Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2997009"
| Line 53: | Line 53: | ||
===TyrP and TAL Assay=== | ===TyrP and TAL Assay=== | ||
| − | To confirm the protein activity of TAL and TyrP, we performed a functional test using n-octanol extraction method, [https://2019.igem.org/Team:NCKU_Tainan/Protocols TyrP and TAL Assay], which was previously proposed by iGEM Uppsala 2013 and has been verified by HPLC[4]. The <i>p</i>-Coumaric acid concentration was measured through the absorbance value at 310nm wavelength under Nanodrop UV-Vis wavelength. The standard curve of <i>p</i>-Coumaric acid was drawn in Fig.11 to determine the relationship between <i>p</i>-Coumaric acid concentrations and its 310nm arbitrary unit (a.u). Our samples with TAL constructs were then mapped onto the standard curve, to know how much <i>p</i>-Coumaric acid is being produced. | + | To confirm the protein activity of TAL and TyrP, we performed a functional test using <i>n</i>-octanol extraction method, [https://2019.igem.org/Team:NCKU_Tainan/Protocols TyrP and TAL Assay], which was previously proposed by iGEM Uppsala 2013 and has been verified by HPLC[4]. The <i>p</i>-Coumaric acid concentration was measured through the absorbance value at 310nm wavelength under Nanodrop UV-Vis wavelength. The standard curve of <i>p</i>-Coumaric acid was drawn in Fig.11 to determine the relationship between <i>p</i>-Coumaric acid concentrations and its 310nm arbitrary unit (a.u). Our samples with TAL constructs were then mapped onto the standard curve, to know how much <i>p</i>-Coumaric acid is being produced. |
<html> | <html> | ||
Revision as of 08:35, 20 October 2019
J23100-NRBS-sam8 (J23100-I742106)
Background
Tyrosine ammonia-lyase (TAL) is an enzyme that converts tyrosine into p-Coumaric acid. We engineered E. coli Nissle to express TAL to turn the excess tyrosine inside the gut into p-Coumaric acid, and compare the different constructs for improvement, BBa_K2997009 and BBa_K2997010.
Expression in E.coli
We constructed Tyrosine Ammonia Lyase with a native RBS , and transformed the plasmid into E. coli Nissle 1917 and confirmed it by double digestion. The results are as follows:
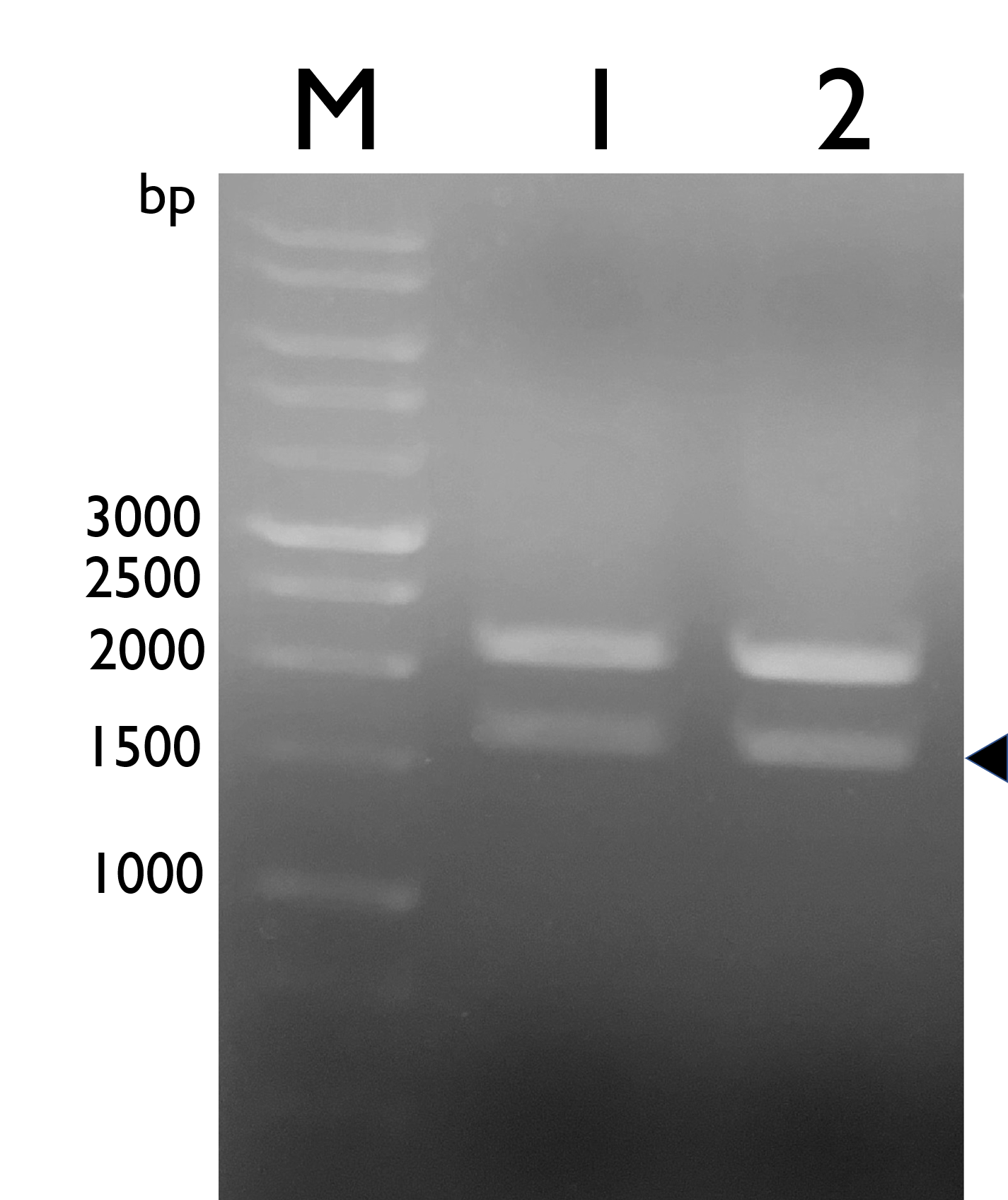
Fig. 1. Confirmation of BBa_K2997009 by double digestion, arrow indicates TAL with NRBS (~1600bp).M: Marker; Lane 1: pSB1C3-BBa_K2997009; Lane 2: BBa_K2997009
Then, we carried out SDS-PAGE to check the protein expression of TAL, and the expected protein size of TAL is 54kDa. As seen in the results below, however, there’s no distinguishable band around both sizes.
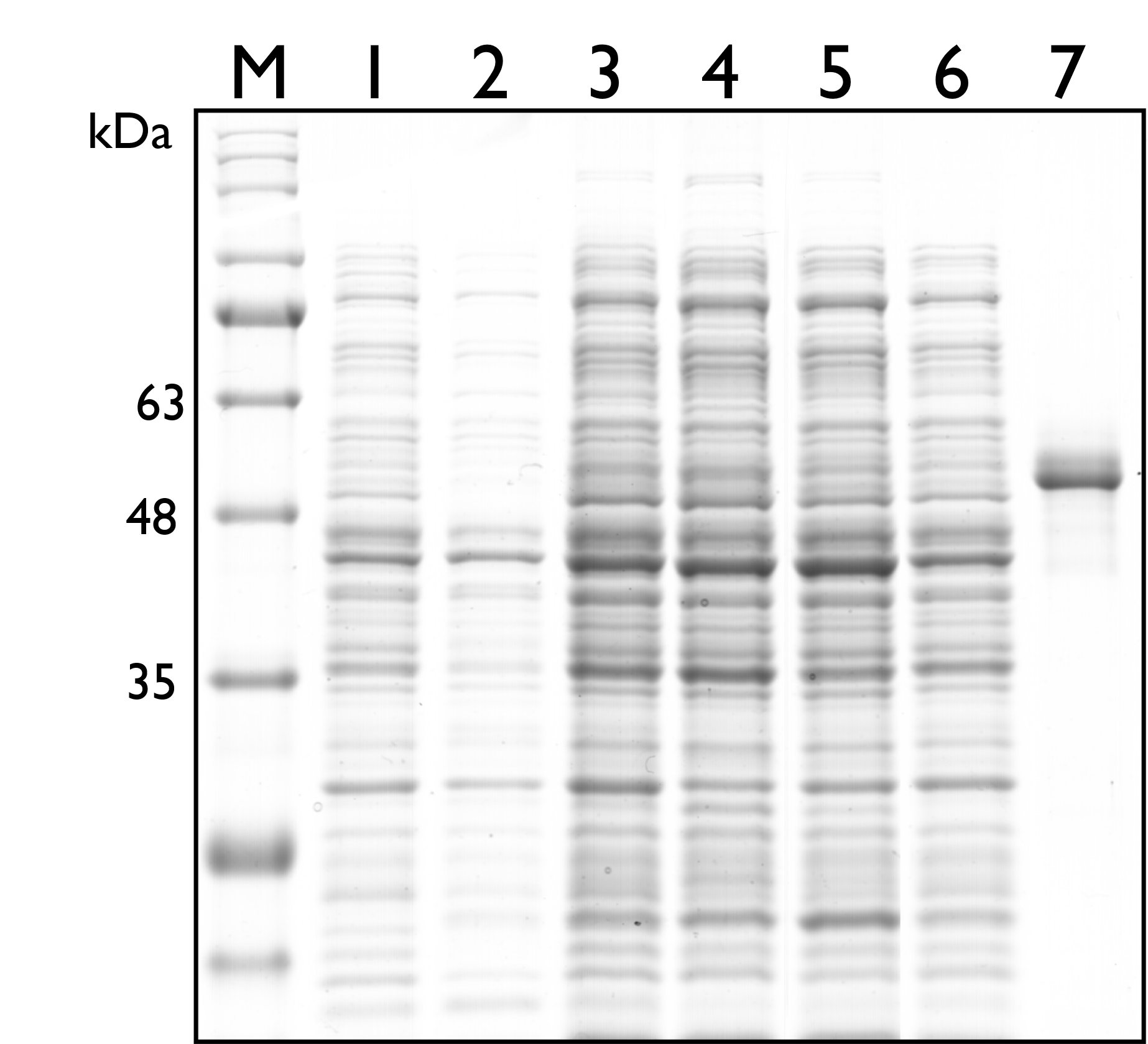
Fig. 2. 12% SDS PAGE of E. coli Nissle 1917 with different plasmids. M: Marker; Lane 1: Wild Type; Lane 2: pSB1C3; Lane 3: BBa_K2997009 ; Lane 4: BBa_K2997010; Lane 5: Dual plasmid containing BBa_K2997009 and BBa_K2997000; Lane 6: Dual plasmid containing BBa_K2997010 and BBa_K2997000; Lane 7: Positive control (c.d. 3392)
RT-PCR
RT-PCR experiment was used to confirm that the constructed TAL Biobrick is being transcribed. As seen in Fig.3, cDNA for both bacteria carrying TAL constructs are being detected by PCR. Confirming that the TAL genes is actually being transcribed in E. coli Nissle.

Fig. 3. Reverse Transcription(RT)-PCR Results to confirm that our construct is being transcribed. (a) Schematics show location of amplified regions and primers. (b) 1.5% Agarose gel shows PCR results. All products have expected size of 250bp as shown in (a). (cDNA: Total cDNA; RNA: Total RNA; plasmid: pSB1C3 containing respective Biobrick.)

Table 1. Description of templates and primers being used in each lane.
TyrP and TAL Assay
To confirm the protein activity of TAL and TyrP, we performed a functional test using n-octanol extraction method, TyrP and TAL Assay, which was previously proposed by iGEM Uppsala 2013 and has been verified by HPLC[4]. The p-Coumaric acid concentration was measured through the absorbance value at 310nm wavelength under Nanodrop UV-Vis wavelength. The standard curve of p-Coumaric acid was drawn in Fig.11 to determine the relationship between p-Coumaric acid concentrations and its 310nm arbitrary unit (a.u). Our samples with TAL constructs were then mapped onto the standard curve, to know how much p-Coumaric acid is being produced.
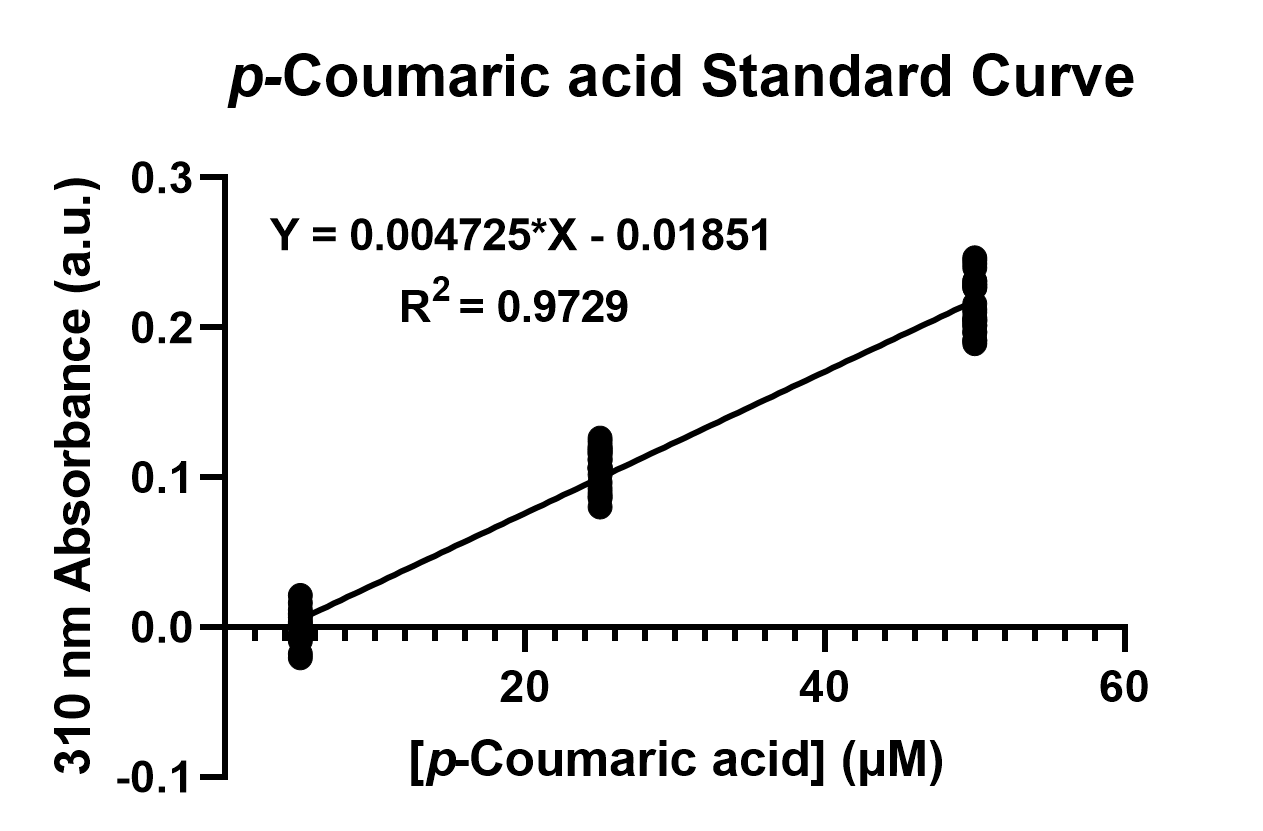
Fig. 4. The standard curve of p-Coumaric acid concentration in correlation with absorbance at 310nm, which is provided by genetic E. coli Nissle in LB broth after 48 hours.
We compared the TAL constructs containing the native and B0034 ribosome binding sites ( BBa_K2997010 ), to determine if p-Coumaric Acid production is improved by changing the ribosome binding sites. From the results seen in Fig. 5, BBa_K2997010 is able to produce a higher amount of p-Coumaric acid. Hence, we are able to prove that by changing the RBS (from Native to B0034), the conversion of tyrosine into p-Coumaric acid can increase by 1.73-fold.
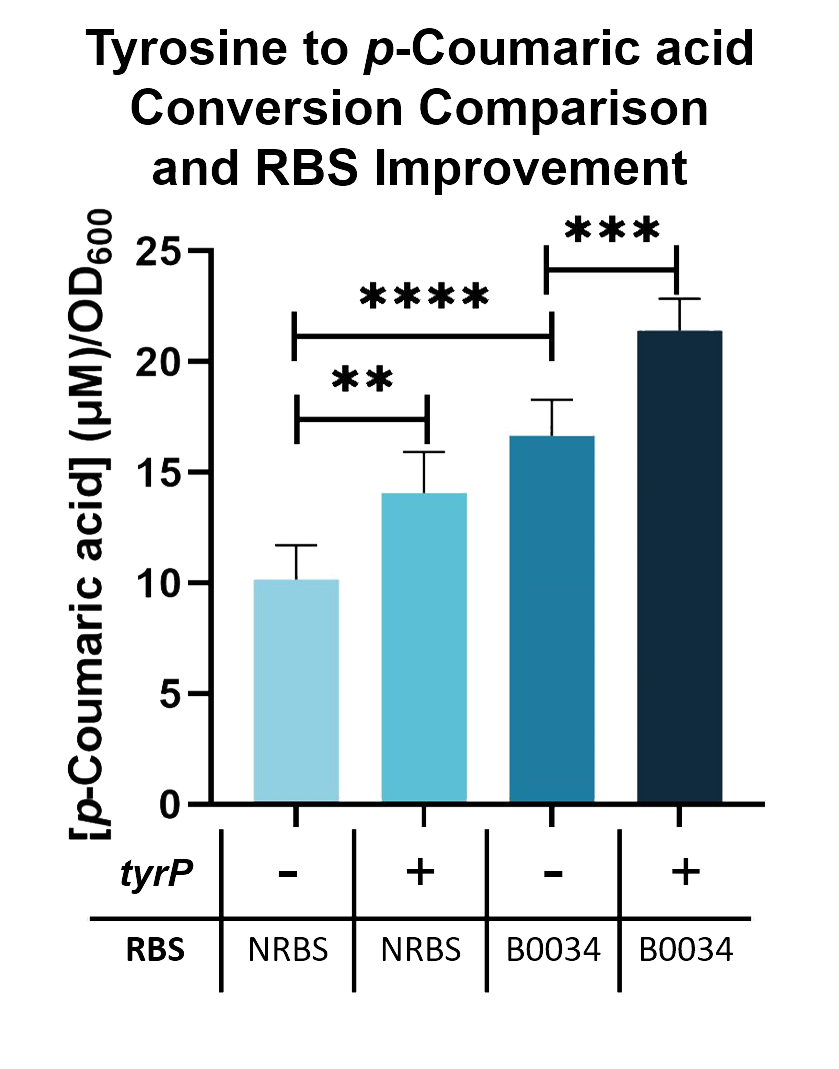
Fig. 5. p-Coumaric acid/O.D.600 levels of E. coli Nissle with TAL and tyrP in LB with 1mM tyrosine
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 457
Illegal BamHI site found at 36 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 232
