Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K4291009"
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
SLC7A5 purification | SLC7A5 purification | ||
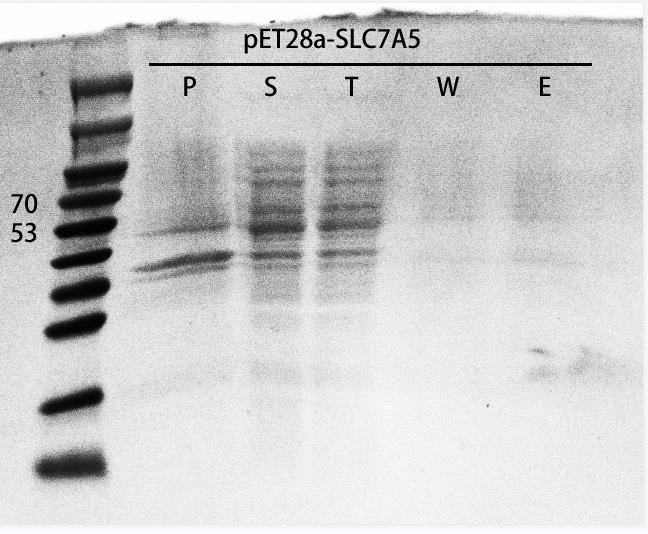
In order to verify if SLC7A5 expression in the E. coli host strain, we transformed the recombinant plasmids into E. coli BL21(DE3), inoculated the recombinants and added IPTG to induce protein expression when the OD600 reached 0.6. After overnight induce and culture, we collected the cells and ultrasonic fragmentation of cells to release the intracellular proteins. Next, we verified the expression level of the target protein by SDS-PAGE (Figure 5). As a result, the recombinants successfully expressed our target protein. | In order to verify if SLC7A5 expression in the E. coli host strain, we transformed the recombinant plasmids into E. coli BL21(DE3), inoculated the recombinants and added IPTG to induce protein expression when the OD600 reached 0.6. After overnight induce and culture, we collected the cells and ultrasonic fragmentation of cells to release the intracellular proteins. Next, we verified the expression level of the target protein by SDS-PAGE (Figure 5). As a result, the recombinants successfully expressed our target protein. | ||
| − | [[File:T-- | + | [[File:T--Canton HS--BBa K4291009-figure 55.jpg|500px|thumb|center|Figure 5. SDS-page of SLC7A5 purification.]] |
| + | |||
Revision as of 10:25, 26 September 2022
SLC7A5
SLC7A5
Characterization by Canton_HS
BBa_K4291009
Name: SLC7A5 Base Pairs: 1524 bp Origin: Homo sapiens, genome Properties: amino acid transporter
Usage and biology
Solute carrier transporter 7a5 (SLC7A5), also known as LAT1, belongs to the APC (amino acid, polyamine, choline) superfamily. The heterodimer SLC7A5 and glycoprotein CD98 linked through a conserved disulfide is responsible for the uptake of essential amino acids in crucial body districts such as the placenta and blood-brain barrier. The SLC7A5 transports the so-called branched-chain amino acids (BCAA) into the brain. Mutation in this gene reduces branched-chain amino acid levels in the brain and interferes with neural cell protein synthesis which shows reduced social interactions and other changes. There are many different genetic mutations causing autism, and this heterogeneity makes it difficult to develop effective treatments.
= Construct design
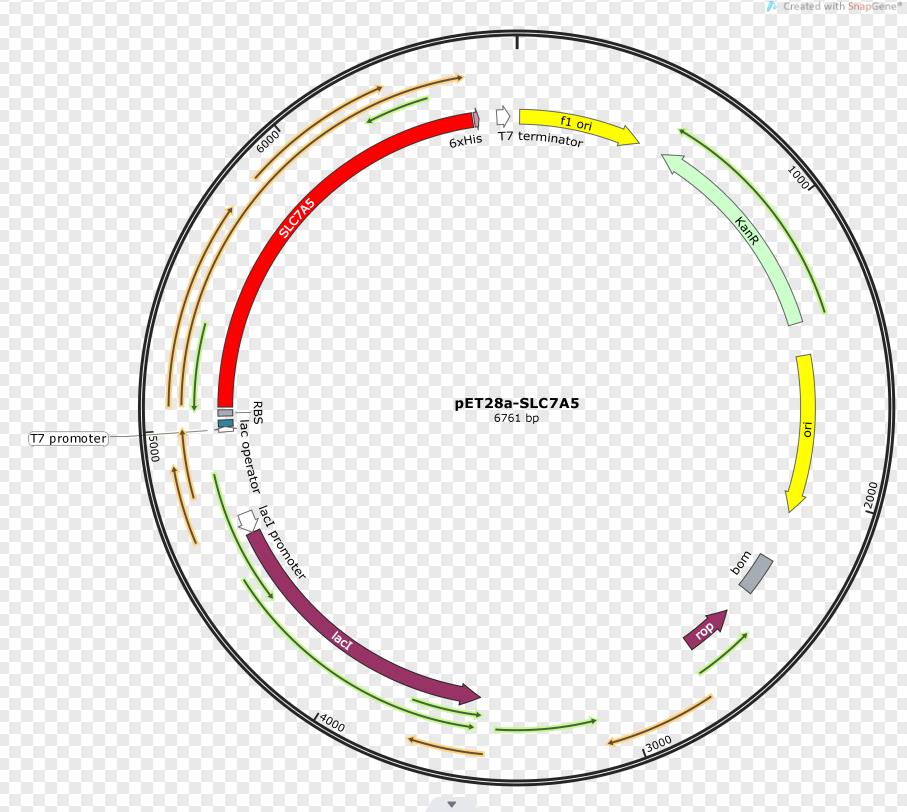
SLC7A5 transporter is expressed under the promoter T7. The gene fragment was inserted into pET28a.
Experimental approach
1.1 Construction of biosensor expression plasmids In order to build our plasmids, we let the synthetic company synthesize the SLC7A5 DNA sequence and inserted it into the pUC57 vector. We amplified the SLC7A5 from the plasmid by PCR (Figure 1A) and inserted it into the EcoRI and XhoI sites of the pET28a vector. We transformed it into E. coli Top10 competent cells.
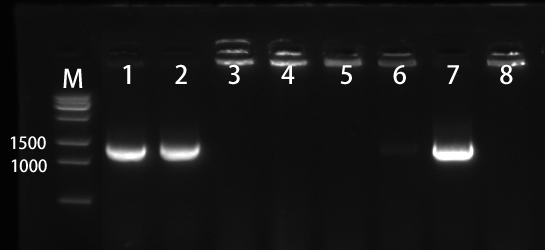
1.2 Colony PCR of pET28a-SLC7A5 We selected the 8 colonies to perform by colony-PCR (Figure 3). The electrophoresis result showed that No. 1, 2, and 7 has correct bands.
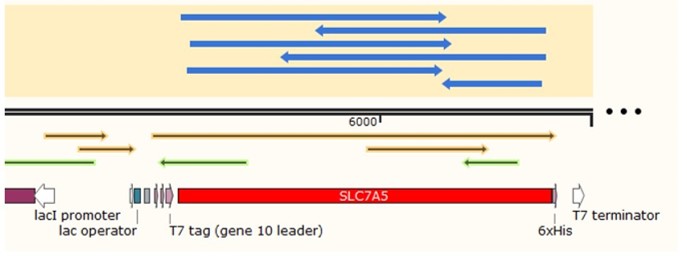
1.2 Sanger sequencing of recombinant plasmid We inoculated the correct colonies in LB (Kan+) liquid medium and extracted the plasmids and sent them to the company for Sanger sequencing. The returned sequencing data showed that there were no mutations in the gene region which means we successfully constructed the recombinant plasmid.
Proof of function
SLC7A5 purification In order to verify if SLC7A5 expression in the E. coli host strain, we transformed the recombinant plasmids into E. coli BL21(DE3), inoculated the recombinants and added IPTG to induce protein expression when the OD600 reached 0.6. After overnight induce and culture, we collected the cells and ultrasonic fragmentation of cells to release the intracellular proteins. Next, we verified the expression level of the target protein by SDS-PAGE (Figure 5). As a result, the recombinants successfully expressed our target protein.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 30
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 39
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 108 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]