Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K4011010"
Azahraonng (Talk | contribs) |
(→Characterization) |
||
| Line 29: | Line 29: | ||
==Characterization== | ==Characterization== | ||
| + | |||
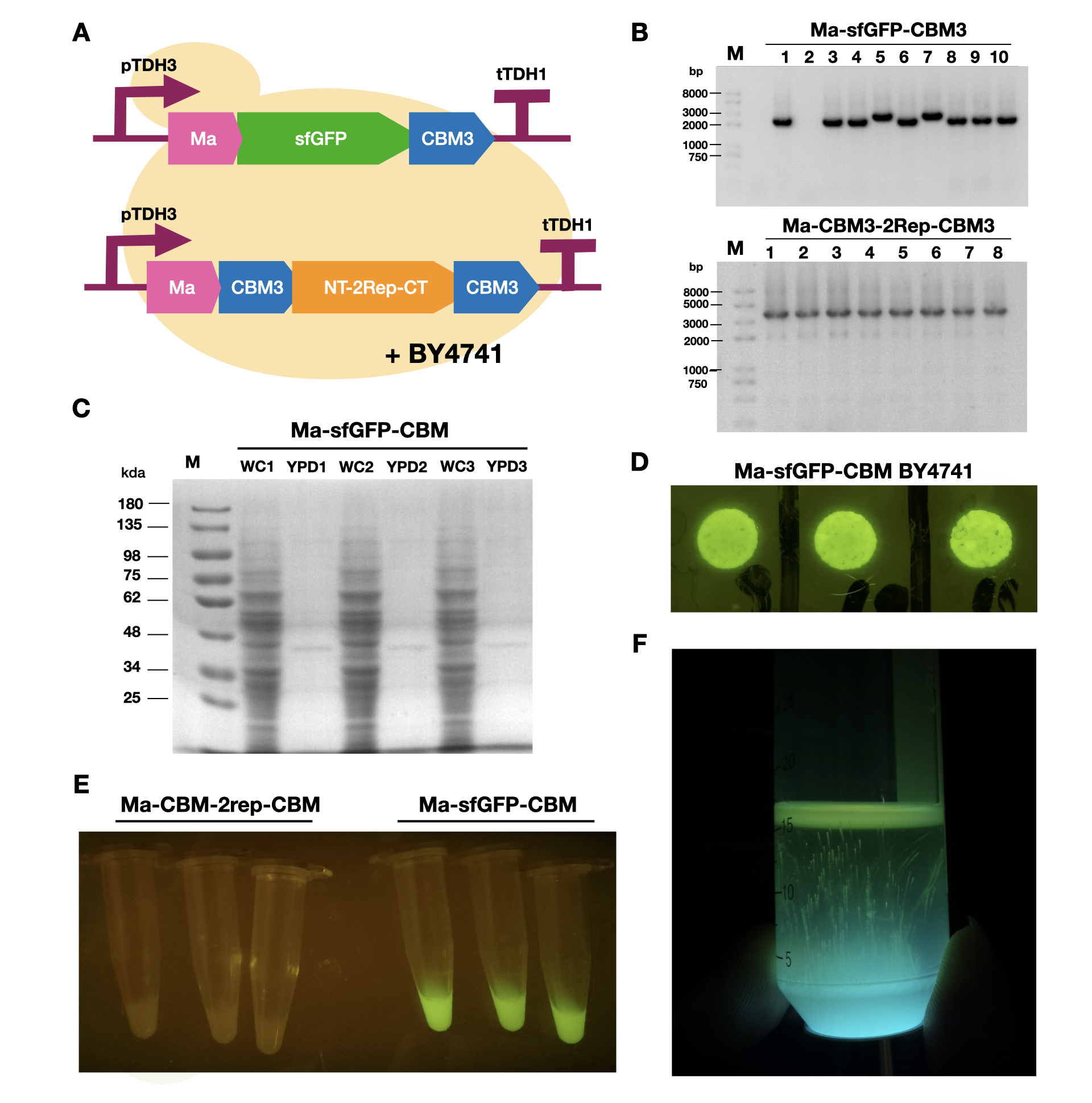
| + | To enable secretion of proteins in yeast, we attached a short signal peptide called maturation factor alpha (Ma) to our protein. Aza et al have already characterized Mα and mutated it to become more efficient at protein secretion. For our project, we selected Ma A9D; A20T; Q32H; F48S; G62D (referred to as Ma_Mut) as it had one of the highest secretion rates. We constructed two plasmids, Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 and Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 (Fig. 1B), and transformed both plasmids into yeast (Fig. 1A). | ||
| + | |||
| + | On YPD plates, secretion of Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 can be seen by the green halo surrounding each individual colony (Fig. 1D). After culturing Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 and Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 yeast in liquid YPD (Fig. 1E), we performed SDS-PAGE analysis on both the whole cell and growth media (Fig. 1C). We discovered that only a small portion of the expressed proteins were found in the media for Ma-sfGFP-CBM3, and an unobservable amount of secreted protein was found in the Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 media. This meant that most likely, only a small amount of CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 will be secreted, not enough to significantly alter the characteristics of the resulting BCM. As a proof of concept, we cultured SCOBY using Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 (Fig. 1F). In the future, we hope to increase the expression of secretion rate of Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 and Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 to achieve in situ modification of BCM (Mohammadi et al, 2019). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:T--LINKS China--Figure 18.png|thumbnail|750px|center|'''Figure 1:''' Expression and measurement of Ma proteins in <i>Saccharomyces cerevisiae</i>. A). Schematic of Ma plasmids transformed into <i>S. cerevisiae</i> BY4741 B) Gel electrophoresis results of Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 and Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 C) SDS-PAGE analysis of yeast whole cell and YPD media for Ma-sfGFP-CBM3. D) Pictures of single colonies of Ma-sfGFP-CBM3. E) Liquid cultures of Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 and Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3. F) BCM produced using Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 <i>S. cerevisiae</i> BY4741SCOBY. ]] | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Revision as of 15:32, 21 October 2021
Ma-sfGFP-CBM3
Ma-Mut is a mutated protein tag derived from the protein secretion tag (Ma) of mating type alpha Saccharomyces cerevisiae. In yeast cells, proteins with the Ma tag will be secreted out of the cell. This year, we will use Ma-Mut to enable secretion of proteins fused with cellulose binding domain 3 (CBM3) from yeast. CBM3 BBa_K4011000 is an artificial protein derived from Ruminiclostridium thermocellum (Protein Data Bank (PDB) accession: 1NBC) and will bind to cellulose fibers. This will allow for modification of our bacterial cellulose membrane produced by a co-culture of Komagataeibacter and yeast. We will use Ma_Mut to construct composite parts Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 BBa_K4011010 and Ma-CBM3-NT2RepCT-CBM3 BBa_K4011011.
Other teams can utilize our Ma sequence for S. cerevisiae protein secretion.
Usage and Biology
The alpha-factor preproleader sequence is responsible for protein secretion in mating type alpha Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mα_Mut is derived from the preproleader sequence and first characterized by Aza et al in 2021, who mutated the sequence to increase protein secretion efficiency.
Natural Mα contains 89 amino acids with three functional regions: a pre-region (19 amino acids), pro-region (64 amino acids), and a spacer (6 amino acids). During S. cerevisiae modification, the preproleader will translocate the protein across the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER), and the pre-region will be cleaved. Then, the pro-region will direct the protein to the Golgi Apparutus for final modifications before release into media.
CBM3s allow for fused proteins to be bound to cellulose, and sfGFP have fluorescent properties suitable for easy detection.
Source
Ma comes from S. cerevisiae, sfGFP is a highly characterized sequence used in synbio, CBM3 comes from Ruminiclostridium thermocellum.
Design Considerations
1. The following mutations are added in Ma_Mut: A9D, A20T, Q32H, F48S, and G62R.
2. All codons were optimized for S. cerevisiae based on S. cerevisiae codon bias.
3. Linker EAEAFGS used between Ma and sfGFP, flexible linker GGGGS used between sfGFP and CBM3.
Characterization
To enable secretion of proteins in yeast, we attached a short signal peptide called maturation factor alpha (Ma) to our protein. Aza et al have already characterized Mα and mutated it to become more efficient at protein secretion. For our project, we selected Ma A9D; A20T; Q32H; F48S; G62D (referred to as Ma_Mut) as it had one of the highest secretion rates. We constructed two plasmids, Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 and Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 (Fig. 1B), and transformed both plasmids into yeast (Fig. 1A).
On YPD plates, secretion of Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 can be seen by the green halo surrounding each individual colony (Fig. 1D). After culturing Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 and Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 yeast in liquid YPD (Fig. 1E), we performed SDS-PAGE analysis on both the whole cell and growth media (Fig. 1C). We discovered that only a small portion of the expressed proteins were found in the media for Ma-sfGFP-CBM3, and an unobservable amount of secreted protein was found in the Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 media. This meant that most likely, only a small amount of CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 will be secreted, not enough to significantly alter the characteristics of the resulting BCM. As a proof of concept, we cultured SCOBY using Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 (Fig. 1F). In the future, we hope to increase the expression of secretion rate of Ma-sfGFP-CBM3 and Ma-CBM3-2Rep-CBM3 to achieve in situ modification of BCM (Mohammadi et al, 2019).
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 576
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 948
Illegal AgeI site found at 3079
Illegal AgeI site found at 3123
Illegal AgeI site found at 3295
Illegal AgeI site found at 3361 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 424
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 2320
