Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K4391003"
(→References) |
|||
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
| − | + | [1] | |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [2] Rcsb.org. H.M. Berman, J. Westbrook, Z. Feng, G. Gilliland, T.N. Bhat, H. Weissig, I.N. Shindyalov, P.E. Bourne. (2000) The Protein Data Bank Nucleic Acids Research, 28: 235-242. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [3] Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 31 (13), 3406-15, (2003) | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [4]Zhao, Y., et al., Automated and fast building of three-dimensional RNA structures. Scientific Reports, 2012. 2: p. 734. | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [5] http://hex.loria.fr/ | ||
| + | <br> | ||
<!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
Revision as of 16:35, 13 October 2022
ToxR Aptamer
This is an aptamer against the protein ToxR (PDB ID: 4MLO) found in Vibrio sp. bacteria. The aptamer was generated using in-silico aptamer generation techniques to bind to ToxR. THis was developed as a collaboration between Team IISER_Mohali and Team Montpellier, iGEM 2022.
Usage and Biology
We received a protein of interest, ToxR. This protein was chosen as a bio-marker for Vibrio as it is a virulence regulator in Vibrio species. The protein regulates gene loci T3SS1 and Vp-PAI. The protein is involved in Quorum sensing. ToxR is a positive regulator of Thermostable Direct Haemolysin (TDH). TDH causes erythrocytic rupture by interfering with the cell membrane integrity. It is a pore-forming toxin (PFT). Post-oligomerisation forms heptameric complexes that increase the water entry into the cells. It is indicative of Horizontal gene transfer and hence forms a suitable target for our Aptamer. Genes in the loci are TCP (toxin-correlated pillus) and ct (cholera toxin). The positive result from our Aptamer would hence indicate only the presence of pathogenic Vibrio sp. and reduce false positives due to background interference from similar proteins expressed in non-virulent strains.
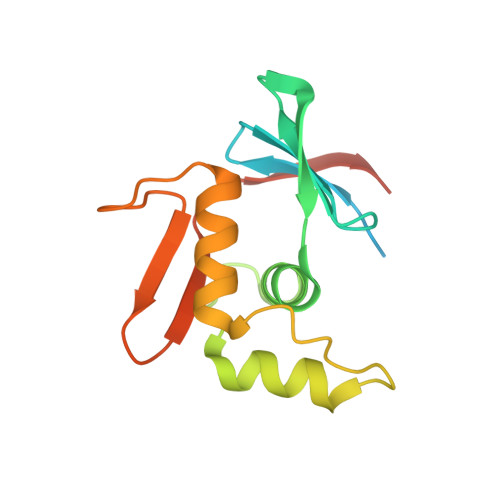
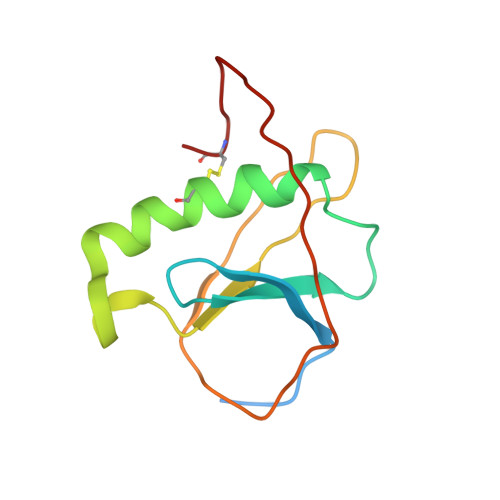
ToxR has a cytoplasmic domain (PDB ID 7NMB) and a periplasmic domain (PDB ID 7NN6), shown in Fig-1 and Fig-2.
Please check out the design section for the step-wise design approach taken for this aptamer
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Modelling
2D folding of Aptamer
The 2D folded structure of the aptamer was generated using mFOLD (UNAFOLD web server). The input was the DNA aptamer sequence and default parameters 25°C, 1.0 M Na+ and 0.0 M Mg++, linear DNA, oligomer correction, 5 percent suboptimality. 2 structures were generated with structure 1 dG = -28.05 kcal/mol and structure 2 dG = -27.89 kcal/mol Model-Fig-1 shows the least energy (most stable) structure 1.
3D structure of Aptamer
The 3D folded structure of the aptamer was generated using Xiao Lab 3dRNA/DNA - An RNA and DNA tertiary structure prediction method (http://biophy.hust.edu.cn/new/3dRNA/create). The input was the DNA aptamer sequence, the 2D structure in Vienna format, obtained from mFOLD and parameters molecule type DNA, Procedure Best, # of Predictions 5. No changes were made in Advanced options. Model-Fig-2 shows the most stable folded 3D structure.
Molecular Docking
Cytoplasmic domain of ToxR, PDB ID 7NMB was chosen at the protein that aptamer binds to.
Model-Table-1 shows the top 10 best docked models. According to HDOCK, a Confidence Score above 0.7 means that the two molecules would be very likely to bind. As all of the top 10 models have high Confidence Score of >8.0, IL-6 and the aptamer are likely to bind very well. Model-Fig-3 shows model_1 which is the most likely docked configuration (lowest Docking Score and highest Confidence Score).
References
[1]
[2] Rcsb.org. H.M. Berman, J. Westbrook, Z. Feng, G. Gilliland, T.N. Bhat, H. Weissig, I.N. Shindyalov, P.E. Bourne. (2000) The Protein Data Bank Nucleic Acids Research, 28: 235-242.
[3] Mfold web server for nucleic acid folding and hybridization prediction. Nucleic Acids Res. 31 (13), 3406-15, (2003)
[4]Zhao, Y., et al., Automated and fast building of three-dimensional RNA structures. Scientific Reports, 2012. 2: p. 734.
[5] http://hex.loria.fr/