Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1807009"
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
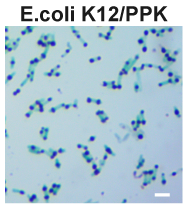
Polyphosphate kinase (PPK) catalyzes the synthesis of polyphosphate (polyP). PolyP is a polyanionic biopolymer and generally stored in cells in the form of polyP granules. Theoretically, the presence of intracellular polyP granules can be observed with light microscopy after the cells had been stained with the cationic dye, such as toluidine blue. To test this, we overexpressed this Part using plasmid pBBR1MCS2 in E. coli K12 and examined polyP granules in toluidine blue stained cells. | Polyphosphate kinase (PPK) catalyzes the synthesis of polyphosphate (polyP). PolyP is a polyanionic biopolymer and generally stored in cells in the form of polyP granules. Theoretically, the presence of intracellular polyP granules can be observed with light microscopy after the cells had been stained with the cationic dye, such as toluidine blue. To test this, we overexpressed this Part using plasmid pBBR1MCS2 in E. coli K12 and examined polyP granules in toluidine blue stained cells. | ||
[[File:CPU-Nanjing-Parts-PPK-1.png|200px|center]] | [[File:CPU-Nanjing-Parts-PPK-1.png|200px|center]] | ||
| − | <center>Figure 1. | + | <center>Figure 1. Microscopic observation of polyP granules in E. coli K12/PPK. Intracellular polyP granules appear blue-purple. Scale bar, 2 μm.</center> |
After staining, polyP can be easily visualized as blue-purple granules. | After staining, polyP can be easily visualized as blue-purple granules. | ||
Revision as of 10:49, 27 September 2022
Polyphosphate kinase enzyme from Escherichia coli
Coding sequence for the Polyphosphate enzyme (PPK) from Escherichia coli.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 317
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 1671
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Experimental characterization added by CPU-Nanjing 2022 TEAM
Team Cpu-Nanjing has added new experimental characterization on this existing Part.
Polyphosphate kinase (PPK) catalyzes the synthesis of polyphosphate (polyP). PolyP is a polyanionic biopolymer and generally stored in cells in the form of polyP granules. Theoretically, the presence of intracellular polyP granules can be observed with light microscopy after the cells had been stained with the cationic dye, such as toluidine blue. To test this, we overexpressed this Part using plasmid pBBR1MCS2 in E. coli K12 and examined polyP granules in toluidine blue stained cells.
After staining, polyP can be easily visualized as blue-purple granules.
iGEM2021_Nanjing-China Experiment
Group: Nanjing-China 2021
Author: Hao Yin
Polyphosphate kinase(PPK) polymerizes the terminal phosphate of ATP to a long chain of polyphosphate(polyP) in a freely reversible reaction. Here polyphosphate kinase was purified and characterized by SDS-PAGE. Bands of 69kDa showed the existence of PPK in the Escherichia coli.
Additionally, efficiency of polyP synthesis by PPK was measured at 1mM ATP. As shown in the diagram, polyP synthesis was linear with time for about 40 min. However, if the concentration of ATP is lower than 5 μM, there is virtually no synthesis of polyP for 20 min.
Reference: Kyunghye Ahn and Arthur Kornberg. Polyphosphate Kinase from Escherichia coli[J]. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 1990, 265, 20, 11734-11739.
iGEM2019_Nanjing China Experiment
This year our team develops a simple solo medium-copy plasmid-based polyphosphate kinase (PPK1) overexpression strategy for achieving maximum intracellular polyphosphate accumulation, so the data can provide some reference to this part.
We test supernatant Pi concentration and optical density of Ecoil(DH5a) and DH5a-MDPP in Synthetic municipal wastewater(SMW).
Ps: SMW means Synthetic municipal wastewater
DH5a-MDPP means solo medium-copy DH5a ppk in DH5a