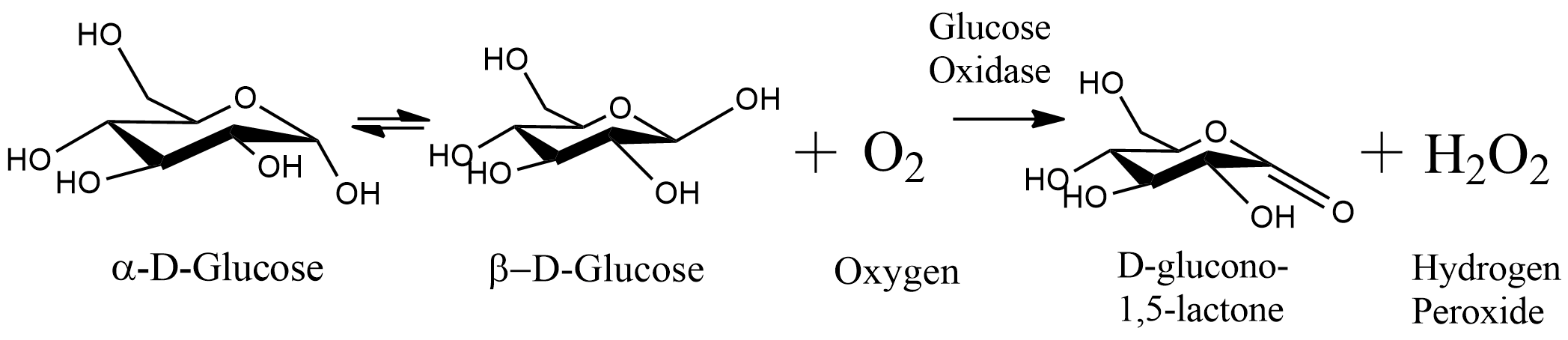Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2934000"
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K2934000 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K2934000 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
| + | ===Glucose Oxidase assay=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Glucose Oxidase (GOx) catalyzes the oxidation of glucose to D-gluconic-lactone and hydrogen peroxide. Therefore, a precise method to determine the amount of hydrogen peroxide found in the solution could indicate the activity of the glucose oxidase. In this experiment, we used the assistance of another commercial enzyme- horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS). Using hydrogen peroxide, the HRP catalyzes the oxidation of reduced ABTS, which is colorless, to oxidized ABTS, which is turquoise. While using excess ABTS and HRP, the absorbance of 416 nm light could indicate to us the amount of hydrogen peroxide created by the glucose oxidase, and therefore - the glucose oxidase activity. | ||
| + | |||
| + | To verify that the absorbance-activity relation remains linear under the experiment's conditions, we performed the experiment using commercial GOx with increasing activity, measured the 416 nm light absorbance and plotted a graph to demonstrate that relation. Fortunately, we have proved the absorbance-activity relation linearity under the experiment's conditions (Figure 2). | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:T--Technion-Israel--GOxCalibration.jpeg|500px|thumb|center|figure 2: Calibration curve for glucose oxidase activity – change in absorbance at 416 nm in different activity values]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | After the cloning process had been completed, we performed the activity test on both the supernatant and the lysate of genetically engineered bacteria as well as WT bacteria as control. The first colony tested contained a gene for glucose oxidase and the AmyE signal peptide. The absorbance detected in the recombinant Bacteria was significantly higher, in both supernatant and lysate (Figure 3). The evaluated activity of glucose oxidase is 0.46U/ml in the bacterial supernatant and 0.45U/ml in the lysate solution. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:T--Technion-Israel--amyE-GOx-activity.jpeg|500px|thumb|center|figure 3: The activity of glucose oxidase and AmyE in different samples, indicated by the absorbance at 416 nm.]] | ||
Revision as of 07:01, 21 October 2019
Glucose Oxidase-Histag A. niger optimized for B. subtilis
Glucose Oxidase gene is coding for the Glucose Oxidase (GOx) enzyme, which catalyzes the oxidation of glucose to D-glucono-lacton and release of hydrogen peroxide. The sequence includes histag (6xHis), connected with seven amino acids linker protein at the N terminal of the protein. The enzyme origin is from A. niger and is optimized for B. subtilis.
Usage and Biology
Glucose oxidase (GOx) catalyzes the oxidation of glucose to using molecular oxygen to create hydrogen peroxide and D-glucono lactone. GOx requires the cofactor flavin adenine dinucleotide (FAD) that acts as an electron acceptor in a redox reaction. It is reduced to FADH2, then it is oxidized by molecular oxygen, which is then reduced to hydrogen peroxide [1].
References
[1] Frederick KR, Tung J, Richard S. Emerick F, Chamberlain SH, Vasavada A, Steven R, Chakraborty S, Schopter LM, Schopter LM, Massey V. 1990. Glucose Oxidase from Aspergillus niger. J Biol Chem 265:3793–3802.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 30
Illegal BsaI site found at 361
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 307
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 1132
Glucose Oxidase assay
Glucose Oxidase (GOx) catalyzes the oxidation of glucose to D-gluconic-lactone and hydrogen peroxide. Therefore, a precise method to determine the amount of hydrogen peroxide found in the solution could indicate the activity of the glucose oxidase. In this experiment, we used the assistance of another commercial enzyme- horseradish peroxidase (HRP) and 2,2'-azino-bis(3-ethylbenzothiazoline-6-sulphonic acid) (ABTS). Using hydrogen peroxide, the HRP catalyzes the oxidation of reduced ABTS, which is colorless, to oxidized ABTS, which is turquoise. While using excess ABTS and HRP, the absorbance of 416 nm light could indicate to us the amount of hydrogen peroxide created by the glucose oxidase, and therefore - the glucose oxidase activity.
To verify that the absorbance-activity relation remains linear under the experiment's conditions, we performed the experiment using commercial GOx with increasing activity, measured the 416 nm light absorbance and plotted a graph to demonstrate that relation. Fortunately, we have proved the absorbance-activity relation linearity under the experiment's conditions (Figure 2).
After the cloning process had been completed, we performed the activity test on both the supernatant and the lysate of genetically engineered bacteria as well as WT bacteria as control. The first colony tested contained a gene for glucose oxidase and the AmyE signal peptide. The absorbance detected in the recombinant Bacteria was significantly higher, in both supernatant and lysate (Figure 3). The evaluated activity of glucose oxidase is 0.46U/ml in the bacterial supernatant and 0.45U/ml in the lysate solution.