Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3078102"
| Line 3: | Line 3: | ||
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | Complete 4-HPA sensing system from E. coli W, including 4-HpaA and HpaX. This system will sense 4-HPA sensitivity and initiate PBC downstream gene expression when 4-HPA is present. | + | Complete 4-HPA sensing system from <i>E. coli W</i>, including 4-HpaA and HpaX. This system will sense 4-HPA sensitivity and initiate PBC downstream gene expression when 4-HPA is present. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
| Line 10: | Line 10: | ||
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | This part is capable of sensing 4-HPA, a molecule secreted by C. albicans specifically, which gives the engineered bacteria the ability to sense the presence of C. albicans with great specificity. It consists of a transporter (HpaX), a transcription factor (HpaA) and an inducible promoter. After imported inside by HpaX, 4-HPA can bind to HpaA, forming a complex which can activate | + | This part is capable of sensing 4-HPA, a molecule secreted by C. albicans specifically, which gives the engineered bacteria the ability to sense the presence of C. albicans with great specificity. It consists of a transporter (HpaX), a transcription factor (HpaA) and an inducible promoter. After imported inside by HpaX, 4-HPA can bind to HpaA, forming a complex which can activate P<sub>BC</sub> promoter and start the expression of downstream genes. |
</p> | </p> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| Line 46: | Line 46: | ||
<h5> | <h5> | ||
<P style="text-indent:2em;"> | <P style="text-indent:2em;"> | ||
| − | To detect the expression of pVE-HpaX-HpaA-sfGFP in E. coli, the constructions were transformed into E. coli BL21(DE3). When the | + | To detect the expression of pVE-HpaX-HpaA-sfGFP in <i>E. coli</i>, the constructions were transformed into <i>E. coli</i> BL21(DE3). When the OD<sub>600</sub> of the culture reached 0.3, 4-HPA of gradient was added. However, according to our results, compared with the group without 4-HPA, the experimental group with high concentration of 4-HPA did not show significant fluorescence. |
</p> | </p> | ||
</h5> | </h5> | ||
[[File:Bcam3.png|600px|center|Bcam3]] | [[File:Bcam3.png|600px|center|Bcam3]] | ||
<center style="text-align:left;"> | <center style="text-align:left;"> | ||
| − | Figure 3. Fluorescence intensity of sfGFP under different concentration of 4-HPA. The emission intensity at 528 nm were measured at the excitation wavelength of 485 nm. Then measure | + | Figure 3. Fluorescence intensity of sfGFP under different concentration of 4-HPA. The emission intensity at 528 nm were measured at the excitation wavelength of 485 nm. Then measure OD<sub>600</sub>. After that, measure these values at the 18th hour. |
</center> | </center> | ||
Latest revision as of 23:43, 21 October 2019
Complete 4-HPA sensing system.
Complete 4-HPA sensing system from E. coli W, including 4-HpaA and HpaX. This system will sense 4-HPA sensitivity and initiate PBC downstream gene expression when 4-HPA is present.
1. Usage and Biology
This part is capable of sensing 4-HPA, a molecule secreted by C. albicans specifically, which gives the engineered bacteria the ability to sense the presence of C. albicans with great specificity. It consists of a transporter (HpaX), a transcription factor (HpaA) and an inducible promoter. After imported inside by HpaX, 4-HPA can bind to HpaA, forming a complex which can activate PBC promoter and start the expression of downstream genes.
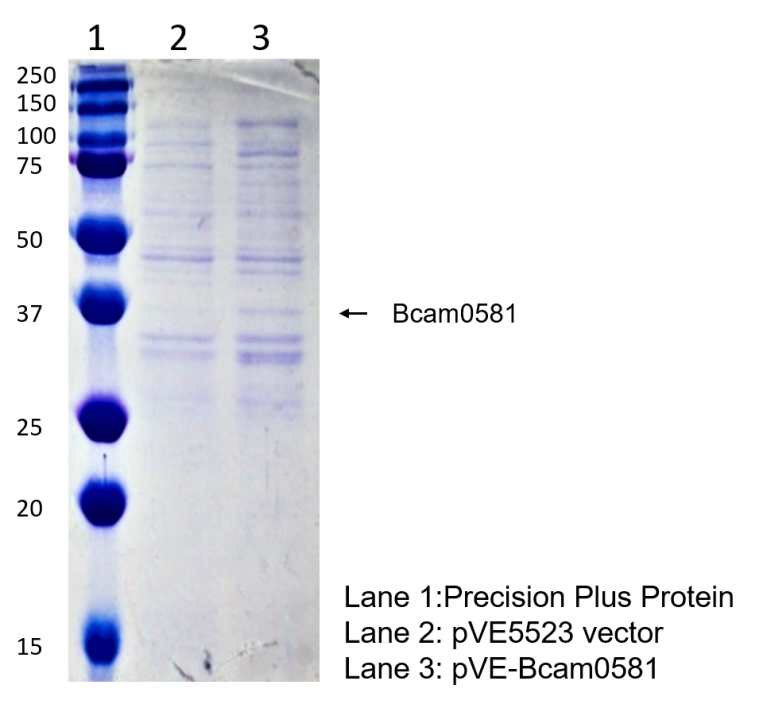
We characterised Bcam0581 by inserting it into pVE vector.
2. Characterization
2.1 Validation of HpaX-HpaA-sfGFP construction
To verify the construction of pVE-HpaX-HpaA-sfGFP which we generated, the digestion by AgeI or XmaI was performed by a standard protocol followed by electrophoresis (Figure 1).
Figure 1. Digestion and electrophoresis of pVE-HpaX-HpaA-sfGFP. pVE-HpaX-HpaA-sfGFP can be digested into 1446 bp band and 900 bp band by AgeI and XmaI respectively. And it was verified by AgeI electrophoresis, showing that our construction was success.
2.2 Validation of pVE-HpaX-GFP construction
To verify the construction of pVE-HpaX-sfGFP which we generated, the digestion by AgeI or XmaI was performed by a standard protocol followed by electrophoresis (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Digestion and electrophoresis of pVE-HpaX-sfGFP. pVE-HpaX-sfGFP can be digested into 1446 bp and 11369 bp band by AgeI and XmaI respectively. And it was verified by AgeI electrophoresis, showing that our construction was success.
2.3 Expression of pVE-HpaX-HpaA-sfGFP
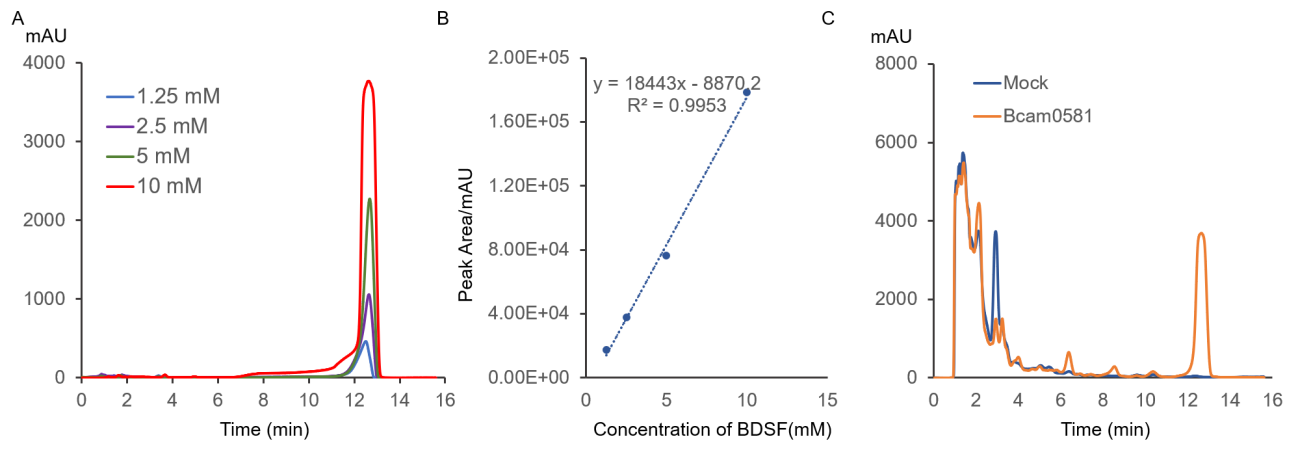
To detect the expression of pVE-HpaX-HpaA-sfGFP in E. coli, the constructions were transformed into E. coli BL21(DE3). When the OD600 of the culture reached 0.3, 4-HPA of gradient was added. However, according to our results, compared with the group without 4-HPA, the experimental group with high concentration of 4-HPA did not show significant fluorescence.
Figure 3. Fluorescence intensity of sfGFP under different concentration of 4-HPA. The emission intensity at 528 nm were measured at the excitation wavelength of 485 nm. Then measure OD600. After that, measure these values at the 18th hour.
3. Conclusion
We observed fluorescence intensity. Unfortunately, the result was less than satisfactory. But the construct and identification of it has been proved by reference, which had manifested this part could sense the C. albicans in engineered bacteria.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 996
Illegal BglII site found at 1462
Illegal BglII site found at 1891
Illegal BamHI site found at 2392
Illegal XhoI site found at 3150 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 614
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]