Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3017064"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
[[File:T--Hong Kong HKUST--as_RFP_white.jpeg|thumb|Secondary structure of the transcription product of this part, predicted by NUPACK]] | [[File:T--Hong Kong HKUST--as_RFP_white.jpeg|thumb|Secondary structure of the transcription product of this part, predicted by NUPACK]] | ||
| − | <p>asRNA is the key to the reversibility of the CRISPRi switch. The asRNA binds to the artificial linker loop of the sgRNA, and extend the loop to become a linear structure. It is proven that this linearization of the loop causes derepression.</p> | + | <p>asRNA is the key to the reversibility of the CRISPRi switch. The asRNA binds to the artificial linker loop of the sgRNA, and extend the loop to become a linear structure. It is proven that this linearization of the loop causes derepression[1].</p> |
<p>The synthetic asRNA is composed of 2 functional domains, extensor, for linearizing the loop, and Spot 42, aiding the stability of the asRNA.</p> | <p>The synthetic asRNA is composed of 2 functional domains, extensor, for linearizing the loop, and Spot 42, aiding the stability of the asRNA.</p> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 17: | ||
<h2>Extensor</h2> | <h2>Extensor</h2> | ||
| − | <p>The extensor sequence is complementary to the artificial linker loop. By forming a duplex, the loop is extended. It was thought in the study that an asRNA complementary to the spacer would displace the DNA target and yield a higher depression effect. But after optimization, the study found out that changing the sgRNA’s secondary structure by extending a loop formed by the artificial linker would maximize the derepression effect to at least 95%, compared to only 15-55% of complementing the spacer.</p> | + | <p>The extensor sequence is complementary to the artificial linker loop. By forming a duplex, the loop is extended. It was thought in the study[1] that an asRNA complementary to the spacer would displace the DNA target and yield a higher depression effect. But after optimization, the study found out that changing the sgRNA’s secondary structure by extending a loop formed by the artificial linker would maximize the derepression effect to at least 95%, compared to only 15-55% of complementing the spacer[1].</p> |
<p>The derepression is specific to the <i>rfp</i> gene BBa_E1010. Therefore asRNA extensor in the transcription product of this part targets sgRNA artificial linker of transcription product of part KK3017002.</p> | <p>The derepression is specific to the <i>rfp</i> gene BBa_E1010. Therefore asRNA extensor in the transcription product of this part targets sgRNA artificial linker of transcription product of part KK3017002.</p> | ||
| Line 27: | Line 27: | ||
<h2>Spot 42</h2> | <h2>Spot 42</h2> | ||
| − | <p>Bacterial Hfq protein is known to modulate the stability or the translation of mRNAs and interact with small regulatory RNAs. A study provides evidence that Hfq strongly cooperates in intermolecular base pairing between the asRNA and its target RNA. Spot 42 is an RNA antisense regulator that has several A/U-rich regions that provide specificity to Hfq protein. Hfq protein also provide protection to the asRNA at these A/U-rich regions.</p> | + | <p>Bacterial Hfq protein is known to modulate the stability or the translation of mRNAs and interact with small regulatory RNAs. A study provides evidence that Hfq strongly cooperates in intermolecular base pairing between the asRNA and its target RNA. Spot 42 is an RNA antisense regulator that has several A/U-rich regions that provide specificity to Hfq protein. Hfq protein also provide protection to the asRNA at these A/U-rich regions[5].</p> |
| − | <p>Same Spot 42 sequence is present in every asRNA we have designed as it is highly specific to Hfq protein and the duplex is necessary for the asRNA to work. Hfq is endogenous to <i>E.coli</i>, therefore the protein is not encoded in any part of the circuit.</p> | + | <p>Same Spot 42 sequence is present in every asRNA we have designed as it is highly specific to Hfq protein and the duplex is necessary for the asRNA to work. Hfq is endogenous to <i>E.coli</i>, therefore the protein is not encoded in any part of the circuit[6].</p> |
Revision as of 12:26, 20 October 2019
CRISPRi antisense RNA for derepressing rfp - transcription template with terminator
This part is a transcription template CRISPRi asRNA for rfp DNA binding with a T0 terminator (BBa_K3017005). In our project, the T0 terminator terminates the in vitro transcription of antisense RNA (BBa_K3017003 and BBa_K3017004) without forming secondary structures with the RNA itself, avoiding functional interferences. Users can add their own choice of promoter before this part for in vitro transcription.
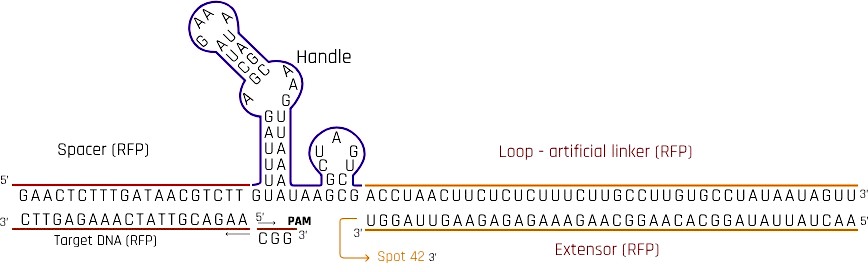
asRNA is the key to the reversibility of the CRISPRi switch. The asRNA binds to the artificial linker loop of the sgRNA, and extend the loop to become a linear structure. It is proven that this linearization of the loop causes derepression[1].
The synthetic asRNA is composed of 2 functional domains, extensor, for linearizing the loop, and Spot 42, aiding the stability of the asRNA.
Extensor
The extensor sequence is complementary to the artificial linker loop. By forming a duplex, the loop is extended. It was thought in the study[1] that an asRNA complementary to the spacer would displace the DNA target and yield a higher depression effect. But after optimization, the study found out that changing the sgRNA’s secondary structure by extending a loop formed by the artificial linker would maximize the derepression effect to at least 95%, compared to only 15-55% of complementing the spacer[1].
The derepression is specific to the rfp gene BBa_E1010. Therefore asRNA extensor in the transcription product of this part targets sgRNA artificial linker of transcription product of part KK3017002.
Spot 42
Bacterial Hfq protein is known to modulate the stability or the translation of mRNAs and interact with small regulatory RNAs. A study provides evidence that Hfq strongly cooperates in intermolecular base pairing between the asRNA and its target RNA. Spot 42 is an RNA antisense regulator that has several A/U-rich regions that provide specificity to Hfq protein. Hfq protein also provide protection to the asRNA at these A/U-rich regions[5].
Same Spot 42 sequence is present in every asRNA we have designed as it is highly specific to Hfq protein and the duplex is necessary for the asRNA to work. Hfq is endogenous to E.coli, therefore the protein is not encoded in any part of the circuit[6].
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]