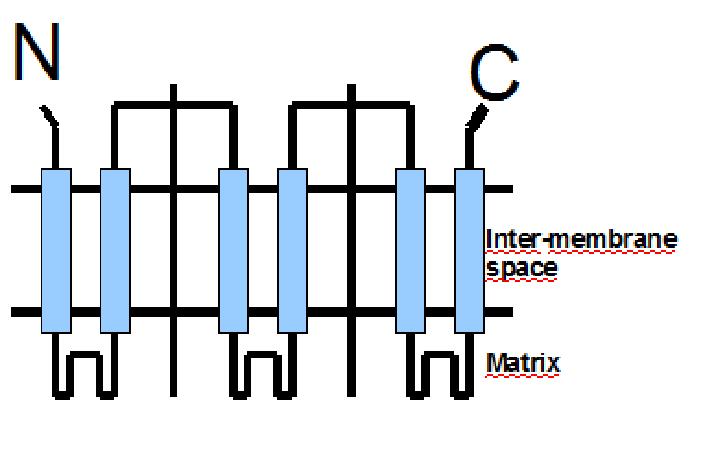
The protein has a tripartite structure. The structure displays an around 100 residues region which is three times repeated. Each part encodes for two transmembrane segments and one long hydrophilic loop.The functional carrier unit is an homodimer.
|
The main difference between UCP1 and most of the proteins with a nuclear codification is the lack of the importation targeting to the mitochondria in UCP+ proteins.
The condition that determines the mitochondria as the protein target lays in the first loop which protudes in the mitochondrial matrix.
The second loop of the matrix is essential for the insertion of the protein in the inner mitochondrial matrix. Purine nucleotides act as inhibitors of protein activity and esterificated fatty acids act as inductors.
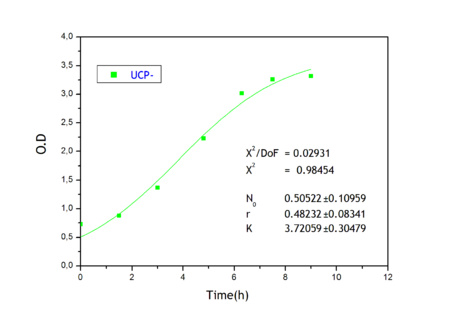
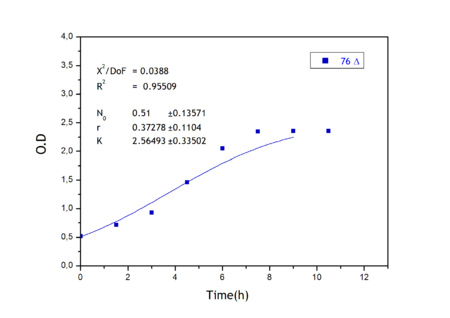
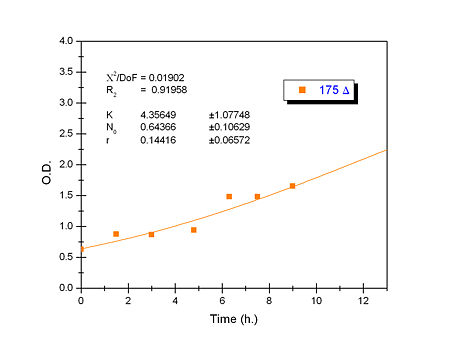
Apart from monitoring temperature evolution, we also characterized O.D. variations of each of our strains. We took O.D. measures every one a half hours for nine hours. We carried out this experiment both in Erlenmeyer flasks in the 30ºC shaking stove and in our LCCs. This measurements were useful in order to determine some parameters for our Black Box Model. Besides, we were able to prove that the UCP was indeed being produced even though we could not see the temperature increase. Since our mutant strains Gly175Δ and Gly76Δ do not have the same growing rate as UCP+ when they are expressing the protein, the difference between the results in the strains showed that the reason for our lack of temperature increase was that we had not found the optimum conditions yet. This results made us keep on working until we obtained successful results.
Strains growth equations:
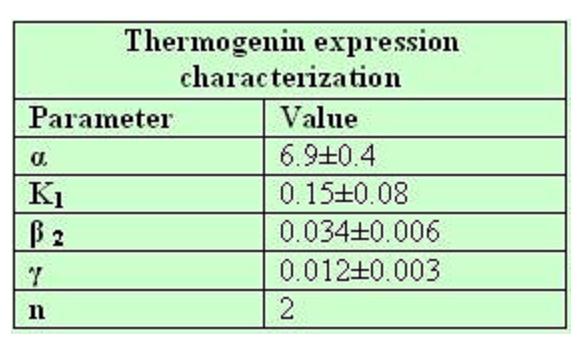
Model caonstants and parameters:
The black box model simulates the temperature evolution of the system as a function of the growth rate, galactose concentration and thermogenin expresion. We assume that our system can be reproduced by the following system of equations:
where:
- first equation: Growth of the culture: logistic growth of the different mutants used in our experiments.
- second equation: Galactose evolution: Galactose is the metabolite which induces the thermogenin expresion.
- third equation: Thermogenin concentration level.
- Fourth equation: Temperature evolution. the first term of the equation represents the losses to the ambient of the calorimeter and the second one the temperature increase as a consequence of the thermogenin expresion.
From a sample of 10 experiments in which the evolution of the temperature of the four strain was measured we perform a fit using the software simulink.
Common parameters values:
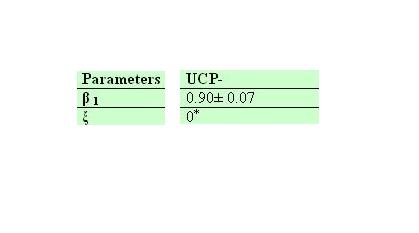
Ucp- own parameters
Galactose comsumption and heat effects.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 47
Illegal BglII site found at 347
Illegal BamHI site found at 835 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 58
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Contribution: NUDT_CHINA 2023
In our project for iGEM2023, we aims to design a system that can effectively deliver the uncoupling protein UCP1 into adipocytes via PVCs.Herein,one composite part from the registry was used to generate the plasmid for functionality of EGFP-UCP1 Payload Protein in HEK-293T Cells .Remarkably,this part,uncoupling protein UCP1, was submitted by team iGEM08_Valencia.However, we found important information missing on the registry pages of this part. Therefore, we made efforts to provide experimental validation data and our protocol to enable the PVC-based delivery of the UCP1 part into target cells.
Methods
To validate the function of Pdp1NTD-3*GGSGG-EGFP-2*GGSGG- UCP1,we transfected HEK-293T cells with pNC088 and observed the cellular localization of the fusion protein 48 hours post-transcription by widefield fluorescent microscopy and live-cell confocal imaging. We also analyzed the glucose consumption of the transfected cells by measuring the glucose levels in the culture medium. This analysis represented the lev