Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3991006"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3991006 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3991006 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | pro-ArsD-amilGFP | + | |
| + | == Profile == | ||
| + | == BBa_K3991006 == | ||
| + | ==== Name: pro-ArsD-amilGFP ==== | ||
| + | ==== Base Pairs: 1200 bp ==== | ||
| + | ==== Origin: Escherichia coli (strain: LST424C, nat-host: Homo sapiens) ==== | ||
| + | ==== Properties: Gene technology for protecting patented bacterial strains ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | == Usage and Biology == | ||
| + | According to the WHO, arsenic levels above 10 parts per billion in water are harmful to humans. Levels in Bangladesh, however, are five times as much. The Bangladesh arsenic contamination is pending a solution. "I have no alternative." Uddin, a villager in Bangladesh, helplessly expresses his views towards drinking arsenic-contaminated well water. | ||
| + | What comes to your mind first when talking about arsenic? Arsenic is a naturally occurring element that is widely distributed in the earth's crust. It is found in water, air, food, and soil. In recent years, reports of arsenic poisoning have been increasing year by year. | ||
| + | Arsenic seeps into groundwater through rocks and soil, resulting in drinking water from surface sources (such as wells) that often contain higher levels of arsenic than water from, for example, lakes or reservoirs. In addition to groundwater, arsenic levels of 1.7 μg/L have been detected in the ocean, far exceeding the international regulation of 0.0175 μg/L (Neff, 2009). Irrigation with arsenic-contaminated water sources makes arsenic hazardous to human health from the food side. In addition, arsenic can also enter the human body from external sources, such as paints, textiles, and metal adhesives, through direct ingestion, gaseous inhalation, or skin absorptio. Or it can be absorbed by humans as a component of tobacco (WHO, 2018). Long-term exposure to high levels of arsenic can be harmful to humans, especially to developing infants and children. Although arsenic is not well understood, once it enters the body, the skin and various systems such as the nervous, respiratory, cardiopulmonary, immune, and endocrine systems are affected. In addition, the liver, kidneys, bladder, and prostate, which are responsible for detoxification, are damaged and cannot function effectively (National Institute of Environment Health Science, 2021). | ||
| + | For example, in a village in Hunan, China, 1200 in total 3000 residents have been tested for arsenic poisoning, which was mainly caused by the mining of realgar ore. According to the local hospital, 400 of 600 miners who have been tested for arsenic poisoning died from cancer. For instance, a family of 7 people all died from cancer, and 5 of the cases were determined that they were caused by arsenic poisoning (Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2014). | ||
| + | Not only for humans but excessive levels of arsenic can also affect plants and animals in the natural environment. For example, aquatic plants (e.g. algae), zooplankton, and amphibians, or aquatic animals (e.g. snails, fish, crustacean larvae, marine mammals) are all exposed to inorganic arsenic toxicity (Neff, 2009). | ||
| + | Arsenic is a microelement that is omnipresent in the environment. However, it is this common microelement that could be harmful to human body. If we take in more than 50 µg/L of arsenic, the function of our body will be disrupted. Also, the level of arsenic throughout the world is gradually increasing every year, and has already exceeded the level that human body can metabolize. | ||
| + | Areas close to factories whose product involves arsenic usually have a high arsenic concentration. Thus, we need arsenic detectors to ensure the security of people who work in these factories. According to the questionnaires and street research we did, although the general public did not know much about arsenic, most people believed that having an inexpensive and accurate sensor to detect arsenic is necessary. In addition, environmental and market scientists also considered that the current testing methods in the market are too cumbersome, so equipment that can detect arsenic levels easily and efficiently is required. | ||
| + | |||
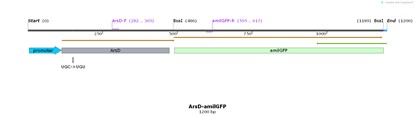
| + | == Construct design == | ||
| + | [[File:T--Shanghai United--BBa K3991006-figure1.jpg|500px|thumb|center|Figure 1. Plasmid diagram..]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | == BBa_K3991000 == | ||
| + | ==== Name: ArsD ==== | ||
| + | ==== Base Pairs: 1200 bp ==== | ||
| + | ==== Origin: Escherichia coli (strain: LST424C, nat-host: Homo sapiens) ==== | ||
| + | ==== Properties: Gene technology for protecting patented bacterial strains ==== | ||
| + | ArsD is a trans-acting repressor of the arsRDABC operon that confers resistance to arsenicals and antimonials in Escherichia coli. | ||
| + | |||
| + | == BBa_K592010 == | ||
| + | ==== Name: amilGFP ==== | ||
| + | ==== Base Pairs: 699bp ==== | ||
| + | ==== Origin: Acropora millepora ==== | ||
| + | ==== Properties: A yellow chromoprotein ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==== Usage and Biology ==== | ||
| + | This part is useful as a reporter and it naturally exhibits strong yellow color when expressed. | ||
| + | In the process of cultivating microorganisms, namely Escherichia coli, because of their small size, they cannot be directly observed with the naked eye, and a certain method is needed for monitoring. In cell biology and molecular biology, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene is often used as a reporter gene. Through genetic engineering technology, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene can be transferred into the genomes of different species and continue to be expressed in offspring. . Therefore, we constructed the amilGFP engineered bacteria to show the growth status (number and vitality) of E. coli by observing the strength of the green fluorescent protein signal. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | |||
<!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | <!-- Add more about the biology of this part here | ||
Revision as of 08:30, 19 October 2021
pro-ArsD-amilGFP
Profile
BBa_K3991006
Name: pro-ArsD-amilGFP
Base Pairs: 1200 bp
Origin: Escherichia coli (strain: LST424C, nat-host: Homo sapiens)
Properties: Gene technology for protecting patented bacterial strains
Usage and Biology
According to the WHO, arsenic levels above 10 parts per billion in water are harmful to humans. Levels in Bangladesh, however, are five times as much. The Bangladesh arsenic contamination is pending a solution. "I have no alternative." Uddin, a villager in Bangladesh, helplessly expresses his views towards drinking arsenic-contaminated well water. What comes to your mind first when talking about arsenic? Arsenic is a naturally occurring element that is widely distributed in the earth's crust. It is found in water, air, food, and soil. In recent years, reports of arsenic poisoning have been increasing year by year. Arsenic seeps into groundwater through rocks and soil, resulting in drinking water from surface sources (such as wells) that often contain higher levels of arsenic than water from, for example, lakes or reservoirs. In addition to groundwater, arsenic levels of 1.7 μg/L have been detected in the ocean, far exceeding the international regulation of 0.0175 μg/L (Neff, 2009). Irrigation with arsenic-contaminated water sources makes arsenic hazardous to human health from the food side. In addition, arsenic can also enter the human body from external sources, such as paints, textiles, and metal adhesives, through direct ingestion, gaseous inhalation, or skin absorptio. Or it can be absorbed by humans as a component of tobacco (WHO, 2018). Long-term exposure to high levels of arsenic can be harmful to humans, especially to developing infants and children. Although arsenic is not well understood, once it enters the body, the skin and various systems such as the nervous, respiratory, cardiopulmonary, immune, and endocrine systems are affected. In addition, the liver, kidneys, bladder, and prostate, which are responsible for detoxification, are damaged and cannot function effectively (National Institute of Environment Health Science, 2021). For example, in a village in Hunan, China, 1200 in total 3000 residents have been tested for arsenic poisoning, which was mainly caused by the mining of realgar ore. According to the local hospital, 400 of 600 miners who have been tested for arsenic poisoning died from cancer. For instance, a family of 7 people all died from cancer, and 5 of the cases were determined that they were caused by arsenic poisoning (Chinese Center for Disease Control and Prevention, 2014). Not only for humans but excessive levels of arsenic can also affect plants and animals in the natural environment. For example, aquatic plants (e.g. algae), zooplankton, and amphibians, or aquatic animals (e.g. snails, fish, crustacean larvae, marine mammals) are all exposed to inorganic arsenic toxicity (Neff, 2009). Arsenic is a microelement that is omnipresent in the environment. However, it is this common microelement that could be harmful to human body. If we take in more than 50 µg/L of arsenic, the function of our body will be disrupted. Also, the level of arsenic throughout the world is gradually increasing every year, and has already exceeded the level that human body can metabolize. Areas close to factories whose product involves arsenic usually have a high arsenic concentration. Thus, we need arsenic detectors to ensure the security of people who work in these factories. According to the questionnaires and street research we did, although the general public did not know much about arsenic, most people believed that having an inexpensive and accurate sensor to detect arsenic is necessary. In addition, environmental and market scientists also considered that the current testing methods in the market are too cumbersome, so equipment that can detect arsenic levels easily and efficiently is required.
Construct design
BBa_K3991000
Name: ArsD
Base Pairs: 1200 bp
Origin: Escherichia coli (strain: LST424C, nat-host: Homo sapiens)
Properties: Gene technology for protecting patented bacterial strains
ArsD is a trans-acting repressor of the arsRDABC operon that confers resistance to arsenicals and antimonials in Escherichia coli.
BBa_K592010
Name: amilGFP
Base Pairs: 699bp
Origin: Acropora millepora
Properties: A yellow chromoprotein
Usage and Biology
This part is useful as a reporter and it naturally exhibits strong yellow color when expressed. In the process of cultivating microorganisms, namely Escherichia coli, because of their small size, they cannot be directly observed with the naked eye, and a certain method is needed for monitoring. In cell biology and molecular biology, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene is often used as a reporter gene. Through genetic engineering technology, the green fluorescent protein (GFP) gene can be transferred into the genomes of different species and continue to be expressed in offspring. . Therefore, we constructed the amilGFP engineered bacteria to show the growth status (number and vitality) of E. coli by observing the strength of the green fluorescent protein signal.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]