Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K4140024"
Ahmed Mattar (Talk | contribs) (→Usage) |
Ahmed Mattar (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K4140025 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K4140025 short</partinfo> | ||
==Part Description== | ==Part Description== | ||
| − | The LacZ-alpha fragment is encoded by this region and is derived from the pUC19 cloning vector. Because it is smaller than the LacZ-omega region, the LacZ-alpha fragment can be easily incorporated into a plasmid when the two non-functional LacZ gene fragments (alpha and omega) are co-expressed. X-gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoyl-d-galactopyranoside), a soluble colourless molecule that is a substrate of ß-galactosidase and generates a blue product when cleaved, is used to detect the alpha-complementation. It's linked to KP-SP ISA secreting peptide signal at the N-terminus of the reporter protein to transmit it from intra cellular to extra cellular | + | The LacZ-alpha fragment is encoded by this region and is derived from the pUC19 cloning vector. Because it is smaller than the LacZ-omega region, the LacZ-alpha fragment can be easily incorporated into a plasmid when the two non-functional LacZ gene fragments (alpha and omega) are co-expressed. X-gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoyl-d-galactopyranoside), a soluble colourless molecule that is a substrate of ß-galactosidase and generates a blue product when cleaved, is used to detect the alpha-complementation. It's linked to KP-SP ISA secreting peptide signal at the N-terminus of the reporter protein to transmit it from intra cellular to extra cellular. |
| + | |||
==Usage== | ==Usage== | ||
In order to detect the increased levels of phenylalanine in PKU patients, we used the lacZ alpha gene which encodes beta-galactosidase, which catalyzes the cleavage of lactose to form galactose and glucose that utilizes X-gal to change the color into blue as shown in figure 1. | In order to detect the increased levels of phenylalanine in PKU patients, we used the lacZ alpha gene which encodes beta-galactosidase, which catalyzes the cleavage of lactose to form galactose and glucose that utilizes X-gal to change the color into blue as shown in figure 1. | ||
[[File:wcb.png|Figure 1. (shows the whole cell-based biosensor.) ]] | [[File:wcb.png|Figure 1. (shows the whole cell-based biosensor.) ]] | ||
| + | |||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
Revision as of 17:27, 6 October 2022
PAH releasing device
Part Description
The LacZ-alpha fragment is encoded by this region and is derived from the pUC19 cloning vector. Because it is smaller than the LacZ-omega region, the LacZ-alpha fragment can be easily incorporated into a plasmid when the two non-functional LacZ gene fragments (alpha and omega) are co-expressed. X-gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoyl-d-galactopyranoside), a soluble colourless molecule that is a substrate of ß-galactosidase and generates a blue product when cleaved, is used to detect the alpha-complementation. It's linked to KP-SP ISA secreting peptide signal at the N-terminus of the reporter protein to transmit it from intra cellular to extra cellular.
Usage
In order to detect the increased levels of phenylalanine in PKU patients, we used the lacZ alpha gene which encodes beta-galactosidase, which catalyzes the cleavage of lactose to form galactose and glucose that utilizes X-gal to change the color into blue as shown in figure 1.
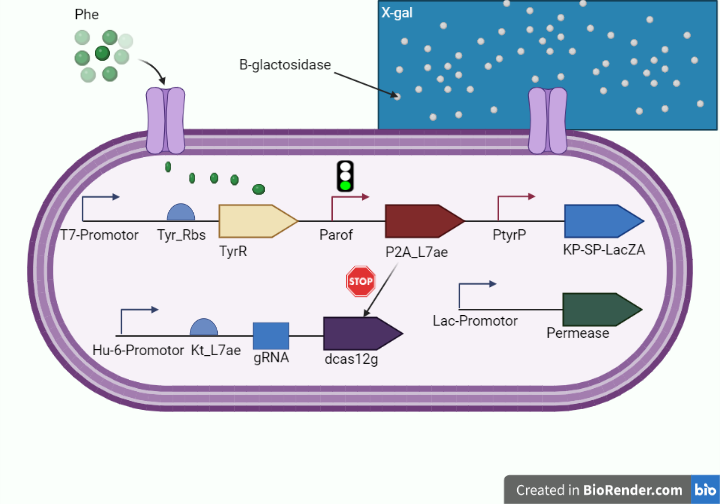
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 383
Illegal BamHI site found at 910
Illegal XhoI site found at 620 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
