Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K823038"
(→b) Purification of HRP-Strep (BBa_K3037009)) |
|||
| Line 91: | Line 91: | ||
===== b) Purification of HRP-Strep ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3037009 BBa_K3037009)] ===== | ===== b) Purification of HRP-Strep ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K3037009 BBa_K3037009)] ===== | ||
| − | The protocol used was “Expression and purification of proteins using Strep-Tactin” of IBA Lifescience [1] preparing the same buffers described in this protocols without EDTA to not harm the activity of HRP. From the results of the purifications we concluded that the Strep-tag is not working properly for column purification and should therefore only be used for Western Blots | + | The protocol used was “Expression and purification of proteins using Strep-Tactin” of IBA Lifescience [1] preparing the same buffers described in this protocols without EDTA to not harm the activity of HRP. From the results of the purifications we concluded that the Strep-tag is not working properly for column purification and should therefore only be used for Western Blots. |
Revision as of 00:27, 22 October 2019
Strep-tag (Freiburg standard+RBS)
Streptavidin - tag with RBS in Freiburg standard.
Find out more about the design of our prefix with ribosome binding site.
prefix:GAATTCCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGATAAGGAGGAACTACTATGGCCGGC
suffix:ACCGGTTAATACTAGTAGCGGCCGCTGCAGT
The Strep-tag is a mimicry peptide of biotin which binds to Streptavidin ([http://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1050386299000339 Skerra, A. and Schmidt, T.G.M. (1999)]). Its sequence is WSHPQFEK. It can be used for protein purification, immobilisation with Streptavidin or Strep-tactin ([http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/9415448 Voss, S. and Skerra, A. (1997)]) or detection with Strep-tactin or antibodies.
This is a part created by the LMU-Munich 2012 team. We added five tags to the registry, all in the Freiburg standard for N-and C-terminal fusions:
- Strep - tag
Visit our project page for more usefull parts of our [http://2012.igem.org/Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus_BioBricks BacillusBioBrickBox]. This part was also evaluated in the publication [http://www.jbioleng.org/content/7/1/29 The Bacillus BioBrick Box: generation and evaluation of essential genetic building blocks for standardized work with Bacillus subtilis] by Radeck et al..
Evaluation
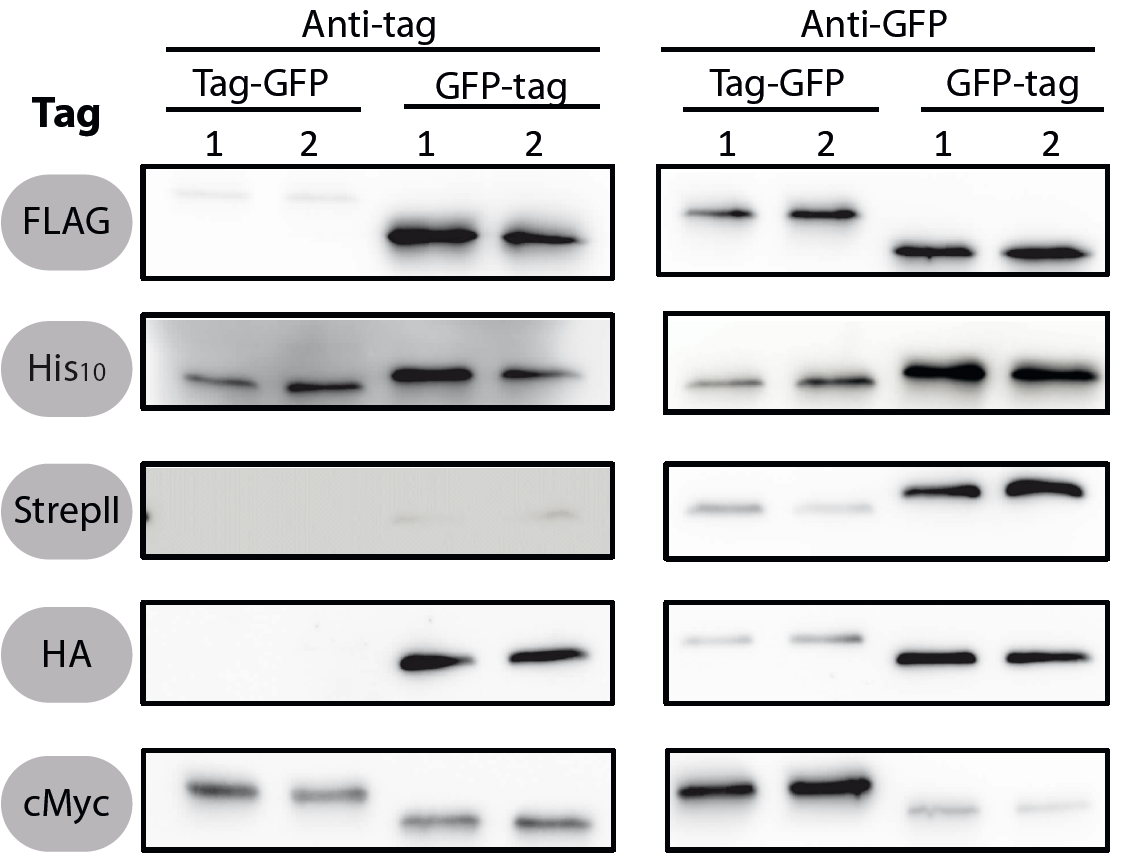
All 5 epitope tags were fused C- and N-terminally to GFP using the NgoMIV and AgeI restriction sites. These constructs were expressed in Bacillus subtils using pSBBs0K-Pspac. This vector did not need to be induced by IPTG due to a premature stop codon in the lacI gene.
|
Methods
To verify the functionality of the epitope tags, Western blot analyses of the strains TMB1920-TMB1929 were performed. LB medium (15 ml) was inoculated 1:100 from overnight culture and grown at 37°C and 200 rpm to OD600 ~ 0.5. Of this, 10 ml were harvested by centrifugation (8000 × g, 5 min) and the pellets stored at -20°C. Pellets were resuspended in 1 ml disruption buffer (50 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.5, 100 mM NaCl) and lysed by sonication. Samples (12 μl of lysate) were loaded per lane on two 12.5% SDS-polyacrylamide gels and SDS-PAGE was performed according standard procedure [60]. One gel was stained with colloidal coomassie, the other one was used for protein transfer to a PVDF membrane (Merck Millipore, Billerica, MA, USA) by submerged blotting procedure (Mini Trans-Blot Electrophoretic Transfer Cell (Bio-Rad, Hercules, CA, USA)). After protein transfer, the membranes were treated with the following antibodies and conditions. Detailed protocols can be found [http://www.jbioleng.org/content/7/1/29/suppl/S3 here].
GFP
Probing with primary antibodies takes place with rabbit anti-GFP antibodies (1:3000, Epitomics, No. 1533). Horseradish-peroxidase (HRP)-conjugated anti-rabbit antibodies (1:2000, Promega, W401B) were used as secondary antibody. Hybridization of both antibodies was carried out in Blotto-buffer (2.5% (w/v) skim milk powder, 1 × TBS (50 mM Tris–HCl pH 7.6, 0.15 M NaCl)).
StrepII
Strep-Tactin-HRP conjugate (IBA, Strep-Tactin-HRP conjugate, No. 2-1502-001) 1:100 in 1 × PBS (4 mM KH2PO4; 16 mM Na2HPO4; 115 mM NaCl) with 0.1% (w/v) Tween20 was used.
Chemiluminescence signals were detected after addition of the HRP-substrate Ace Glow (Peqlab, Erlangen, Germany) using a FusionTM imaging system (Peqlab).
Characterization: TU_Dresden 2019
Strep-tag column purification
The Team TU Dresden 2019 used this Biobrick for purification purposes using the “Expression and purification of proteins using Strep-Tactin” protocol of IBA Lifescience [1]. We tried to purify many of our different BioBricks via this method, in order to characterize the proper function of the Strep-tag for purification purposes. However, we were not able to obtain purified constructs, meaning that this Strep-tag should rather be used for Western Blotting instead of for purification. Nevertheless, the different BioBricks that we tried to purify with this Strep-tag have shown to be working properly (see their Registries: BBa_K3037003, BBa_K3037009)
The results of the different purification tests are shown in the following gels:
a) Purification of our Full Construct (BBa_K3037003)
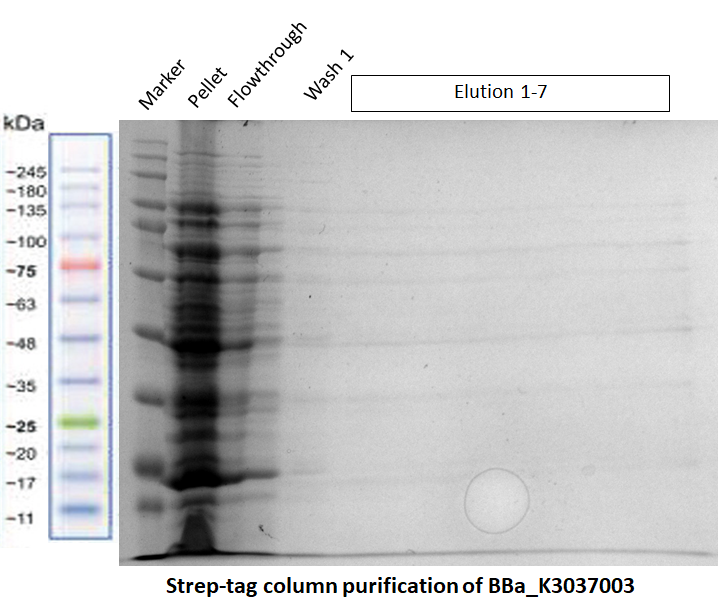
The purification of this construct in Fig. 2 was repeated again by using the same protocol, but this time a successful MBP-tag purification was performed first (see the registry page of our Full Construct for more details BBa_K3037003). As shown in the gel of Fig. 3, the Strep-tag column purification did not work.
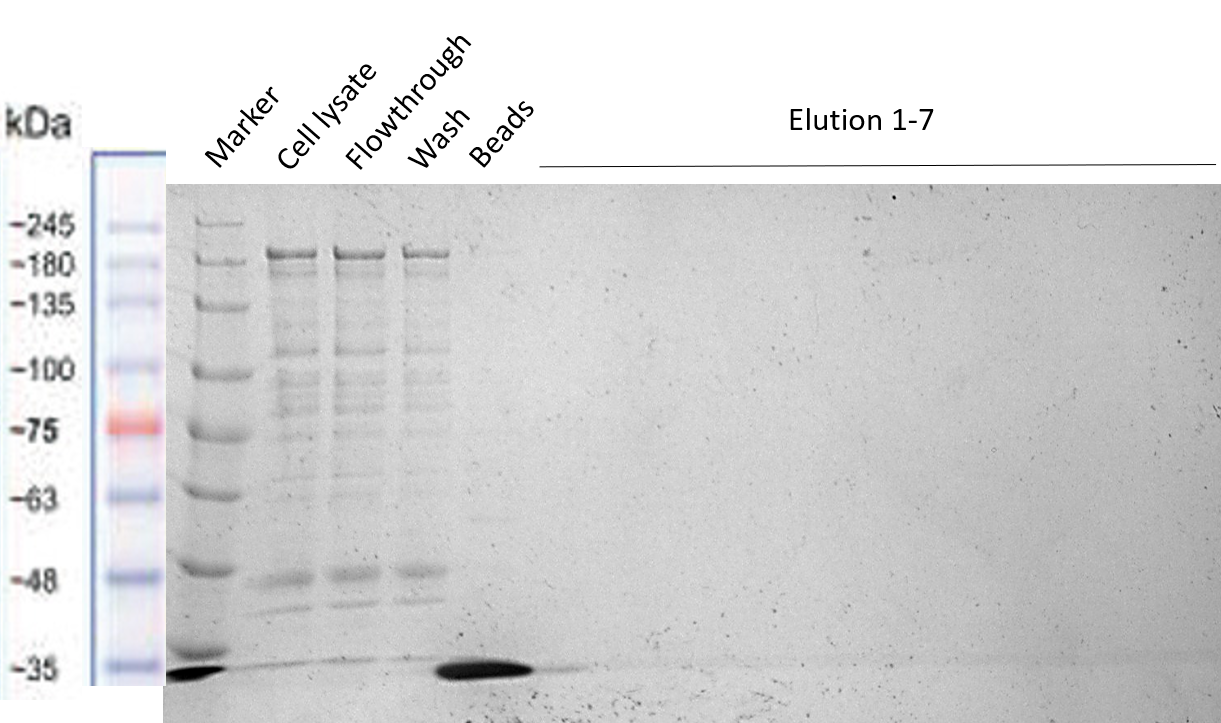
b) Purification of HRP-Strep (BBa_K3037009)
The protocol used was “Expression and purification of proteins using Strep-Tactin” of IBA Lifescience [1] preparing the same buffers described in this protocols without EDTA to not harm the activity of HRP. From the results of the purifications we concluded that the Strep-tag is not working properly for column purification and should therefore only be used for Western Blots.
Conclusions
From the results of these purifications in Fig. 2 to 4, we can conclude that the Strep-tag does not properly work for column purification and should rather be used for Western Blotting.
References
[1] https://www.iba-lifesciences.com/isotope/2/2-3206-100-Manual-Twin--Strep-tag.pdf
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]