Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K141000"
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K141000 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K141000 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | The | + | The uncoupling protein UCP+ is a proton carrier characteristic of brown adipose tissue. |
| − | + | UCP+ uncouples the respiratory chain of ATP production, converting the metabolic energy in heat. | |
| − | + | [[Image:function.jpg]] | |
| − | The | + | UCP+ is a 33kd protein which is exclusively located in the brown adipocites. |
| + | It is an integral protein present in inner mitocondrial membrane. | ||
| + | The protein has a tripartite structure. The structure displays an around 100 residues region which is three times repeated. Each part encodes for two transmembrane segments and one long hydrophilic loop.The functional carrier unit is an homodimer. | ||
| + | [[Image:Structure.jpg]] | ||
| + | The main difference between UCP+ and most of the proteins with a nuclear codification is the lack of the importation targeting to the mitochondria in UCP+ proteins. | ||
| + | The condition that determines the mitochondria as the protein target lays in the first loop which protudes in the mitochondrial matrix. | ||
| + | The second loop of the matrix is essential for the insertion of the protein in the inner mitochondrial matrix. | ||
| + | Purine nucleotides act as inhibitors of protein activity and esterificated fatty acids act as inductors. | ||
| + | |||
| + | |||
Revision as of 13:37, 8 October 2008
Ucp1
The uncoupling protein UCP+ is a proton carrier characteristic of brown adipose tissue.
UCP+ uncouples the respiratory chain of ATP production, converting the metabolic energy in heat.
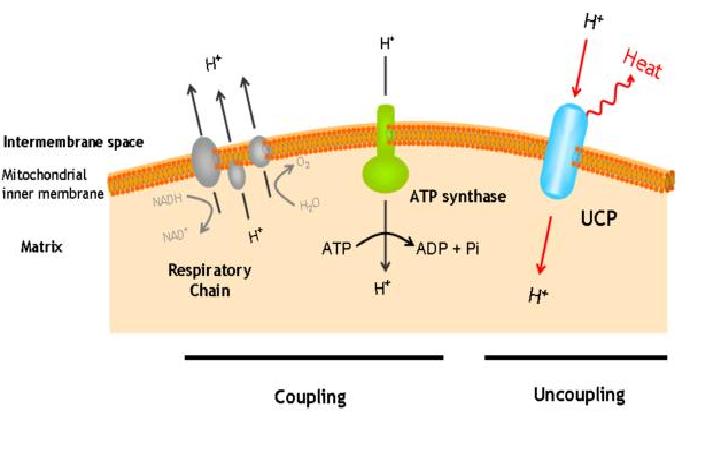 UCP+ is a 33kd protein which is exclusively located in the brown adipocites.
It is an integral protein present in inner mitocondrial membrane.
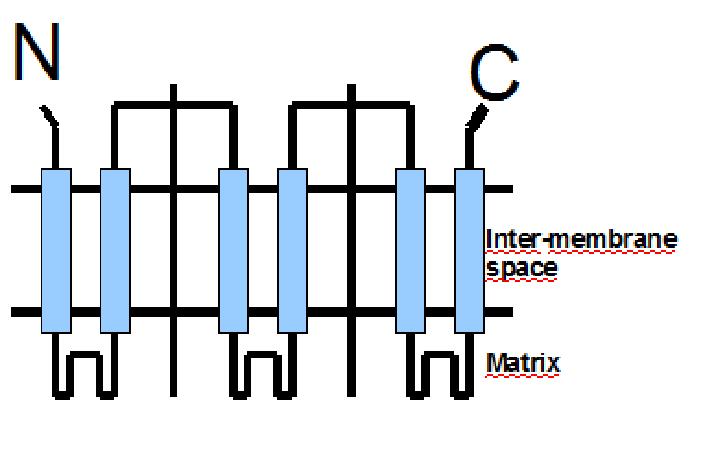
The protein has a tripartite structure. The structure displays an around 100 residues region which is three times repeated. Each part encodes for two transmembrane segments and one long hydrophilic loop.The functional carrier unit is an homodimer.
UCP+ is a 33kd protein which is exclusively located in the brown adipocites.
It is an integral protein present in inner mitocondrial membrane.
The protein has a tripartite structure. The structure displays an around 100 residues region which is three times repeated. Each part encodes for two transmembrane segments and one long hydrophilic loop.The functional carrier unit is an homodimer.
 The main difference between UCP+ and most of the proteins with a nuclear codification is the lack of the importation targeting to the mitochondria in UCP+ proteins.
The condition that determines the mitochondria as the protein target lays in the first loop which protudes in the mitochondrial matrix.
The second loop of the matrix is essential for the insertion of the protein in the inner mitochondrial matrix.
Purine nucleotides act as inhibitors of protein activity and esterificated fatty acids act as inductors.
The main difference between UCP+ and most of the proteins with a nuclear codification is the lack of the importation targeting to the mitochondria in UCP+ proteins.
The condition that determines the mitochondria as the protein target lays in the first loop which protudes in the mitochondrial matrix.
The second loop of the matrix is essential for the insertion of the protein in the inner mitochondrial matrix.
Purine nucleotides act as inhibitors of protein activity and esterificated fatty acids act as inductors.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 47
Illegal BglII site found at 347
Illegal BamHI site found at 835 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 58
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
