Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3113009"
Theresakeil (Talk | contribs) |
Theresakeil (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<h2>Characterization</h2> | <h2>Characterization</h2> | ||
| + | <h3>Secretion efficiency</h3> | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html> | ||
| + | <figure class="figure"> | ||
| + | <img src="https://2019.igem.org/wiki/images/e/ec/T--Munich--Secretionefficiency_2.png" width="75%" class="figure-img img-fluid rounded" alt=""> | ||
| + | <figcaption style="font-size: 80%"> | ||
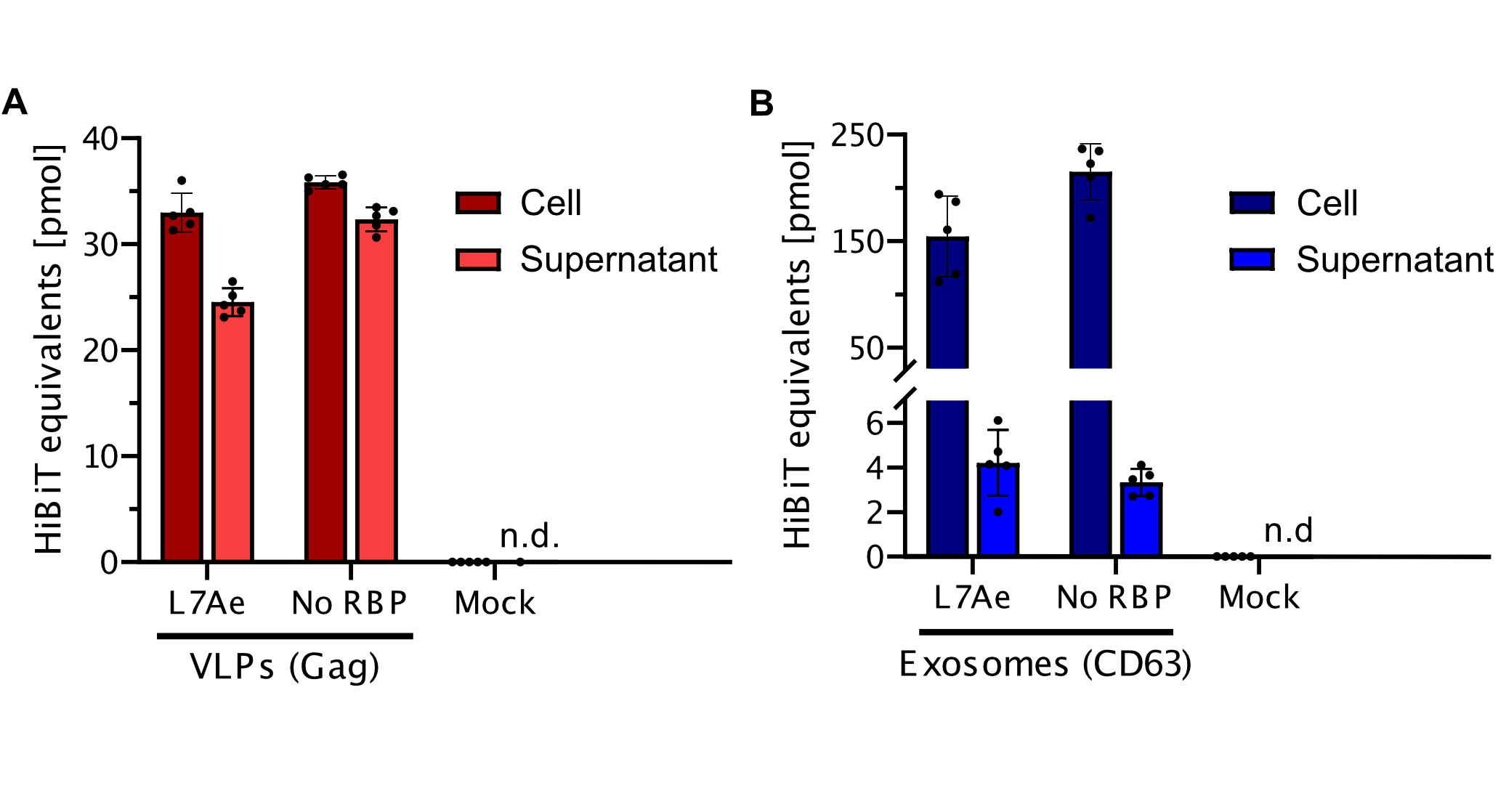
| + | <b>Figure 1: Virus-like particle (VLP) display higher secretion efficiency in comparison to exosomes.</b> The HiBiT signal was determined from cells as well as the corresponding supernatant including the vesicles. The experiment was executed with n = 5. To demonstrate specific HiBiT assay for engineered VLPs and Exosomes a negative control containing iRFP (Mock). A) Cells were transfected with plasmids carrying the VLP (Gag) and RNA binding protein (L7Ae) or negative control (No RNA binding protein, RBP) displayed a high secretion efficiency of vesicles. B) Cells were transfected with plasmids carrying the engineered exosomes (CD63) and RNA binding protein (L7Ae) or negative control (No RNA binding protein, RBP) displayed low secretion efficiency. | ||
| + | </figcaption> | ||
| + | </figure> | ||
| + | </html> | ||
Revision as of 22:55, 21 October 2019
L7Ae
L7Ae is a 50S ribosomal protein found in Archea. It is a multifunctional RNA-binding protein that recognizes the K-turn motif in ribosomal RNA, the RNA component of RNase P, box H/ACA, box C/D, box C'/D' sRNAs. This RNA-binding protein can be used as an adapter for RNA binding in the extracellular vesicles.
Usage
The informational readout of ALiVE is RNA. To load a specific RNA into the vesicles we fused it to RNA-motifs which are bound specifically by RNA binding proteins. Two combinations of binding protein and motif were tested. One was the archaeal RNA binding protein L7Ae which binds to the k-turns in the box C/D snoRNP.
Biology
The archaeal L7Ae and eukaryotic 15.5kD protein homologs are members of the L7Ae/15.5kD protein family that characteristically recognize K-turn motifs found in both archaeal and eukaryotic RNAs. In Archaea, the L7Ae protein uniquely binds the K-loop motif found in box C/D.[1] The k-turn is a ubiquitous structural motif in RNA forming a very tight kink in the axis of helical RNA that plays an important role in many aspects of RNA function. L7Ae is a member of a superfamily of proteins that bind k-turns in RNA, stabilizing the tightly kinked conformation. They are extremely widespread and are important in the assembly of RNA–protein complexes central to translation, splicing and site-specific RNA modification. [2]
Characterization
Secretion efficiency
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
References
- ↑ Gagnon, Keith T et al. “Signature amino acids enable the archaeal L7Ae box C/D RNP core protein to recognize and bind the K-loop RNA motif.” RNA (New York, N.Y.) vol. 16,1 (2010): 79-90. doi:10.1261/rna.1692310
- ↑ Lilley, D. M. J. (2019). "The L7Ae proteins mediate a widespread and highly functional protein–RNA interaction." The Biochemist 41(2): 40-44.
