Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K431007"
BrianSebZhou (Talk | contribs) m |
BrianSebZhou (Talk | contribs) (→ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
''Pichia pastoris'' initially gained attention as an expression system after recognition of its methylotrophic capabilities and the high levels of alcohol oxidase(AOX) present when induced by methanol. By isolating the promoter (pAOX1 )responsible for AOX production, this system can be utilized to obtain high yields of heterologous protein. The promoter provides not only high expression but very tight regulation as well. Vectors providing protein expression under the control of pAOX1 are the primary system used for ''P. pastoris'' | ''Pichia pastoris'' initially gained attention as an expression system after recognition of its methylotrophic capabilities and the high levels of alcohol oxidase(AOX) present when induced by methanol. By isolating the promoter (pAOX1 )responsible for AOX production, this system can be utilized to obtain high yields of heterologous protein. The promoter provides not only high expression but very tight regulation as well. Vectors providing protein expression under the control of pAOX1 are the primary system used for ''P. pastoris'' | ||
==ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization== | ==ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization== | ||
| + | '''Methanol induction of the AOX1 promoter''' | ||
The AOX1 (alcohol oxidase 1, PAS_chr4_0821) promoter used in this plasmid, homogenous to Pichia pastoris, is a very strong promoter that is tightly regulated by the carbon source present in the media: it is strongly inhibited by glucose and glycerol, but significantly induced when methanol is present as the only carbon source. This characteristic allows P. pastoris to be a very preferable strain for regulated bioreactor production. | The AOX1 (alcohol oxidase 1, PAS_chr4_0821) promoter used in this plasmid, homogenous to Pichia pastoris, is a very strong promoter that is tightly regulated by the carbon source present in the media: it is strongly inhibited by glucose and glycerol, but significantly induced when methanol is present as the only carbon source. This characteristic allows P. pastoris to be a very preferable strain for regulated bioreactor production. | ||
| − | |||
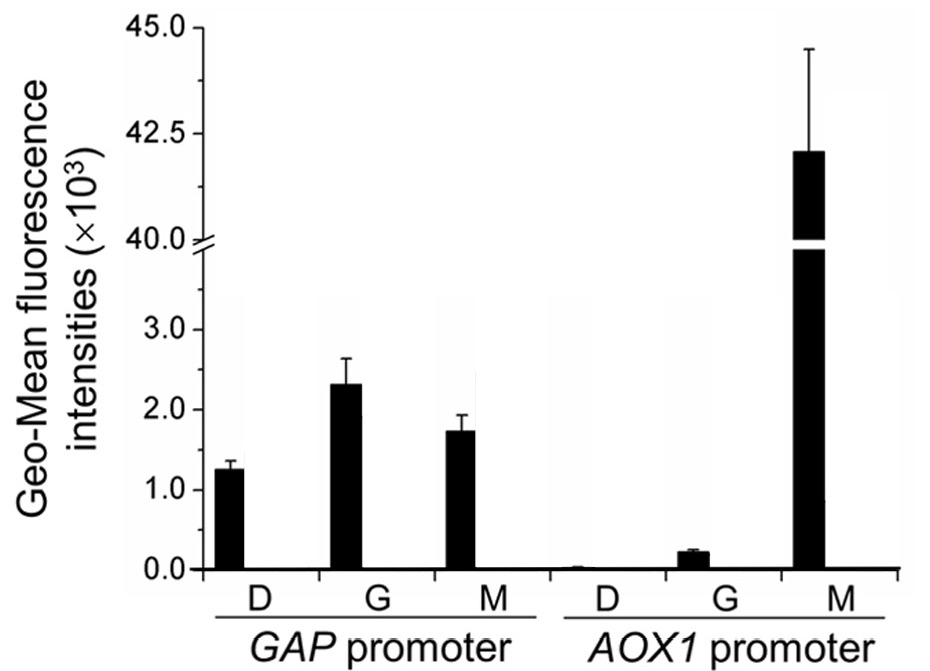
The activity of the AOX1 promoter is characterized by GFP fluorescence and is compared to that of the GAP promoter, a strong constitutive promoter in P. pastoris. Specifically, GFP is expressed by either of the promoters and these constructed strains of P. pastoris are incubated for 12 hours in YNB medium (0.67% yeast nitrogenous base without amino acids) and 50 mg/mL histidine supplemented with 1% glucose (YND), 1% glycerol (YNG), or 0.5% methanol(YNM). The geometric mean of the fluorescence of the GFP expressed is then measured by an enzyme-labeled instrument (Synergy 2 by BioTek Instruments) and normalized to unit cell concentrations (in terms of arbitrary units as represented by OD600 measured by the enzyme-labeled instrument). | The activity of the AOX1 promoter is characterized by GFP fluorescence and is compared to that of the GAP promoter, a strong constitutive promoter in P. pastoris. Specifically, GFP is expressed by either of the promoters and these constructed strains of P. pastoris are incubated for 12 hours in YNB medium (0.67% yeast nitrogenous base without amino acids) and 50 mg/mL histidine supplemented with 1% glucose (YND), 1% glycerol (YNG), or 0.5% methanol(YNM). The geometric mean of the fluorescence of the GFP expressed is then measured by an enzyme-labeled instrument (Synergy 2 by BioTek Instruments) and normalized to unit cell concentrations (in terms of arbitrary units as represented by OD600 measured by the enzyme-labeled instrument). | ||
Revision as of 16:26, 16 October 2019
Alcohol Oxidase 1 promoter
Pichia pastoris initially gained attention as an expression system after recognition of its methylotrophic capabilities and the high levels of alcohol oxidase(AOX) present when induced by methanol. By isolating the promoter (pAOX1 )responsible for AOX production, this system can be utilized to obtain high yields of heterologous protein. The promoter provides not only high expression but very tight regulation as well. Vectors providing protein expression under the control of pAOX1 are the primary system used for P. pastoris
ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization
Methanol induction of the AOX1 promoter The AOX1 (alcohol oxidase 1, PAS_chr4_0821) promoter used in this plasmid, homogenous to Pichia pastoris, is a very strong promoter that is tightly regulated by the carbon source present in the media: it is strongly inhibited by glucose and glycerol, but significantly induced when methanol is present as the only carbon source. This characteristic allows P. pastoris to be a very preferable strain for regulated bioreactor production.
The activity of the AOX1 promoter is characterized by GFP fluorescence and is compared to that of the GAP promoter, a strong constitutive promoter in P. pastoris. Specifically, GFP is expressed by either of the promoters and these constructed strains of P. pastoris are incubated for 12 hours in YNB medium (0.67% yeast nitrogenous base without amino acids) and 50 mg/mL histidine supplemented with 1% glucose (YND), 1% glycerol (YNG), or 0.5% methanol(YNM). The geometric mean of the fluorescence of the GFP expressed is then measured by an enzyme-labeled instrument (Synergy 2 by BioTek Instruments) and normalized to unit cell concentrations (in terms of arbitrary units as represented by OD600 measured by the enzyme-labeled instrument).
As illustrated by figure 1, the activity of the GAP promoter remains largely unchanged relative to the carbon source in the media. The activity of the AOX1 promoter, however, is minimal in glycerol and glucose media, yet very significant in methanol media.
In wild type P. pastoris, alcohol oxidase 1 allows the methylotrophic yeast to metabolize methanol. The regulation of the AOX1 promoter indicates high specificity in the expression of alcohol oxidase 1 and therefore makes P. pastoris a very attractive candidate for regulated fermentation on an industrial scale, especially if the production of a certain chemical needs to be precisely controlled: the protein expressed by the AOX1 promoter can be relatively simply controlled by shifting the carbon source present in the media.
This experiment is published in Wang et al.,2016.
Complete AOX1 promoter sequence:
GATCTAACATCCAAAGACGAAAGGTTGAATGAAACCTTTTTGCCATCCGACATCCACAGGTCCATTCTCACACATAAGTG CCAAACGCAACAGGAGGGGATACACTAGCAGCAGACCGTTGCAAACGCAGGACCTCCACTCCTCTTCTCCTCAACACC CACTTTTGCCATCGAAAAACCAGCCCAGTTATTGGGCTTGATTGGAGCTCGCTCATTCCAATTCCTTCTATTAGGCTACTA ACACCATGACTTTATTAGCCTGTCTATCCTGGCCCCCCTGGCGAGGTTCATGTTTGTTTATTTCCGAATGCAACAAGCTCC GCATTACACCCGAACATCACTCCAGATGAGGGCTTTCTGAGTGTGGGGTCAAATAGTTTCATGTTCCCCAAATGGCCCAAA ACTGACAGTTTAAACGCTGTCTTGGAACCTAATATGACAAAAGCGTGATCTCATCCAAGATGAACTAAGTTTGGTTCGTTGA AATGCTAACGGCCAGTTGGTCAAAAAGAAACTTCCAAAAGTCGGCATACCGTTTGTCTTGTTTGGTATTGATTGACGAATGC TCAAAAATAATCTCATTAATGCTTAGCGCAGTCTCTCTATCGCTTCTGAACCCCGGTGCACCTGTGCCGAAACGCAAATGGG GAAACACCCGCTTTTTGGATGATTATGCATTGTCTCCACATTGTATGCTTCCAAGATTCTGGTGGGAATACTGCTGATAGCCT AACGTTCATGATCAAAATTTAACTGTTCTAACCCCTACTTGACAGCAATATATAAACAGAAGGAAGCTGCCCTGTCTTAAACC TTTTTTTTTATCATCATTATTAGCTTACTTTCATAATTGCGACTGGTTCCAATTGACAAGCTTTTGATTTTAACGACTTTTAACG ACAACTTGAGAAGATCAAAAAACAACTAATTATTCGAAACG
Reference
Wang, X., Wang, Q., Wang, J., Zhou, M., Shi, L., Zhou, X., … Shen, W. (2016). Mit1 Transcription Factor Mediates Methanol Signaling and Regulates the Alcohol Oxidase 1 ( AOX1 ) Promoter in Pichia pastoris. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 291(12), 6245–6261. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m115.692053
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]