Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3447001"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K3447001 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K3447001 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | P<sub>C</sub> is a constitutive promoter that expresses the downstream <i>araC</i> gene. P<sub>BAD</sub> promoter is an inducible promoter, P<sub>BAD</sub> contains sequences of P<sub>C</sub>. It was verified by iGEM 2017 Amazonas_Brazil team that the induction effect of arabinose could be realized by using only <i>araC</i> and P<sub>BAD</sub>. | + | P<sub>C</sub> is a constitutive promoter that expresses the downstream <i>araC</i> gene. P<sub>BAD</sub> promoter is an inducible promoter, P<sub>BAD</sub> contains sequences of P<sub>C</sub>. It was verified by iGEM 2017 Amazonas_Brazil team that the induction effect of arabinose could be realized by using only <i>araC</i> and P<sub>BAD</sub>.<br> |
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| − | Arabinose operon is composed of AraC protein, P<sub>BAD</sub> and P<sub>C</sub>. The <i>araC</i> gene translates from the P<sub>C</sub> to the left. | + | Arabinose operon is composed of AraC protein, P<sub>BAD</sub> and P<sub>C</sub>. The <i>araC</i> gene translates from the P<sub>C</sub> to the left. We used the P<sub>C</sub> promoter to express AraC constitutively, and constituted the sensing part of the arabinose sensing system.<br> |
| − | We used the P<sub>C</sub> promoter to express AraC constitutively, and constituted the sensing part of the arabinose sensing system. | + | |
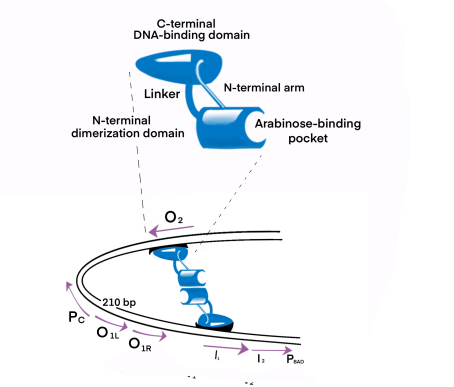
AraC gene expression product belongs to araC protein family, which is a type of two monomers with dimer structure, and each monomer with DNA binding sites of the spiral screw - corner - functional areas. It’s amino terminal determines the inducibility and it’s carboxyl terminal determines the DNA binding ability. Through this helix-rotation-helix structure, araC contacts and binds to four large sulcus regions adjacent to the DNA. <br> | AraC gene expression product belongs to araC protein family, which is a type of two monomers with dimer structure, and each monomer with DNA binding sites of the spiral screw - corner - functional areas. It’s amino terminal determines the inducibility and it’s carboxyl terminal determines the DNA binding ability. Through this helix-rotation-helix structure, araC contacts and binds to four large sulcus regions adjacent to the DNA. <br> | ||
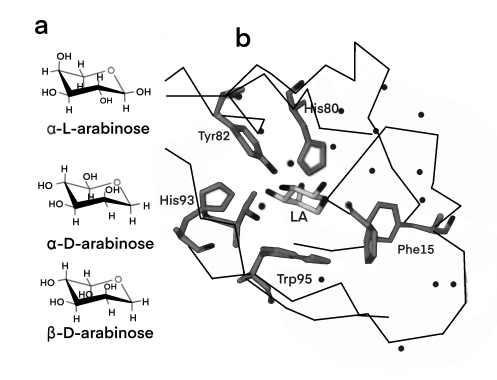
| − | [[Image: Diagram of araC binding with α-L-Arabinose.jpg|center|frame|100px|<b>Figure 1. Diagram of araC binding with α-L-Arabinose. </b> (a)α-L-arabinose, α-D-arabinose and β-D-arabinose structures. (b) A wild-type AraC combined with L-Arabinose (LA) binds to the crystalline structure of the pocket. The amino acids identified here are residues that play an important role in ligand binding.]] | + | [[Image: Diagram of araC binding with α-L-Arabinose.jpg|center|frame|100px|<b>Figure 1. Diagram of araC binding with α-L-Arabinose. </b> (a)α-L-arabinose, α-D-arabinose and β-D-arabinose structures. (b) A wild-type AraC combined with L-Arabinose (LA) binds to the crystalline structure of the pocket. The amino acids identified here are residues that play an important role in ligand binding.]]<br> |
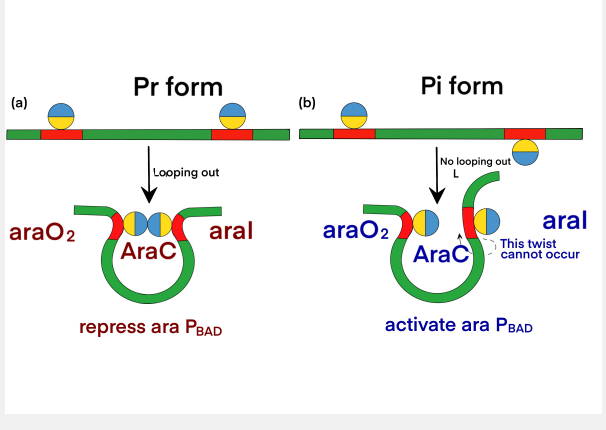
The dimerization domain is formed by folding into a pocket, combining arabinose, and dimerized by an antiparallel coiled coil. AraC stimulates RNA polymerase binding to DNA and the rate of formation of open complexes. The presence or absence of arabinose may alter the DNA contact of the upstream subunit of homodimer AraC, thereby affecting the binding of RNA polymerase. In the absence of L-arabinose, the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of the AraC dimer binds the I<sub>1</sub> and O<sub>2</sub> halves (separated by 210 bases) and inhibits transcription by forming a DNA ring upstream of the dimer. After P<sub>BAD</sub> binds to L-arabinose, the dimer changes the conformation, making DBD bind to the adjacent I<sub>1</sub> and I<sub>2</sub> halves, thus leading to transcriptional activation through interaction with RNA polymerase in P<sub>BAD</sub>. The regulatory characteristics of AraC are due to the sensitive conversion between the two conformation Pr and Pi, and the specific interaction with the inducer.<br> | The dimerization domain is formed by folding into a pocket, combining arabinose, and dimerized by an antiparallel coiled coil. AraC stimulates RNA polymerase binding to DNA and the rate of formation of open complexes. The presence or absence of arabinose may alter the DNA contact of the upstream subunit of homodimer AraC, thereby affecting the binding of RNA polymerase. In the absence of L-arabinose, the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of the AraC dimer binds the I<sub>1</sub> and O<sub>2</sub> halves (separated by 210 bases) and inhibits transcription by forming a DNA ring upstream of the dimer. After P<sub>BAD</sub> binds to L-arabinose, the dimer changes the conformation, making DBD bind to the adjacent I<sub>1</sub> and I<sub>2</sub> halves, thus leading to transcriptional activation through interaction with RNA polymerase in P<sub>BAD</sub>. The regulatory characteristics of AraC are due to the sensitive conversion between the two conformation Pr and Pi, and the specific interaction with the inducer.<br> | ||
| Line 21: | Line 20: | ||
Arabinose induces endotoxin expression: (链接a01+c07)<br> | Arabinose induces endotoxin expression: (链接a01+c07)<br> | ||
| − | Arabinose induces green fluorescent protein expression: (链接a01+c09) | + | Arabinose induces green fluorescent protein expression: (链接a01+c09)<br> |
==<b>Design</b>== | ==<b>Design</b>== | ||
| Line 31: | Line 30: | ||
===Source=== | ===Source=== | ||
| − | We found this sequence data in the previous iGEM teams (Glasgow 2017) and in GenBank. | + | We found this sequence data in the previous iGEM teams (Glasgow 2017) and in GenBank.<br> |
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
Revision as of 18:17, 26 October 2020
Arabinose sensing system
PC is a constitutive promoter that expresses the downstream araC gene. PBAD promoter is an inducible promoter, PBAD contains sequences of PC. It was verified by iGEM 2017 Amazonas_Brazil team that the induction effect of arabinose could be realized by using only araC and PBAD.
Usage and Biology
Arabinose operon is composed of AraC protein, PBAD and PC. The araC gene translates from the PC to the left. We used the PC promoter to express AraC constitutively, and constituted the sensing part of the arabinose sensing system.
AraC gene expression product belongs to araC protein family, which is a type of two monomers with dimer structure, and each monomer with DNA binding sites of the spiral screw - corner - functional areas. It’s amino terminal determines the inducibility and it’s carboxyl terminal determines the DNA binding ability. Through this helix-rotation-helix structure, araC contacts and binds to four large sulcus regions adjacent to the DNA.
The dimerization domain is formed by folding into a pocket, combining arabinose, and dimerized by an antiparallel coiled coil. AraC stimulates RNA polymerase binding to DNA and the rate of formation of open complexes. The presence or absence of arabinose may alter the DNA contact of the upstream subunit of homodimer AraC, thereby affecting the binding of RNA polymerase. In the absence of L-arabinose, the DNA-binding domain (DBD) of the AraC dimer binds the I1 and O2 halves (separated by 210 bases) and inhibits transcription by forming a DNA ring upstream of the dimer. After PBAD binds to L-arabinose, the dimer changes the conformation, making DBD bind to the adjacent I1 and I2 halves, thus leading to transcriptional activation through interaction with RNA polymerase in PBAD. The regulatory characteristics of AraC are due to the sensitive conversion between the two conformation Pr and Pi, and the specific interaction with the inducer.
In our project, we used this part together with PC and PBAD to form the arabinose sensing system, and achieved different functions by linking different target genes downstream of PBAD.
Arabinose induces endotoxin expression: (链接a01+c07)
Arabinose induces green fluorescent protein expression: (链接a01+c09)
Design
Design Notes
We added some synonymous mutations to avoid part rules.
Source
We found this sequence data in the previous iGEM teams (Glasgow 2017) and in GenBank.
References
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 1216
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 1155
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 990
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 1
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 1245
Illegal SapI site found at 972