Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa M10052"
Susanychen (Talk | contribs) |
Susanychen (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_M10052 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_M10052 short</partinfo> | ||
| Line 6: | Line 4: | ||
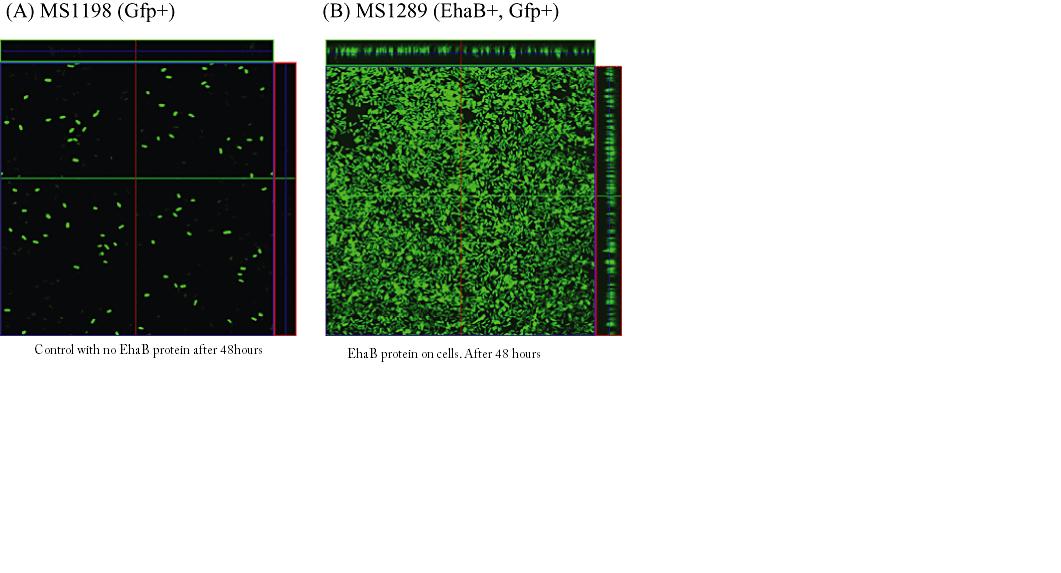
The EhaB part codes for an autotransporter protein that can transport itself across the bacterial membrane and go to the cell surface. Like other autotransporter proteins, the EhaB part has an N-terminal signal sequence, a passenger domain, and a translocation domain. EhaB expressed in E. Coli MS427 has been shown to form biofilms on polystyrene surfaces. Also, overexpression of the protein in E. Coli K-12 has resulted in biofilm formation under continuous flow conditions. <br> | The EhaB part codes for an autotransporter protein that can transport itself across the bacterial membrane and go to the cell surface. Like other autotransporter proteins, the EhaB part has an N-terminal signal sequence, a passenger domain, and a translocation domain. EhaB expressed in E. Coli MS427 has been shown to form biofilms on polystyrene surfaces. Also, overexpression of the protein in E. Coli K-12 has resulted in biofilm formation under continuous flow conditions. <br> | ||
The EhaB protein expression in E. Coli K12 and EDL933 was shown to promote adhesion to the extracellular matrix proteins collagen I and laminin. Moreover, EhaB can be expressed in vivo and can elicit an IgA immune response. | The EhaB protein expression in E. Coli K12 and EDL933 was shown to promote adhesion to the extracellular matrix proteins collagen I and laminin. Moreover, EhaB can be expressed in vivo and can elicit an IgA immune response. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[Image:Biofilm.jpg|200px]] | ||
---- | ---- | ||
Revision as of 15:43, 10 May 2009
{˂ehaB!}
The EhaB part codes for an autotransporter protein that can transport itself across the bacterial membrane and go to the cell surface. Like other autotransporter proteins, the EhaB part has an N-terminal signal sequence, a passenger domain, and a translocation domain. EhaB expressed in E. Coli MS427 has been shown to form biofilms on polystyrene surfaces. Also, overexpression of the protein in E. Coli K-12 has resulted in biofilm formation under continuous flow conditions.
The EhaB protein expression in E. Coli K12 and EDL933 was shown to promote adhesion to the extracellular matrix proteins collagen I and laminin. Moreover, EhaB can be expressed in vivo and can elicit an IgA immune response.
This part is in BglBricks Standard. It is flanked by BamHI and BglII sites instead of XbaI and SpeI. More information about the BglBricks Standard is available at:
[http://openwetware.org/wiki/Template:AndersonLab:BBb_Standard BglBricks Standard Description Page]
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal PstI site found at 589
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal PstI site found at 589
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal PstI site found at 589
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal PstI site found at 589
Illegal AgeI site found at 132 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]