Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K431007"
BrianSebZhou (Talk | contribs) (→ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization) |
BrianSebZhou (Talk | contribs) (→ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization) |
||
| Line 25: | Line 25: | ||
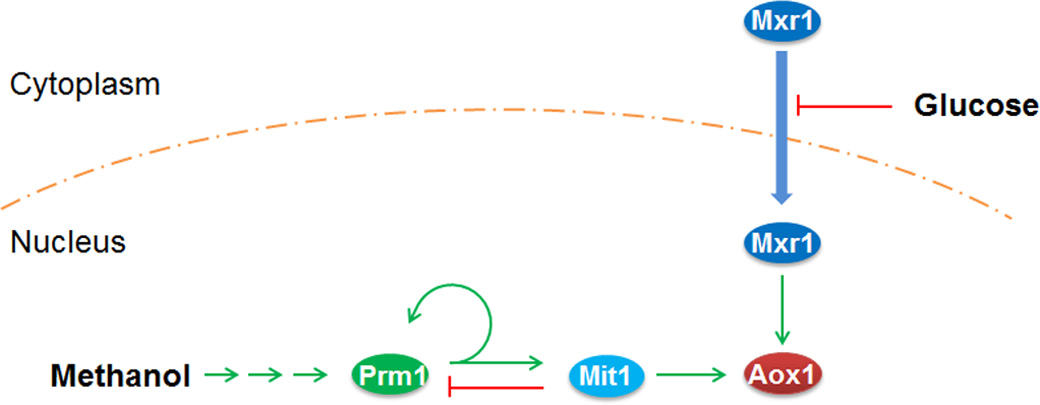
Based on the interpretation in this paper, upon methanol induction, transcription factors Mxr1 and Prm1 are activated. The former derepresses pAOX1 while the latter activates pAOX1. The activation of pAOX1 is further amplified via the self-activation of Prm1 (PRM1 activates its own promoter, pPRM1) and the activation of Mit1, a third transcription factor that activates pAOX1, by Prm1. Given that pAOX1 expresses alcohol oxidase 1 in ''P. pastoris'', the key protein that allows it to metabolize methanol, this strong activation allows the methylotrophic yeast to rapidly respond to the change of carbon source from glucose etc. to methanol. After pAOX1 is strongly activated, over activation is prevented via the suppression of pPRM1 by Mit1. This regulatory pathway is illustrated in Figure 2. | Based on the interpretation in this paper, upon methanol induction, transcription factors Mxr1 and Prm1 are activated. The former derepresses pAOX1 while the latter activates pAOX1. The activation of pAOX1 is further amplified via the self-activation of Prm1 (PRM1 activates its own promoter, pPRM1) and the activation of Mit1, a third transcription factor that activates pAOX1, by Prm1. Given that pAOX1 expresses alcohol oxidase 1 in ''P. pastoris'', the key protein that allows it to metabolize methanol, this strong activation allows the methylotrophic yeast to rapidly respond to the change of carbon source from glucose etc. to methanol. After pAOX1 is strongly activated, over activation is prevented via the suppression of pPRM1 by Mit1. This regulatory pathway is illustrated in Figure 2. | ||
| − | [[File:WT1.png|400px|center|thumb|Figure 2. Methanol induction of pAOX1 in wild type ''P. pastoris''.]] | + | [[File:WT1.png|400px|center|thumb|Figure 2. Methanol induction of pAOX1 in wild type ''P. pastoris'' as published in Wang et al., 2016.]] |
Revision as of 17:21, 16 October 2019
Alcohol Oxidase 1 promoter
Pichia pastoris initially gained attention as an expression system after recognition of its methylotrophic capabilities and the high levels of alcohol oxidase(AOX) present when induced by methanol. By isolating the promoter (pAOX1 )responsible for AOX production, this system can be utilized to obtain high yields of heterologous protein. The promoter provides not only high expression but very tight regulation as well. Vectors providing protein expression under the control of pAOX1 are the primary system used for P. pastoris
ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization
Methanol induction of the AOX1 promoter
The AOX1 (alcohol oxidase 1, PAS_chr4_0821) promoter (pAOX1), homogenous to Pichia pastoris, is a very strong promoter that is tightly regulated by the carbon source present in the media: it is strongly inhibited by glucose and glycerol, but significantly induced when methanol is present as the only carbon source. This characteristic allows P. pastoris to be a very preferable strain for regulated bioreactor production.
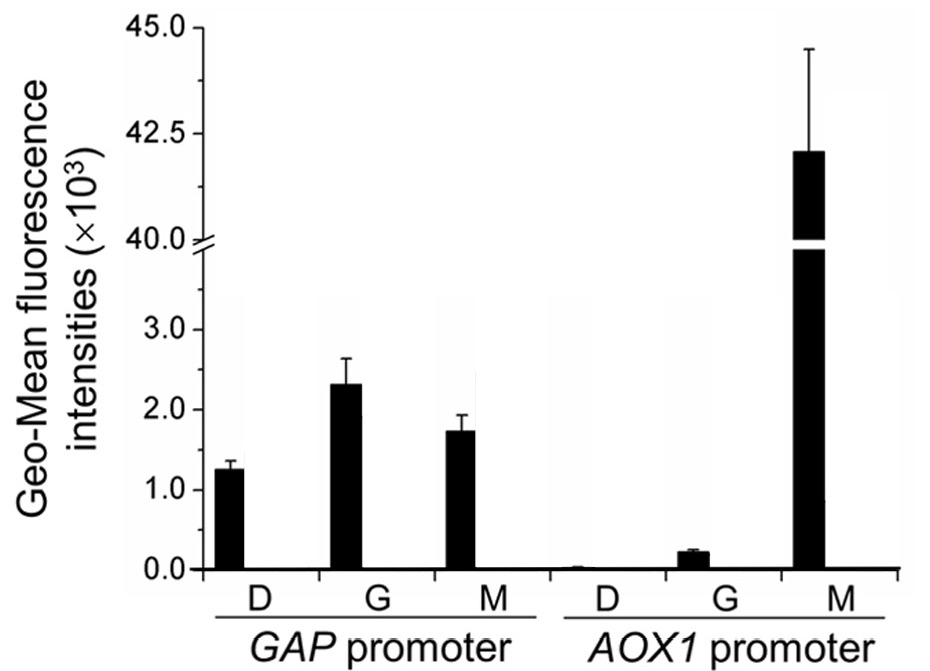
The activity of the AOX1 promoter is characterized by GFP fluorescence and is compared to that of the GAP promoter, a strong constitutive promoter in P. pastoris. Specifically, GFP is expressed by either of the promoters and these constructed strains of P. pastoris are incubated for 12 hours in YNB medium (0.67% yeast nitrogenous base without amino acids) and 50 mg/mL histidine supplemented with 1% glucose (YND), 1% glycerol (YNG), or 0.5% methanol(YNM). The geometric mean of the fluorescence of the GFP expressed is then measured by an enzyme-labeled instrument (Synergy 2 by BioTek Instruments) and normalized to unit cell concentrations (in terms of arbitrary units as represented by OD600 measured by the enzyme-labeled instrument).
As illustrated by figure 1, the activity of the GAP promoter remains largely unchanged relative to the carbon source in the media. The activity of the AOX1 promoter, however, is minimal in glycerol and glucose media, yet very significant in methanol media.
In wild type P. pastoris, alcohol oxidase 1 allows the methylotrophic yeast to metabolize methanol. The regulation of the AOX1 promoter indicates high specificity in the expression of alcohol oxidase 1 and therefore makes P. pastoris a very attractive candidate for regulated fermentation on an industrial scale, especially if the production of a certain chemical needs to be precisely controlled: the protein expressed by the AOX1 promoter can be relatively simply controlled by shifting the carbon source present in the media.
This experiment is published in Wang et al.,2016, and is corroborated by the results from Liang et al., 2012 and Shi et al., 2019.
in trans regulation of pAOX1
In Wang et al,.2016, it is also experimentally demonstrated how pAOX1 is in trans regulated upon methanol induction. Various knockout and knockin strains were produced and the mRNA transcription levels of the proposed transcription factors were evaluated to illustrate the regulation.
Based on the interpretation in this paper, upon methanol induction, transcription factors Mxr1 and Prm1 are activated. The former derepresses pAOX1 while the latter activates pAOX1. The activation of pAOX1 is further amplified via the self-activation of Prm1 (PRM1 activates its own promoter, pPRM1) and the activation of Mit1, a third transcription factor that activates pAOX1, by Prm1. Given that pAOX1 expresses alcohol oxidase 1 in P. pastoris, the key protein that allows it to metabolize methanol, this strong activation allows the methylotrophic yeast to rapidly respond to the change of carbon source from glucose etc. to methanol. After pAOX1 is strongly activated, over activation is prevented via the suppression of pPRM1 by Mit1. This regulatory pathway is illustrated in Figure 2.
Experimental Data Demonstrating pAOX1 activity in methanol media
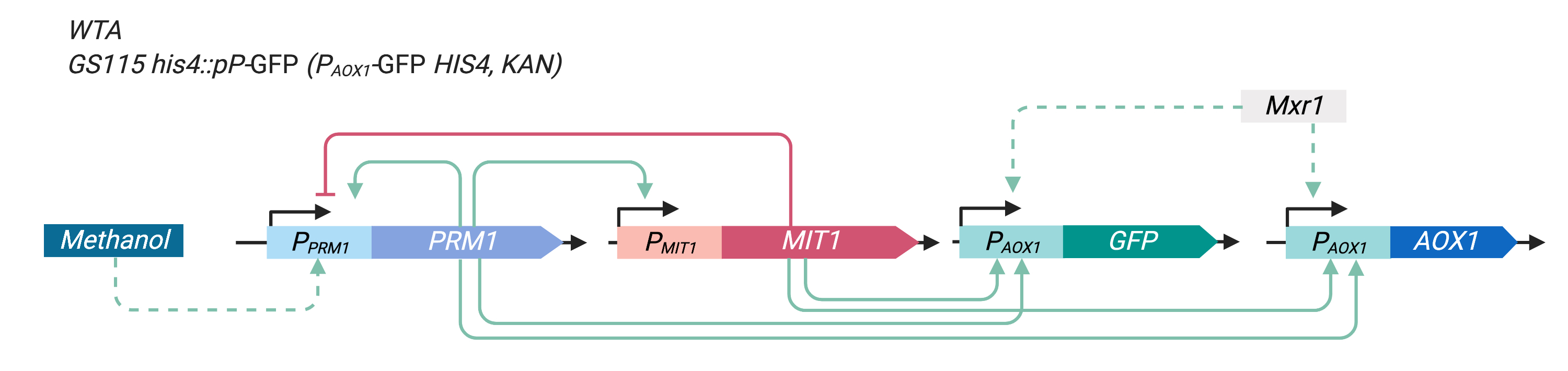
In our experiment, we integrated pAOX1-GFP (yEGFP3 expressed by the AOX1 promoter (pAOX1), BBa_K3239007) into wild type Pichia pastoris GS115 to reflect the expression level of the AOX1 protein in P. pastoris GS115 (the original pAOX1-AOX1 is left intact after the integration, and both yEGFP3 and AOX1 are expressed by pAOX1 regulated in the same way). This is valuable given that the expression of AOX1 is critical to the methanol metabolizing ability of P. pastoris, and in certain uses functional proteins such as insulin progenitors expressed by pAOX1 is integrated into P. pastoris much in the same way as how we integrate pAOX1-GFP into the yeast. Figure 3 illustrates the modified P. pastoris GS115 construct after pAOX1-GFP integration.
Methods
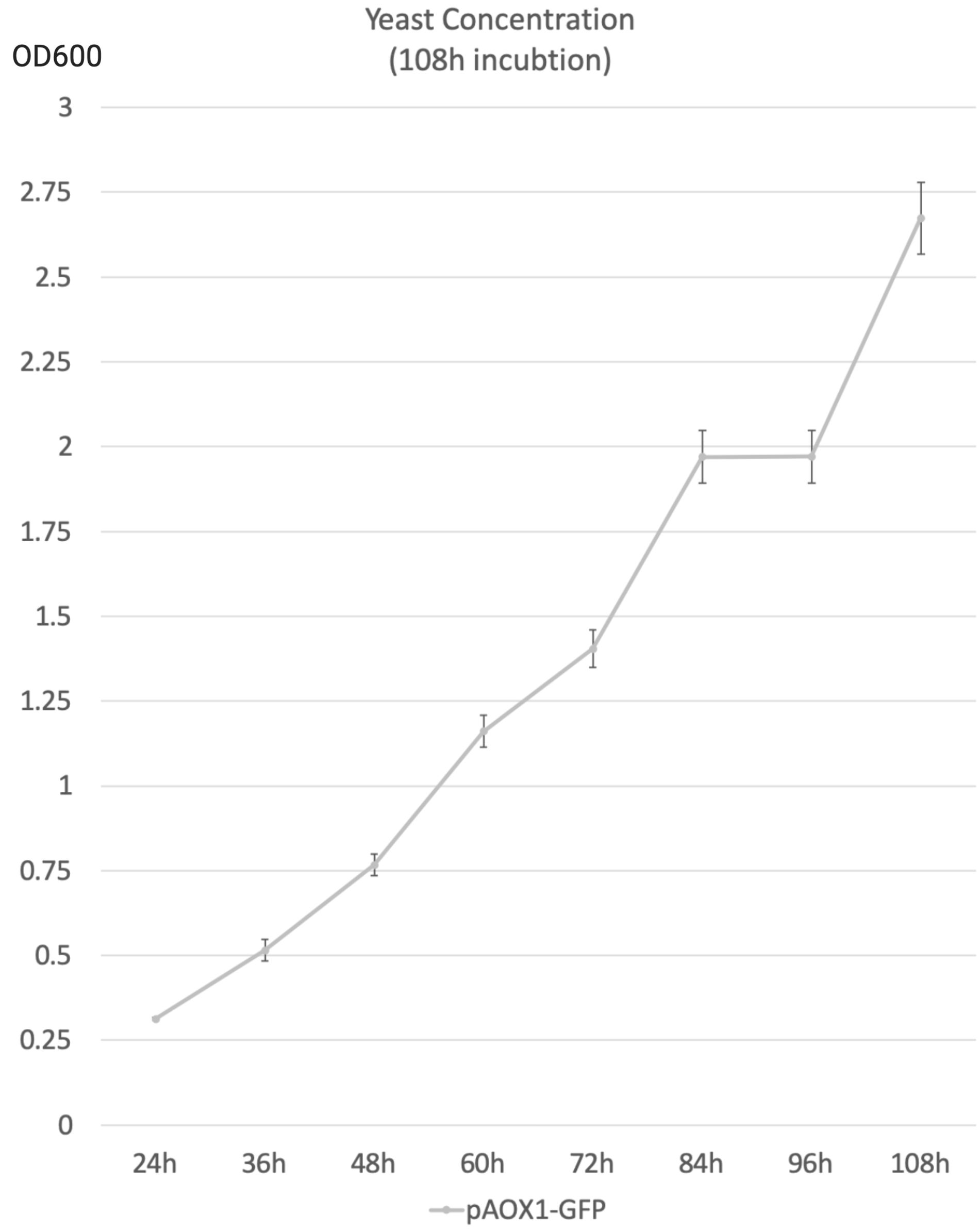
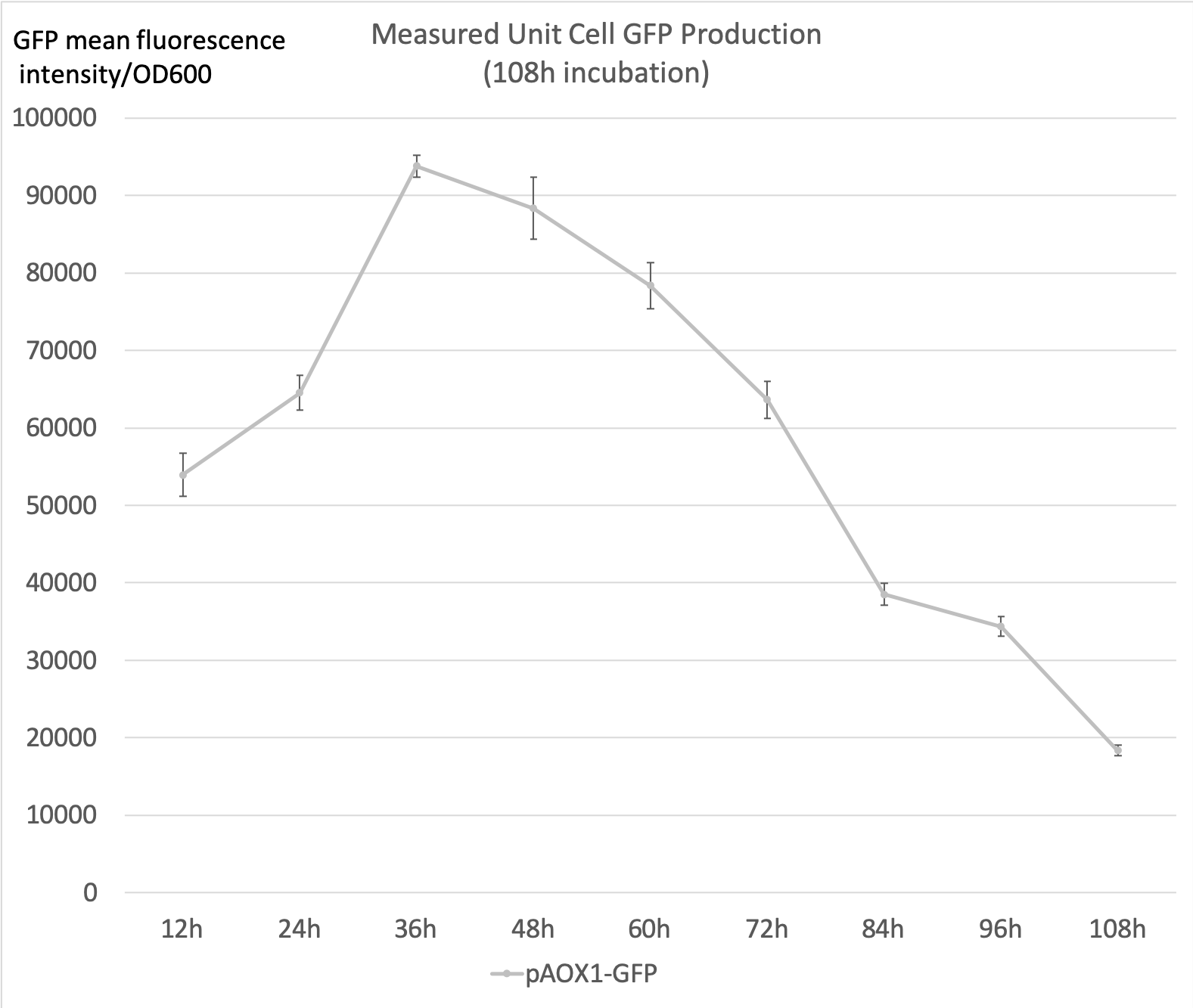
- The following data were acquired after 108h 50mL YNM (1.34% yeat nitrogenous base with 0.5% methanol, 50µg/mL histidine and 40µg/mL biotin) incubation, sampled every 12h. The starting concentration was 1 OD600.
- 0.5%Methanol was added to the media every 24 hours to maintain the methanol concentration.
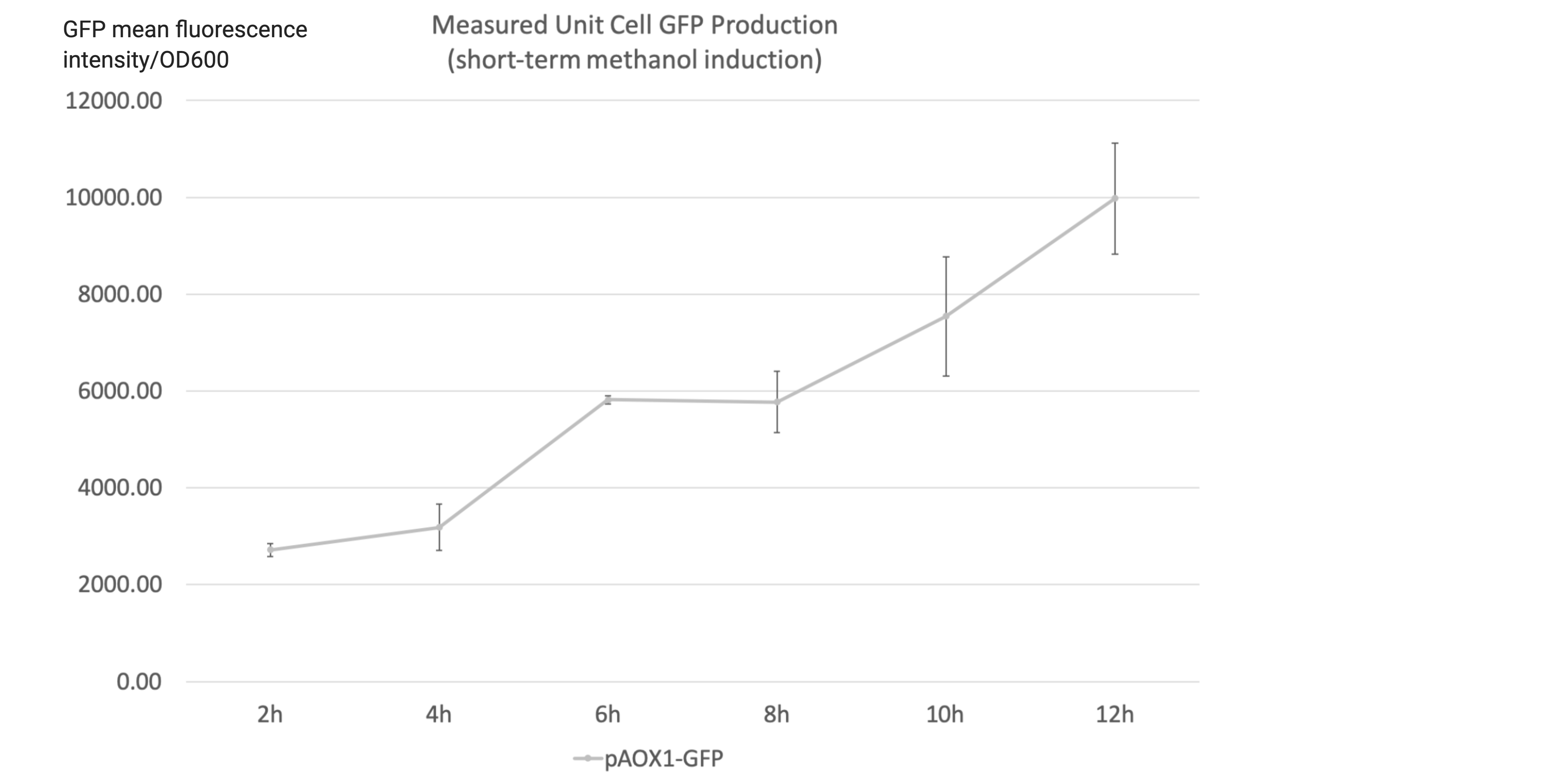
- A short-term methanol induction experiment was performed after the 108h incubation to characterize the instant response to methanol induction after the yeast cells are accustomed to methanol media, hence indicating the overall induction activity of the construct. The yeast cells were collected, rinsed and stored at 4˚C overnight to allow GFP to fully degrade. The strains were then incubated in higher-concentration 50mL YNM media (1.34% yeat nitrogenous base with 0.75% methanol, 50µg/mL histidine and 40µg/mL biotin) for 12 hours and sampled every 2 hours. The starting concentration was 3 OD600.
- Three parallels were performed for each strain.
- We used a Biotek Synergy 2 plate reader to measure the GFP mean fluorescence intensities and the OD600 absorbance of our samples.
- Methanol concentration measurements were performed with a Shenzhen Sieman M100 Biosensors Analyzer.
Data
- OD600 is used as an indicator of yeast concentration in the experiment.
- Measured unit cell GFP production is the ratio of the GFP mean fluorescence intensities to the 0D600 absorbance measured by the plate reader. It shall serve as an indicator of the expression level of GFP at the sampled time point.
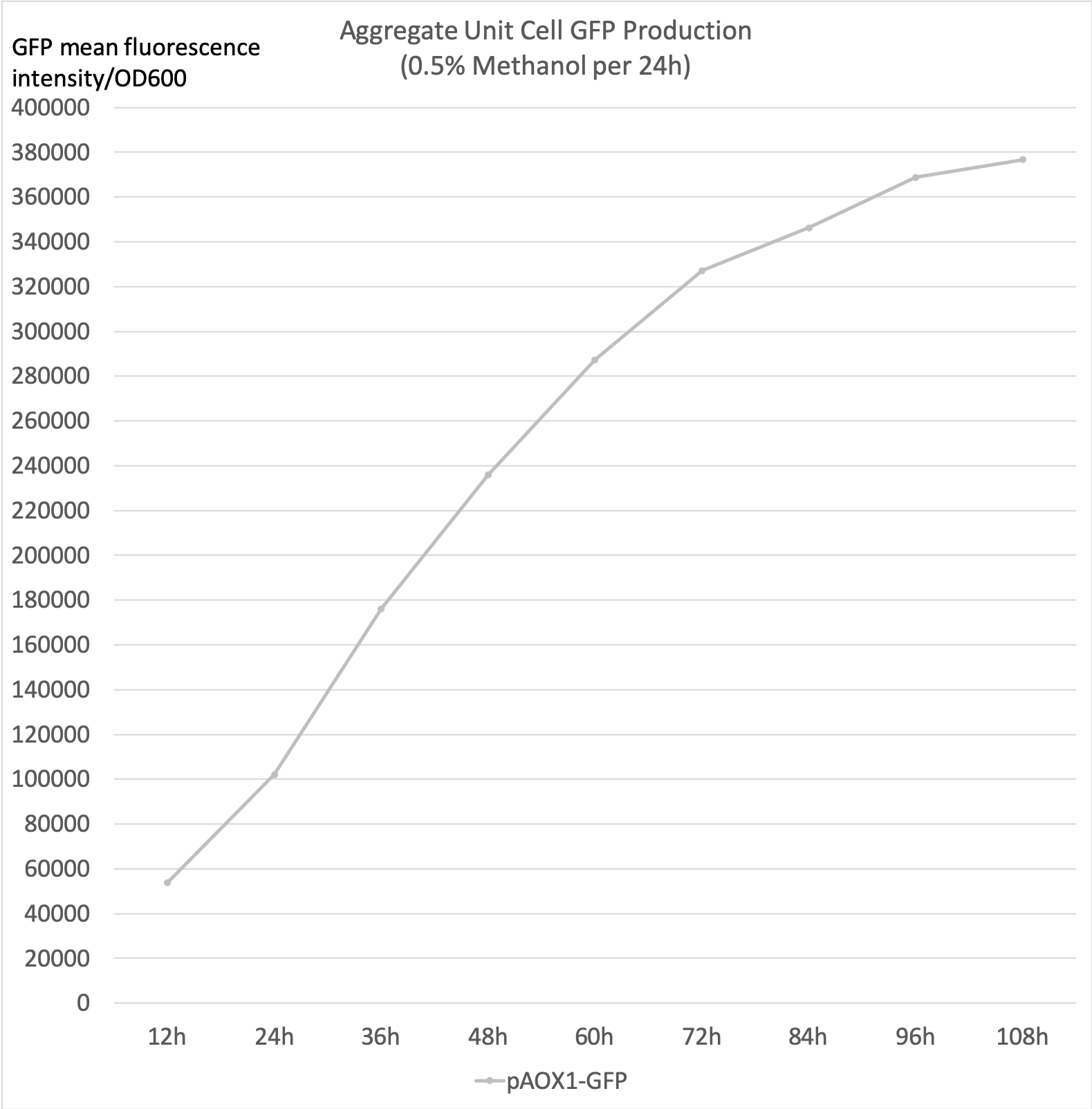
- Aggregate unit cell GFP production is the calculated total unit cell GFP fluorescence intensity. It accounts for the GFP that has degraded over the incubation period to more accurately reflect the aggregate production rate.
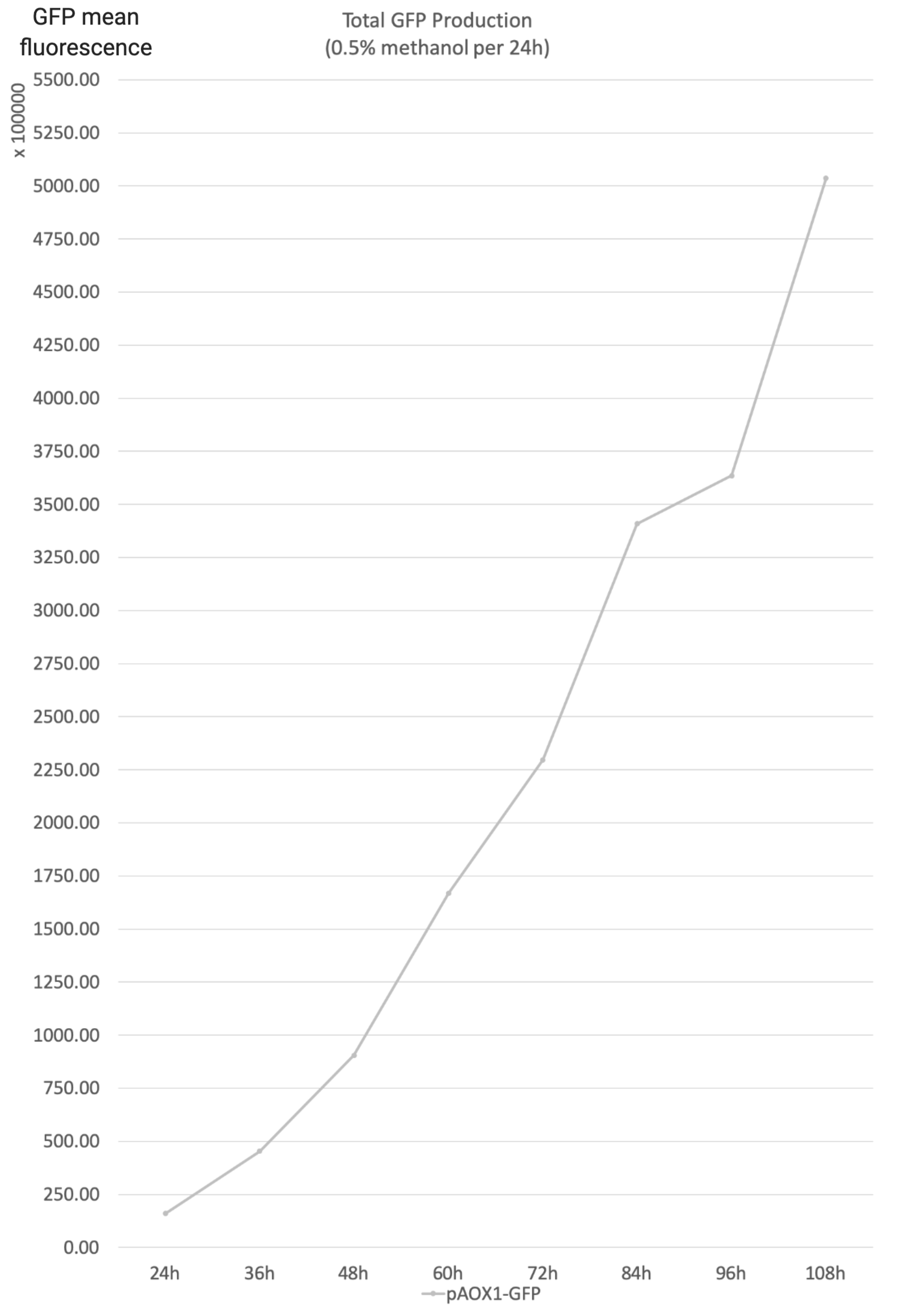
- Total GFP production is the product of the yeast concentration and the aggregate unit cell GFP. It reflects the total GFP production of the reaction system of the strain.
- Total GFP production per gram methanol is the ratio of the total GFP production to the total methanol consumption. It reflects the overall conversion rate of methanol to the product.
- For teams wishing to compare their data to ours, we've provided our data along with our plate reader calibration data in our wiki. Feel free to give it a check!
Reference
Wang, X., Wang, Q., Wang, J., Zhou, M., Shi, L., Zhou, X., … Shen, W. (2016). Mit1 Transcription Factor Mediates Methanol Signaling and Regulates the Alcohol Oxidase 1 ( AOX1 ) Promoter in Pichia pastoris. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 291(12), 6245–6261. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m115.692053
Liang, S., Wang, B., Pan, L., Ye, Y., He, M., Han, S., … Lin, Y. (2012). Comprehensive structural annotation of Pichia pastoris transcriptome and the response to various carbon sources using deep paired-end RNA sequencing. BMC Genomics, 13(1). https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-13-738
Shi, L., Wang, J., Wang, X., Zhang, Y., Song, Z., Cai, M., & Zhou, X. (2019). Transcriptome and metabolome analyses reveal global behaviour of a genetically engineered methanol-independent Pichia pastoris strain. Process Biochemistry, 76(August 2018), 46–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2018.10.014
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]