Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3332057"
Xiaoyu Wang (Talk | contribs) |
AnnaTaylor (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 12: | Line 12: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| − | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/8/82/T--XMU-China--XMU-China_2020-GRHPR%E9%94%9A%E5%AE%9A.png" width=" | + | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/8/82/T--XMU-China--XMU-China_2020-GRHPR%E9%94%9A%E5%AE%9A.png" width="40%" style="float:center"> |
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p style="font-size:1rem"> | <p style="font-size:1rem"> | ||
| Line 26: | Line 26: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| − | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/d/d2/T--XMU-China--XMU-China_2020-J23100_B0034_inpnc-grhpr_B0015.png" width=" | + | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/d/d2/T--XMU-China--XMU-China_2020-J23100_B0034_inpnc-grhpr_B0015.png" width="35%" style="float:center"> |
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p style="font-size:1rem"> | <p style="font-size:1rem"> | ||
| Line 42: | Line 42: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| − | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/b/b2/T--XMU-China--07211.png" width=" | + | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/b/b2/T--XMU-China--07211.png" width="90%" style="float:center"> |
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p style="font-size:1rem"> | <p style="font-size:1rem"> | ||
| Line 58: | Line 58: | ||
<html> | <html> | ||
<figure> | <figure> | ||
| − | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/a/a5/T--XMU-China--XMU-China_2020-GRHPR%E9%94%9A%E5%AE%9A%E9%85%B6%E6%B4%BB.png" width=" | + | <img src="https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/a/a5/T--XMU-China--XMU-China_2020-GRHPR%E9%94%9A%E5%AE%9A%E9%85%B6%E6%B4%BB.png" width="40%" style="float:center"> |
<figcaption> | <figcaption> | ||
<p style="font-size:1rem"> | <p style="font-size:1rem"> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:36, 27 October 2020
J23100-RBS-INPNC-GRHPR-terminator
We anchored GRHPR protein onto membranes through INPNC to catalyze the reaction of reducing glyoxalic acid and consuming NADPH. We use K880005 to construct the expression system and anchor GRHPR on the surface of E.coli.
Biology[1]
Ice nucleoprotein is an anchor protein from Pseudomonas syringae. It can anchor its passenger protein to the cell membrane. N and C terminal of Ice nucleoprotein, which is named after INPNC, can also anchor passenger protein fused with it to the cell membrane. GRHPR, a glyoxylate reductase from human liver, can reduce glyoxylic acid when NADPH is used as cofactor. GRHPR is fused at N terminal with INPNC so that GRHPR can be displayed on the surface of E. coli.
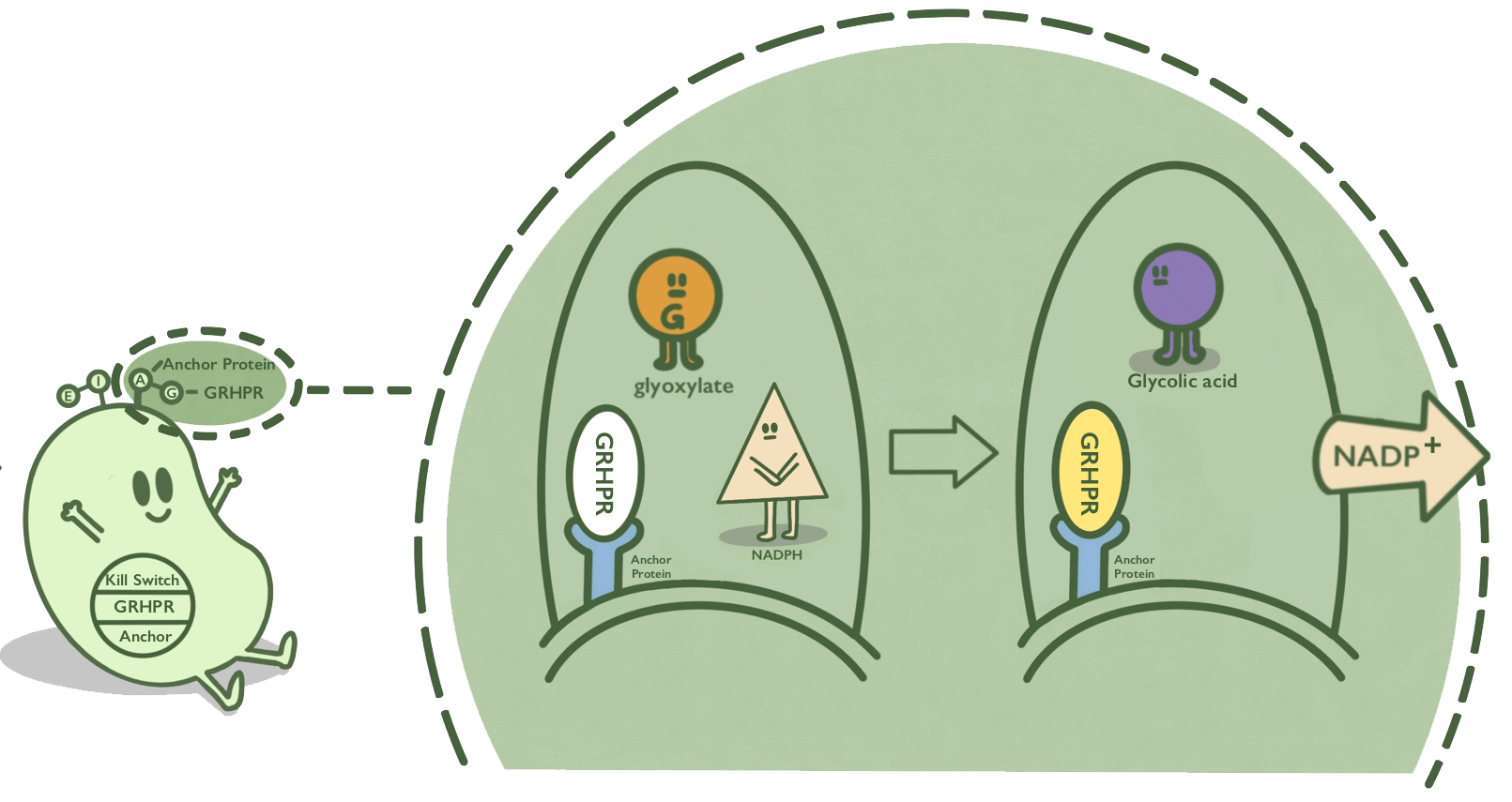
- Fig 1. Mechanism of GRHPR on the surface of E. Coli
Usage[2]
Here, we used BBa_K880005 to construct the expression system and demonstrated the effect of INPNC-GRHPR on the surface of E. coli. We obtained the composite part BBa_K3332057 and transformed the constructed plasmid into E. coli BL21 (DE3) to verify its expression. The positive clones were cultivated.

- Fig 2. Gene circuit of INPNC-GRHPR
Characterization
1. Identification
After receiving the synthesized DNA, PCR was done to certify that the plasmid was correct, and the experimental results were shown in figure 3.

2. Ability of consuming NADPH We mixed glyoxylic acid solution, NADPH solution and bacteria solution carrying INPNC-GRHPR. Then, we immediately measured OD340 changes. TECAN® Infinite M200 Pro was used to detect OD340. And when NADPH is consumed, OD340 declines. We successfully got OD340-Time curves of GRHPR fused with 4 types of anchor protein. When using INPNC-GRHPR, we could see OD340 decreased as the reaction went on. And by using J23100-RBS and GRHPR-Histag as control, we could find that the slopes of experimental and control curves have a significant difference, which means that our fusion protein INPNC-GRHPR is displayed on the surface and works very well. The result is shown in figure 4.

- Fig 4. OD340-Time curves of GRHPR fused with 4 types of anchor protein
References
- ↑ Rumsby G, Cregeen D P. Identification and expression of a cDNA for human hydroxypyruvate/glyoxylate reductase[J]. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Gene Structure and Expression, 1999, 1446(3): 383-388.
- ↑ http://2016.igem.org/Team:TJUSLS_China
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 466
Illegal AgeI site found at 1583 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
