Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa E0422"
| Line 31: | Line 31: | ||
[[File:T--Tianjin--04221.png|500px|thumb|none|Figure 1. Characterization scheme used by Team Tianjin]] | [[File:T--Tianjin--04221.png|500px|thumb|none|Figure 1. Characterization scheme used by Team Tianjin]] | ||
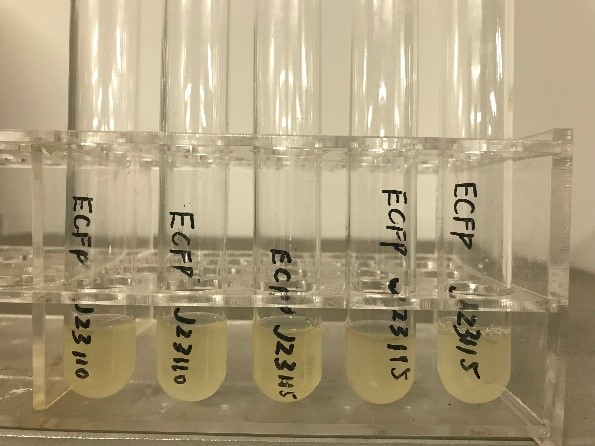
We linked the constructed fragment to the plasmid pRS415 and transformed it into Match 1 strain. Under normal culture conditions (LB+amp solid medium, 37℃), the Match 1 strain was cultured overnight. After about 8 hours, the colony was visible to the naked eye, with no obvious difference in appearance from ordinary e. coli (ECFP was not visible to the naked eye). | We linked the constructed fragment to the plasmid pRS415 and transformed it into Match 1 strain. Under normal culture conditions (LB+amp solid medium, 37℃), the Match 1 strain was cultured overnight. After about 8 hours, the colony was visible to the naked eye, with no obvious difference in appearance from ordinary e. coli (ECFP was not visible to the naked eye). | ||
| − | [[File:T--Tianjin--04222.jpg| | + | [[File:T--Tianjin--04222.jpg|400px|thumb|none|Figure 2. E. coli bacteria with ECFP fluorescent protein]] |
<br> | <br> | ||
The experiment design<br> | The experiment design<br> | ||
1.PCR validation<br> | 1.PCR validation<br> | ||
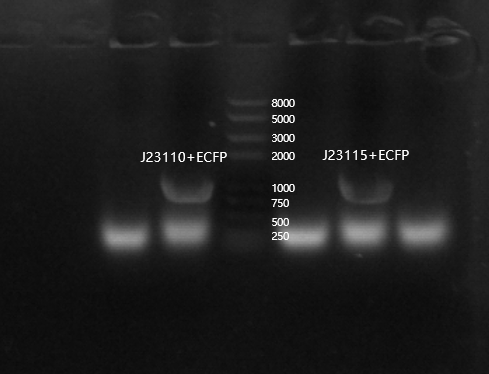
| − | Because ECFP was not visible with the naked eye, we performed colony PCR validation to confirm whether the transformation was successful. | + | Because ECFP was not visible with the naked eye, we performed colony PCR validation to confirm whether the transformation was successful. |
| + | [[File:T--Tianjin--042233.png|500px|thumb|none|Figure 3. Agarose gel electrophoresis analysis]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
2.Determination by fluorescence microplate reader<br> | 2.Determination by fluorescence microplate reader<br> | ||
The bacteria verified in the previous step were cultured separately overnight, then a small number of bacteria were selected and suspended in 200μL ddH2O, and the fluorescence intensity of the same bacteria was measured under emission/excitation of 439/476nm (reference value). | The bacteria verified in the previous step were cultured separately overnight, then a small number of bacteria were selected and suspended in 200μL ddH2O, and the fluorescence intensity of the same bacteria was measured under emission/excitation of 439/476nm (reference value). | ||
| − | [[File:T--Tianjin--04223.png|500px|thumb|none|Figure | + | [[File:T--Tianjin--04223.png|500px|thumb|none|Figure 4. The fluorescence intensity of ECFP compared with the blank control]] |
We did not detect the fluorescence excitation corresponding to this part, which may be due to incorrect culture conditions or some problems of this part itself. We have sent this part to be sequenced for analysis, but until the final freezing, we haven't got the relevant results yet. | We did not detect the fluorescence excitation corresponding to this part, which may be due to incorrect culture conditions or some problems of this part itself. We have sent this part to be sequenced for analysis, but until the final freezing, we haven't got the relevant results yet. | ||
Revision as of 01:35, 22 October 2019
ECFP (RBS+ LVA+ TERM) (B0034.E0022.B0015)
Cyan fluorescent protein with ribosome binding site and terminator
Usage and Biology
This part can be used to test promoter strength or the proper functioning of a regulator device. The LVA tail is particularly useful when testing a regulatory device, for example to assess the efficiency of repressor.
In this experiment, the E0422 part was associated with a cI regulated promoter (part R0051), resulting in K1707028.
Figure 1: Fluorescence microscopy of E. coli DH5alpha bearing K170728
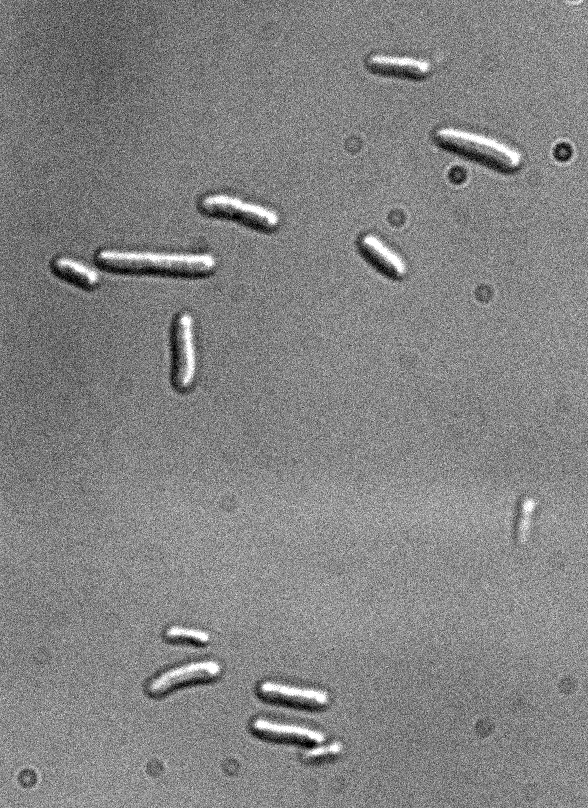 Differential interference contrast
Differential interference contrast
 Excitation with led 437 nm/17nm (CFP), 100 ms of exposure
Sequence and Features
Excitation with led 437 nm/17nm (CFP), 100 ms of exposure
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Team: Tianjin 2019 characterization
2019 Team:Tianjin have tested the fluorescence intensity and detailed fluorescence excitation curve by connecting it to the combined promoters J23110 and J23115. However, our final results are not optimistic. Most of the samples we tested have very low fluorescence excitation intensity.
We linked the constructed fragment to the plasmid pRS415 and transformed it into Match 1 strain. Under normal culture conditions (LB+amp solid medium, 37℃), the Match 1 strain was cultured overnight. After about 8 hours, the colony was visible to the naked eye, with no obvious difference in appearance from ordinary e. coli (ECFP was not visible to the naked eye).
The experiment design
1.PCR validation
Because ECFP was not visible with the naked eye, we performed colony PCR validation to confirm whether the transformation was successful.
2.Determination by fluorescence microplate reader
The bacteria verified in the previous step were cultured separately overnight, then a small number of bacteria were selected and suspended in 200μL ddH2O, and the fluorescence intensity of the same bacteria was measured under emission/excitation of 439/476nm (reference value).
We did not detect the fluorescence excitation corresponding to this part, which may be due to incorrect culture conditions or some problems of this part itself. We have sent this part to be sequenced for analysis, but until the final freezing, we haven't got the relevant results yet.