Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3989023"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
As a microbe- or pathogen-associated molecular pattern (MAMP or PAMP), elf18 can trigger strong plant immune responses, such as cell-wall reinforcement by callose deposition, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and induction of numerous defense-related genes. However, unlike another PAMP [[Part:BBa_K3286138|flg22]], which is perceived by most plants through FLS2 receptor, elf18 can be only perceived by Brassicaceae through EFR receptor. | As a microbe- or pathogen-associated molecular pattern (MAMP or PAMP), elf18 can trigger strong plant immune responses, such as cell-wall reinforcement by callose deposition, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and induction of numerous defense-related genes. However, unlike another PAMP [[Part:BBa_K3286138|flg22]], which is perceived by most plants through FLS2 receptor, elf18 can be only perceived by Brassicaceae through EFR receptor. | ||
| − | At least in A. thaliana, elf18 can trigger mildly stronger immune responses than flg22. | + | At least in for <i>A. thaliana</i> seedlings, elf18 can trigger mildly stronger immune responses than flg22 (Figure 1). |
[[File:flg22vself18.png|500px]] | [[File:flg22vself18.png|500px]] | ||
| − | + | Figure 1. Seedling growth inhibition assay comparing the immunogenicities of flg22 and elf18 | |
| + | |||
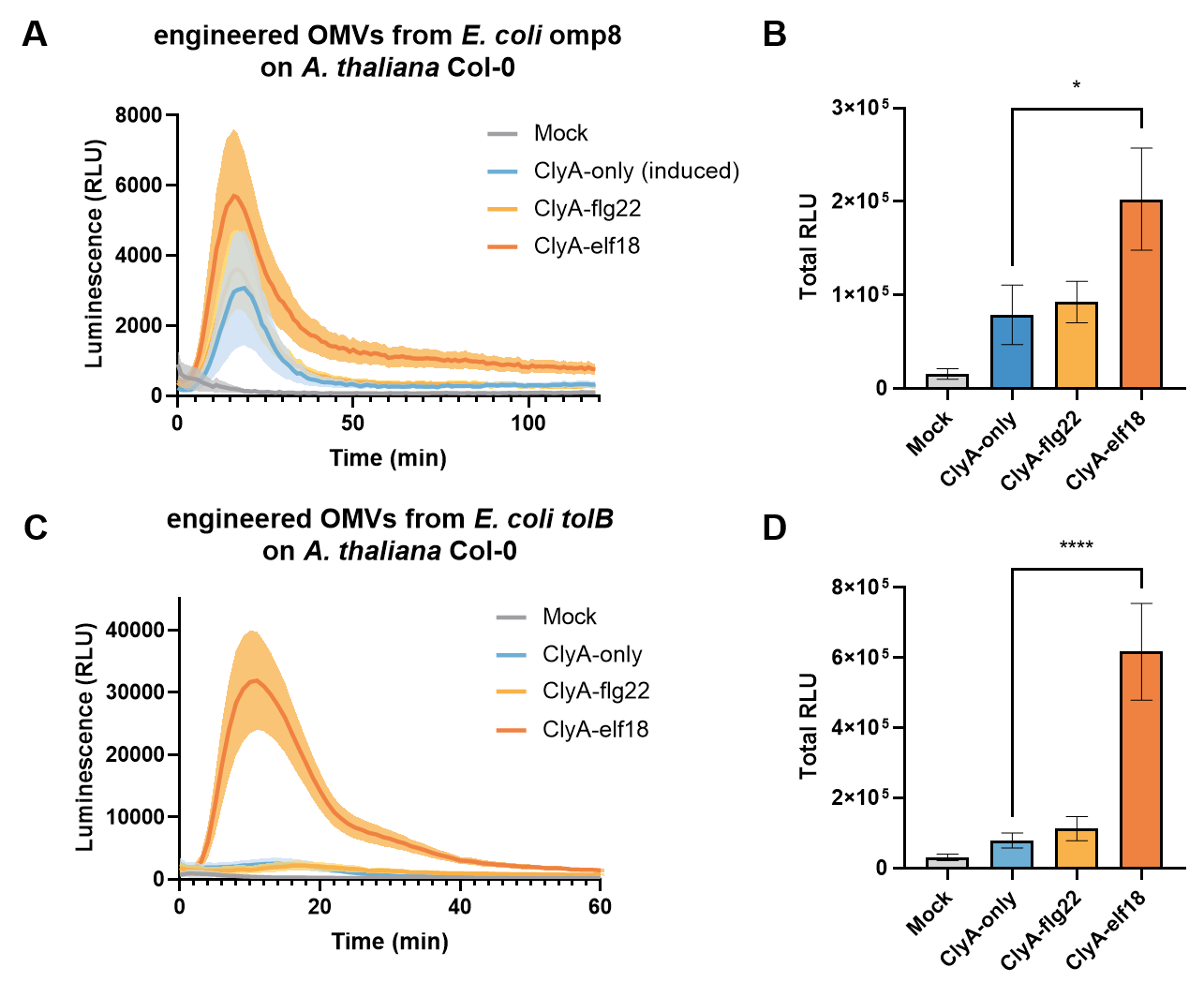
| + | Display of elf18 on outer membrane vesicle (OMV) surface by ClyA protein can further enhance the plant immune responses triggered by OMVs (Figure 2). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:ROS_overall_Col-0.png|500px]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | Figure 2. In ROS burst assay, OMVs with elf18 displayed trigger stronger ROS production than OMVs without elf18. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ====Reference==== | ||
[1] Kunze, G., Zipfel, C., Robatzek, S., Niehaus, K., Boller, T., & Felix, G. (2004). The N terminus of bacterial elongation factor Tu elicits innate immunity in Arabidopsis plants. The Plant Cell, 16(12), 3496-3507. | [1] Kunze, G., Zipfel, C., Robatzek, S., Niehaus, K., Boller, T., & Felix, G. (2004). The N terminus of bacterial elongation factor Tu elicits innate immunity in Arabidopsis plants. The Plant Cell, 16(12), 3496-3507. | ||
Revision as of 23:49, 20 October 2021
elf18
Elf18 is a peptide consisting of 18 conserved amino acids at the N-terminus of bacterial elongation factor Tu (EF-Tu), the most abundant bacterial protein.
As a microbe- or pathogen-associated molecular pattern (MAMP or PAMP), elf18 can trigger strong plant immune responses, such as cell-wall reinforcement by callose deposition, production of reactive oxygen species (ROS), and induction of numerous defense-related genes. However, unlike another PAMP flg22, which is perceived by most plants through FLS2 receptor, elf18 can be only perceived by Brassicaceae through EFR receptor.
At least in for A. thaliana seedlings, elf18 can trigger mildly stronger immune responses than flg22 (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Seedling growth inhibition assay comparing the immunogenicities of flg22 and elf18
Display of elf18 on outer membrane vesicle (OMV) surface by ClyA protein can further enhance the plant immune responses triggered by OMVs (Figure 2).
Figure 2. In ROS burst assay, OMVs with elf18 displayed trigger stronger ROS production than OMVs without elf18.
Reference
[1] Kunze, G., Zipfel, C., Robatzek, S., Niehaus, K., Boller, T., & Felix, G. (2004). The N terminus of bacterial elongation factor Tu elicits innate immunity in Arabidopsis plants. The Plant Cell, 16(12), 3496-3507.
[2] Zipfel, C., Kunze, G., Chinchilla, D., Caniard, A., Jones, J. D., Boller, T., & Felix, G. (2006). Perception of the bacterial PAMP EF-Tu by the receptor EFR restricts Agrobacterium-mediated transformation. Cell, 125(4), 749-760.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]