Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2752003"
Wangyannan (Talk | contribs) (→Characterization) |
Wangyannan (Talk | contribs) |
||
| Line 24: | Line 24: | ||
Part3 is a BL21 strain containing the part3 plasmid. | Part3 is a BL21 strain containing the part3 plasmid. | ||
Part2 is a BL21 strain containing the part2 plasmid. | Part2 is a BL21 strain containing the part2 plasmid. | ||
| − | Part3-with uric acid is a BL21 strain containing part3 plasmid cultured with a uric acid (The final concentration of uric acid was adjusted to 4×10-4M.) | + | Part3-with uric acid is a BL21 strain containing part3 plasmid cultured with a uric acid (The final concentration of uric acid was adjusted to 4×10-4M.) |
| + | <p style="margin-top:24em;">=result=</p> | ||
=result= | =result= | ||
Revision as of 03:50, 21 October 2019
HucR
Binding to hucO in the absence of uric acid prevents transcription. In the case of uric acid, it binds to uric acid and does not prevent transcription.
Sequence and Features
Characterization
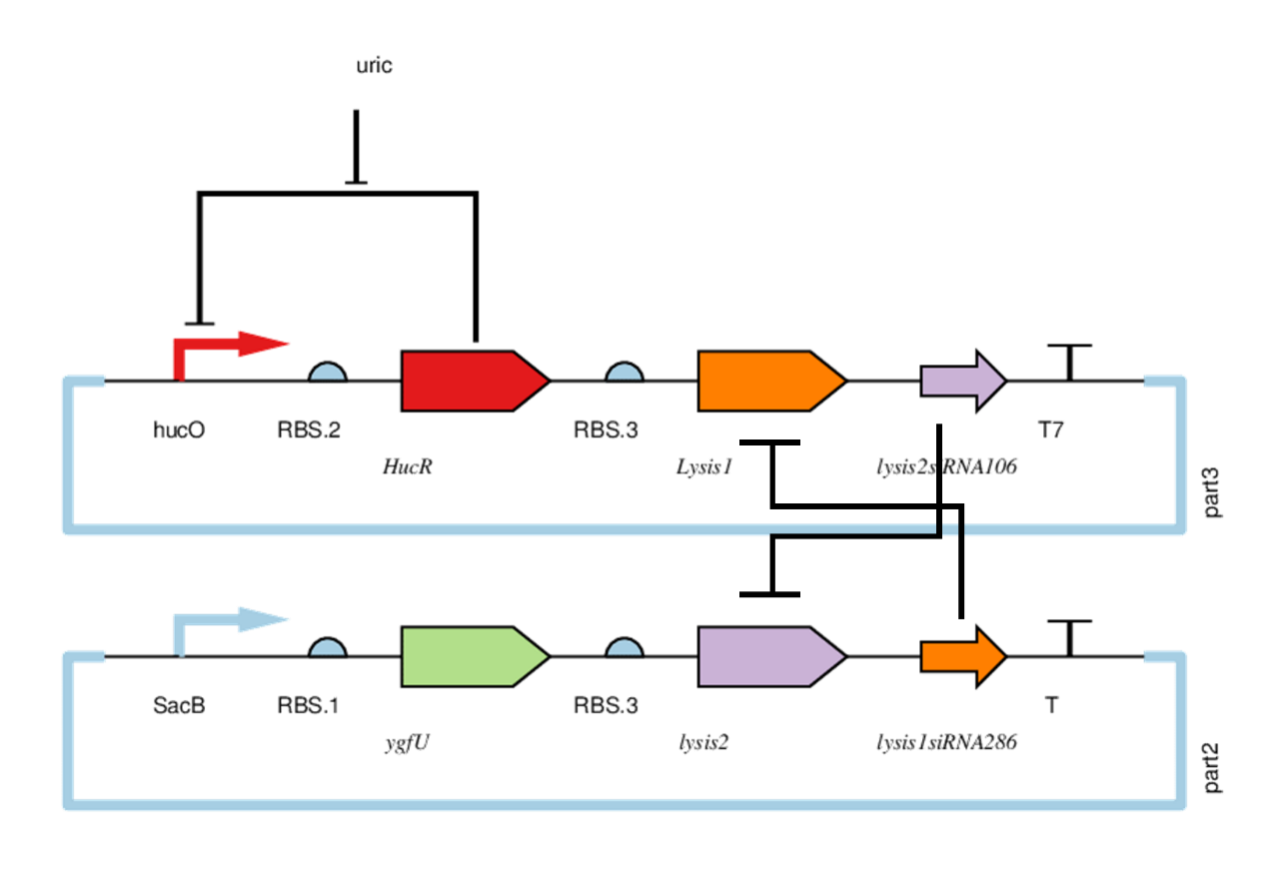
HucO is regulated by HucR. When uric acid is abscent, HucR can bind to hucO making downstream gene silencing. Lysis1 and Lysis2 are lyases. Lysis1siRNA286 can inhibit Lysis1, and Lysis2siRNA106 can inhibit Lysis2. When both plasmids are simultaneously expressed, the lyases are inhibited. But if any plasmid is lost or HucR combined hucO,part3 will not be expressed. And the bacterium is cleaved by the Lysis2 . A series of things happens when bacteria are excreted: First, the concentration of uric acid get lower. Second, the hucO of part3 is suppressed by HucR and cannot work. Next, Lysis2 siRNA106 cannot inhibit Lysis2. Finally, the bacteria are cleaved by Lysis2. To test the lethal ability of part2 and part3, and the regulation of uric acid on part3 we did four sets of experiments.
[[File:Figure 16-colony result.png|400px|thumb|Figure 2. Colony number regulation experiment result。Blank is a plasmid-free BL21 strain.
Part3 is a BL21 strain containing the part3 plasmid.
Part2 is a BL21 strain containing the part2 plasmid.
Part3-with uric acid is a BL21 strain containing part3 plasmid cultured with a uric acid (The final concentration of uric acid was adjusted to 4×10-4M.)
=result=
result
The promoter should be fully activated at the highest uric acid concentration safe to human body (0.465mM). The activity of the promoters were determined by measuring the fluorescence intensity of the enhanced green fluorescent protein (EGFP). The results showed that the Phuc2 had the highest sensitive and activity at the conditions of 0.1mM and 0.01 mM of uric acid. Then, the EGFP coding sequence was replaced by the uricase gene to check whether the module could sense and metabolize the uric acid. As shown in Fig.5, the control group kept constant uric acid levels, but the experimental group displayed reduced uric acid concentrations in a time-dependent manner in the first 3 h of incubation. After that, the uric acid levels kept constant. The data suggested that the expression of uricase was induced at high concentrations of uric acid and repressed at its relatively low concentrations. The result indicated that the expression of uricase was under the control of Phuc2 responsive to the concentration of uric acid.

- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal XhoI site found at 508
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 244
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 208