Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3478891"
Cassandrashi (Talk | contribs) |
Cassandrashi (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 5: | Line 5: | ||
. | . | ||
| − | Description | + | <span style="font-size: 130%;font-weight:bold">Description</span> |
| − | P15A is a composite part composed of vector p15A and MVA pathway including coding atoB, HMGS, HMGR, MK, PMK, and PMD, a combination of the composite parts BBa_K3166057 | + | <p>P15A is a composite part composed of vector p15A and MVA pathway including coding atoB, HMGS, HMGR, MK, PMK, and PMD, a combination of the composite parts BBa_K3166057 |
(https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K3166057) and BBa_K3166056 (https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K3166056). | (https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K3166057) and BBa_K3166056 (https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K3166056). | ||
The MVA pathway expressed by this part can produce DMAPP from Acetyl-CoA. DMAPP is a subtract for GPPS, which are important in linalool synthase in our project. | The MVA pathway expressed by this part can produce DMAPP from Acetyl-CoA. DMAPP is a subtract for GPPS, which are important in linalool synthase in our project. | ||
| − | We used PCR to amplify MVA-1 and MVA-2 which is two fragments of p15A-MVA (figure 1 A) and then purified it (figure 1 B). | + | We used PCR to amplify MVA-1 and MVA-2 which is two fragments of p15A-MVA (figure 1 A) and then purified it (figure 1 B). </p> |
| + | |||
https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/7/76/T--KEYSTONE--mva1.png | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/7/76/T--KEYSTONE--mva1.png | ||
https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/d/d8/T--KEYSTONE--mva2.png | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/d/d8/T--KEYSTONE--mva2.png | ||
| − | Figure 1: the gel DNA gel electrophoresis results. (A) amplification result of gene segments of p15A-MVA-ptac-GPPS-bLIS (BLIS-1 (1015 bp), MVA-vector (6372 bp), MVA-GPPS (6970 bp)), pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS (BLIS-2 (1016 bp), pR6K (5958 bp)) , pSB1K3-ptac-GPPS-LIS (BLIS-3 (1016 bp), Lac1-Ptac-GPPS (2371 bp), PSBIC3 (2111 bp)) , p15A-MVA (MVA-1 (5177 bp), MVA-2 (6922 bp)). (B) result of gene segment purification. BLIS-1 (1015 bp), MVA-vector (6372 bp), MVA-GPPS (6970 bp), BLIS-2 (1016 bp), BLIS-3 (1016 bp), Lac1-Ptac-GPPS (2371 bp), (MVA-1 (5177 bp), MVA-2 (6922 bp). | + | <p>Figure 1: the gel DNA gel electrophoresis results. (A) amplification result of gene segments of p15A-MVA-ptac-GPPS-bLIS (BLIS-1 (1015 bp), MVA-vector (6372 bp), MVA-GPPS (6970 bp)), pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS (BLIS-2 (1016 bp), pR6K (5958 bp)) , pSB1K3-ptac-GPPS-LIS (BLIS-3 (1016 bp), Lac1-Ptac-GPPS (2371 bp), PSBIC3 (2111 bp)) , p15A-MVA (MVA-1 (5177 bp), MVA-2 (6922 bp)). (B) result of gene segment purification. BLIS-1 (1015 bp), MVA-vector (6372 bp), MVA-GPPS (6970 bp), BLIS-2 (1016 bp), BLIS-3 (1016 bp), Lac1-Ptac-GPPS (2371 bp), (MVA-1 (5177 bp), MVA-2 (6922 bp). </p> |
| + | |||
| + | <p>we used Gibson assembly to construct the two gene fragments into a plasmid, and then transformed it into E. Coli DH5α. We sent the bacteria to a biotech company which helped us to do gene sequencing. The result of the gene sequencing indicates that we successfully constructed the composite part p15A-MVA. (figure 2) </p> | ||
| − | |||
https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/a/a2/T--KEYSTONE--mva3.png | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/a/a2/T--KEYSTONE--mva3.png | ||
| − | Figure 2: gene sequencing result of p15A-MVA. | + | <p>Figure 2: gene sequencing result of p15A-MVA. </p> |
| − | We cotransformed p15A-MVA and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS to E. Coli DH5α. and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS is a part that produce GPP synthase and linalool synthase that produces linalool. the substrate of GPP synthase is DMPP. Therefore, the MVA pathway regulated by p15A-MVA provides substrates for GPPS, which allows linalool synthesis to occur. We used IPTG to induce bacteria cotransformed to E. Coli DH5α with15A-MVA and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS, and produced linalool. | + | <p>We cotransformed p15A-MVA and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS to E. Coli DH5α. and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS is a part that produce GPP synthase and linalool synthase that produces linalool. the substrate of GPP synthase is DMPP. Therefore, the MVA pathway regulated by p15A-MVA provides substrates for GPPS, which allows linalool synthesis to occur. We used IPTG to induce bacteria cotransformed to E. Coli DH5α with15A-MVA and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS, and produced linalool.</p> |
| − | We can clearly smell the strong fragrance of linalool in those samples, and samples with glucose have a stronger fragrance than samples that are not treated with glucose. This indicates that glucose may promote the synthesis of linalool in E.coli DH5α. We do not need to knock out the gene in E.coli producing stinky smell because the aroma overcomes the smell of E.coli. Therefore, our E.coli won’t affect the local environment and appearance. | + | <p>We can clearly smell the strong fragrance of linalool in those samples, and samples with glucose have a stronger fragrance than samples that are not treated with glucose. This indicates that glucose may promote the synthesis of linalool in E.coli DH5α. We do not need to knock out the gene in E.coli producing stinky smell because the aroma overcomes the smell of E.coli. Therefore, our E.coli won’t affect the local environment and appearance. |
Besides, we also compared the smell of our sample to standard linalool sample, and standard geraniol, which is the product of pR6K-ptac-GPPS-GES (the plasmid before our improvement) Based on our observation the aroma of geraniol contains sweetness; whereas, the aroma of standard linalool sample has a slight peppery smell. The two smells are quite distinguishable. The small of our samples also have a slightly peppery aroma, which is close to the linalool standard sample. Thus, we have successfully produced linalool. | Besides, we also compared the smell of our sample to standard linalool sample, and standard geraniol, which is the product of pR6K-ptac-GPPS-GES (the plasmid before our improvement) Based on our observation the aroma of geraniol contains sweetness; whereas, the aroma of standard linalool sample has a slight peppery smell. The two smells are quite distinguishable. The small of our samples also have a slightly peppery aroma, which is close to the linalool standard sample. Thus, we have successfully produced linalool. | ||
In addition, through visual observation, we also confirmed that glucose can promote the synthesis of linalool in E.coli. The transparent liquids in the test tubes are purified linalool (figure 3). The volume of the liquid in samples treated with glucose is larger than samples that aren’t treated by glucose. Therefore, E.coli treated with glucose may be able to produce more linalool in the same condition thanE.coli that is not. Our next step may be finding the optimal condition for linalool synthesis in E.coli. However, due to the Covid-19 situation, we do not have enough time in the lab, so we can only do those experiments in the future. | In addition, through visual observation, we also confirmed that glucose can promote the synthesis of linalool in E.coli. The transparent liquids in the test tubes are purified linalool (figure 3). The volume of the liquid in samples treated with glucose is larger than samples that aren’t treated by glucose. Therefore, E.coli treated with glucose may be able to produce more linalool in the same condition thanE.coli that is not. Our next step may be finding the optimal condition for linalool synthesis in E.coli. However, due to the Covid-19 situation, we do not have enough time in the lab, so we can only do those experiments in the future. | ||
| + | </p> | ||
https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/3/3a/T--KEYSTONE--mva4.png | https://2020.igem.org/wiki/images/3/3a/T--KEYSTONE--mva4.png | ||
| − | Figure 3: E.coli DH5α with P15A-MVA and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS was propagated in four separated conical flasks. After the bacteria solutions reach the suitable OD (0.6-0.8), we added 2.5 ml glucose to two of the mediums during and added 25mM of IPTG to By adding n-hexane (4.5ml) to the induced bacteria solution, we can extract pure linalool (transparent layer) | + | <p>Figure 3: E.coli DH5α with P15A-MVA and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS was propagated in four separated conical flasks. After the bacteria solutions reach the suitable OD (0.6-0.8), we added 2.5 ml glucose to two of the mediums during and added 25mM of IPTG to By adding n-hexane (4.5ml) to the induced bacteria solution, we can extract pure linalool (transparent layer) </p> |
| − | + | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
Revision as of 13:24, 27 October 2020
p15A-Lac UV5-atoB-HMGS-HMGR-Trc-MK-PMK-PMD-idi
.
Description
P15A is a composite part composed of vector p15A and MVA pathway including coding atoB, HMGS, HMGR, MK, PMK, and PMD, a combination of the composite parts BBa_K3166057 (https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K3166057) and BBa_K3166056 (https://parts.igem.org/wiki/index.php?title=Part:BBa_K3166056). The MVA pathway expressed by this part can produce DMAPP from Acetyl-CoA. DMAPP is a subtract for GPPS, which are important in linalool synthase in our project. We used PCR to amplify MVA-1 and MVA-2 which is two fragments of p15A-MVA (figure 1 A) and then purified it (figure 1 B).
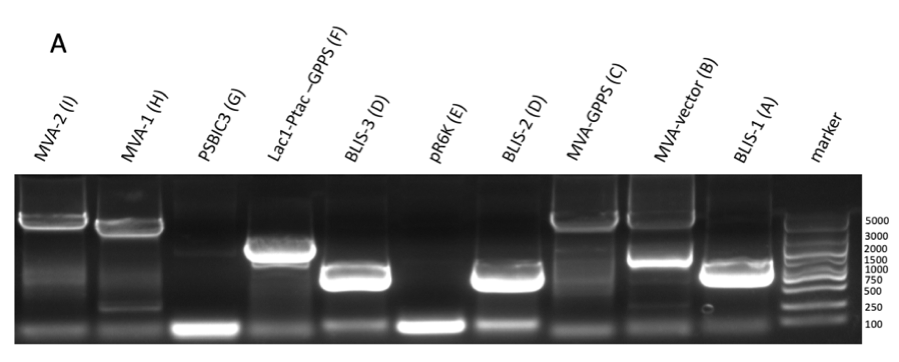
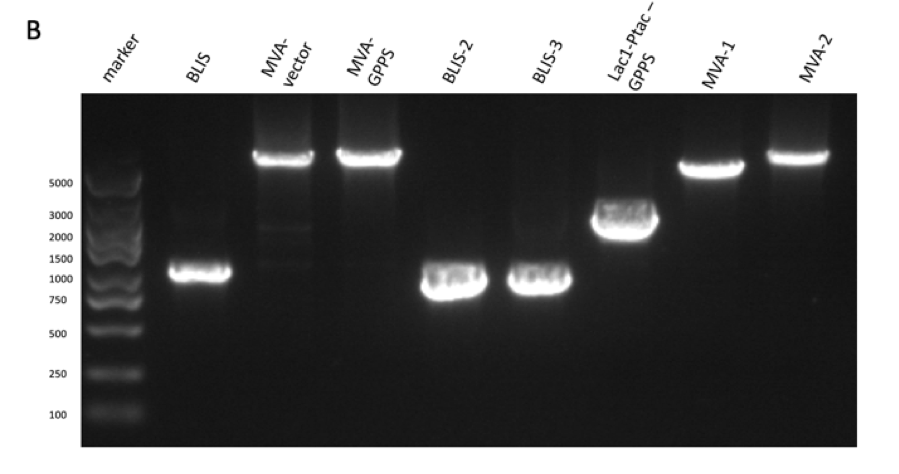
Figure 1: the gel DNA gel electrophoresis results. (A) amplification result of gene segments of p15A-MVA-ptac-GPPS-bLIS (BLIS-1 (1015 bp), MVA-vector (6372 bp), MVA-GPPS (6970 bp)), pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS (BLIS-2 (1016 bp), pR6K (5958 bp)) , pSB1K3-ptac-GPPS-LIS (BLIS-3 (1016 bp), Lac1-Ptac-GPPS (2371 bp), PSBIC3 (2111 bp)) , p15A-MVA (MVA-1 (5177 bp), MVA-2 (6922 bp)). (B) result of gene segment purification. BLIS-1 (1015 bp), MVA-vector (6372 bp), MVA-GPPS (6970 bp), BLIS-2 (1016 bp), BLIS-3 (1016 bp), Lac1-Ptac-GPPS (2371 bp), (MVA-1 (5177 bp), MVA-2 (6922 bp).
we used Gibson assembly to construct the two gene fragments into a plasmid, and then transformed it into E. Coli DH5α. We sent the bacteria to a biotech company which helped us to do gene sequencing. The result of the gene sequencing indicates that we successfully constructed the composite part p15A-MVA. (figure 2)

Figure 2: gene sequencing result of p15A-MVA.
We cotransformed p15A-MVA and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS to E. Coli DH5α. and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS is a part that produce GPP synthase and linalool synthase that produces linalool. the substrate of GPP synthase is DMPP. Therefore, the MVA pathway regulated by p15A-MVA provides substrates for GPPS, which allows linalool synthesis to occur. We used IPTG to induce bacteria cotransformed to E. Coli DH5α with15A-MVA and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS, and produced linalool.
We can clearly smell the strong fragrance of linalool in those samples, and samples with glucose have a stronger fragrance than samples that are not treated with glucose. This indicates that glucose may promote the synthesis of linalool in E.coli DH5α. We do not need to knock out the gene in E.coli producing stinky smell because the aroma overcomes the smell of E.coli. Therefore, our E.coli won’t affect the local environment and appearance. Besides, we also compared the smell of our sample to standard linalool sample, and standard geraniol, which is the product of pR6K-ptac-GPPS-GES (the plasmid before our improvement) Based on our observation the aroma of geraniol contains sweetness; whereas, the aroma of standard linalool sample has a slight peppery smell. The two smells are quite distinguishable. The small of our samples also have a slightly peppery aroma, which is close to the linalool standard sample. Thus, we have successfully produced linalool. In addition, through visual observation, we also confirmed that glucose can promote the synthesis of linalool in E.coli. The transparent liquids in the test tubes are purified linalool (figure 3). The volume of the liquid in samples treated with glucose is larger than samples that aren’t treated by glucose. Therefore, E.coli treated with glucose may be able to produce more linalool in the same condition thanE.coli that is not. Our next step may be finding the optimal condition for linalool synthesis in E.coli. However, due to the Covid-19 situation, we do not have enough time in the lab, so we can only do those experiments in the future.
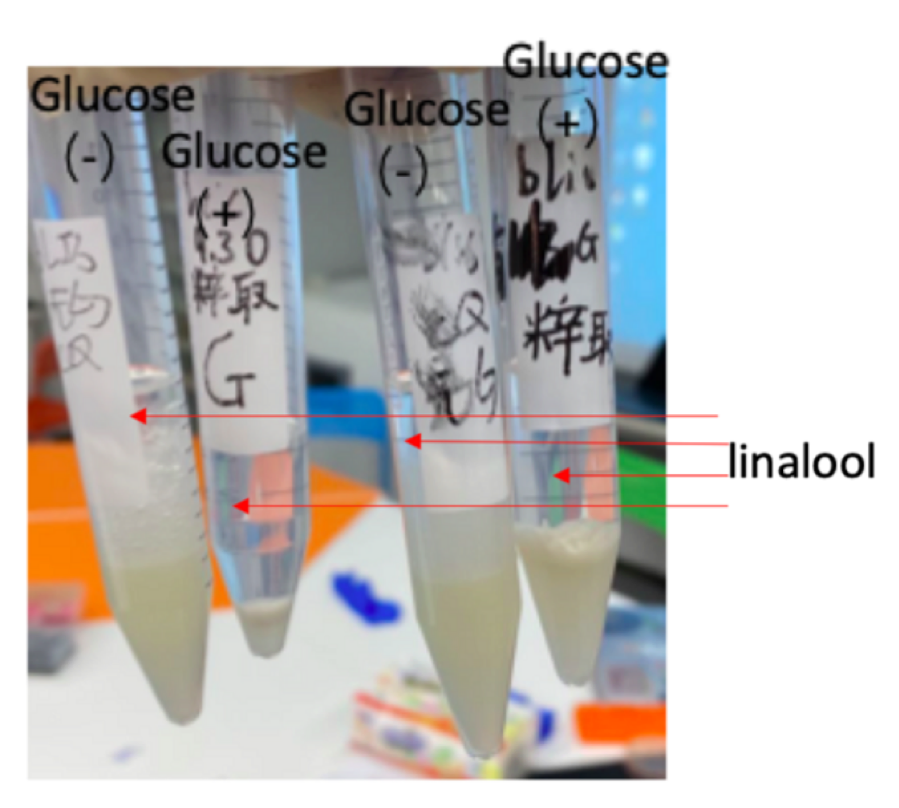
Figure 3: E.coli DH5α with P15A-MVA and pR6K-ptac-GPPS-LIS was propagated in four separated conical flasks. After the bacteria solutions reach the suitable OD (0.6-0.8), we added 2.5 ml glucose to two of the mediums during and added 25mM of IPTG to By adding n-hexane (4.5ml) to the induced bacteria solution, we can extract pure linalool (transparent layer)
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal XbaI site found at 7338
Illegal SpeI site found at 8475
Illegal PstI site found at 2374
Illegal PstI site found at 2602
Illegal PstI site found at 5043
Illegal PstI site found at 5334
Illegal PstI site found at 5679 - 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal SpeI site found at 8475
Illegal PstI site found at 2374
Illegal PstI site found at 2602
Illegal PstI site found at 5043
Illegal PstI site found at 5334
Illegal PstI site found at 5679
Illegal NotI site found at 6171 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal XbaI site found at 7338
Illegal SpeI site found at 8475
Illegal PstI site found at 2374
Illegal PstI site found at 2602
Illegal PstI site found at 5043
Illegal PstI site found at 5334
Illegal PstI site found at 5679 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal XbaI site found at 7338
Illegal SpeI site found at 8475
Illegal PstI site found at 2374
Illegal PstI site found at 2602
Illegal PstI site found at 5043
Illegal PstI site found at 5334
Illegal PstI site found at 5679
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 181
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 3211
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 3403
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 3570
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 4101
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 4277
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 6209
Illegal AgeI site found at 3096
Illegal AgeI site found at 6662 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 5168
Illegal BsaI site found at 7286
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 235
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 5106
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 282
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 3657
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 4610
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 5711
