Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2322005"
BrianSebZhou (Talk | contribs) (→ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization) |
BrianSebZhou (Talk | contribs) (→ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization) |
||
| Line 40: | Line 40: | ||
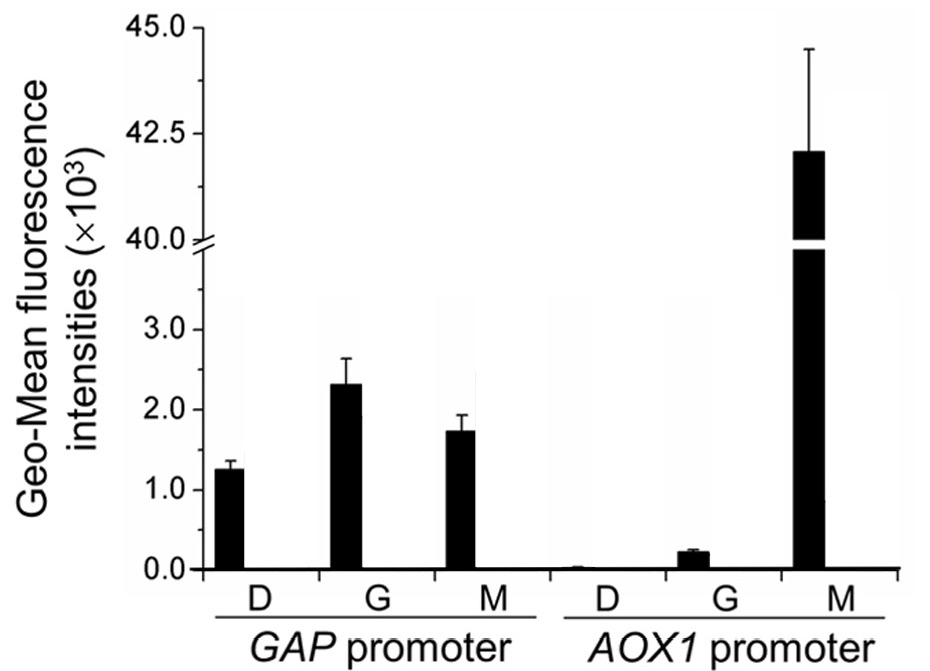
[[Image:J_Biol._Chem.-2016-Wang-6245-61(3).png|400px|thumb|Figure 1. evaluation of the activity of the AOX1 Promoter via a reporter gene (GFP) expression assay in the wild type P.pastoris strain in glucose (D), glycerol (G) and methanol (M) media.]] | [[Image:J_Biol._Chem.-2016-Wang-6245-61(3).png|400px|thumb|Figure 1. evaluation of the activity of the AOX1 Promoter via a reporter gene (GFP) expression assay in the wild type P.pastoris strain in glucose (D), glycerol (G) and methanol (M) media.]] | ||
| + | In wild type P. pastoris, alcohol oxidase allows the methylotrophic yeast to metabolize methanol. The regulation of the AOX1 promoter indicates high specificity in the expression of alcohol oxidase and therefore makes P. pastoris a very attractive candidate for regulated fermentation on an industrial scale, especially if the production of a certain chemical needs to be precisely controlled: the protein expressed by the AOX1 promoter can be relatively simply controlled by shifting the carbon source present in the media. | ||
| Line 48: | Line 49: | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| + | This experiment is published in Wang et al.,2016. | ||
Complete AOX1 promoter sequence: | Complete AOX1 promoter sequence: | ||
| − | |||
GATCTAACATCCAAAGACGAAAGGTTGAATGAAACCTTTTTGCCATCCGACATCCACAGGTCCATTCTCACACATAAGTG | GATCTAACATCCAAAGACGAAAGGTTGAATGAAACCTTTTTGCCATCCGACATCCACAGGTCCATTCTCACACATAAGTG | ||
CCAAACGCAACAGGAGGGGATACACTAGCAGCAGACCGTTGCAAACGCAGGACCTCCACTCCTCTTCTCCTCAACACC | CCAAACGCAACAGGAGGGGATACACTAGCAGCAGACCGTTGCAAACGCAGGACCTCCACTCCTCTTCTCCTCAACACC | ||
Revision as of 05:33, 15 October 2019
-AOX1 promoter-RBS-gltB-
This circuit contains a AOX1 promoter, a ribosome binding site, a gltB gene. This circuit is used to test the expression of gltB. If the circuit work, the gltB will express normally in GS115.
AOX1 promoter: Function: AOX1 is a strong promoter in the pichia pastoris. It is highly effective. It can be restricted by glucose, glycerinum, ethyl alcohol. It can be induced by the methanol. In our experiment, our circuit is in an environment containing methanol. In this circuit, it is used to control and increase the expression of gltB, our targeted gene.
RBS (Ribosome Binding Site): A ribosome binding site is a sequence of mRNA. It is used to make sure the ribosome is on the correct position of the mRNA at the beginning of the translation.Sequence: TCACACAGGAAACA gltB Escherichia coli glutamate acid synthase gene (gltB) is found in the Escherichia coli. Saccharomyces cerevisiae glutamate acid-6-phosphate synthase (GltB ) is found in the Schizosaccharomyces pombe. The Schizosaccharomyces pombe a species of yeast used in traditional brewing and as a common model in synthetic biology. It is belong to the Schizosaccharomycetes class, and Schizosaccharomycetaceae family.

Figure1: The image of Escherichia coli glutamate acid.
It is assumed that gltB can enhance the osmotic pressure tolerance of the Schizosaccharomyces pombe, because it is the essential gene in the synthesis of the glutamate acid. The changing in the expression of gltB can positively affect the amount of glutamate acid in the cell. Glutamate is a key compound in cellular metabolism. It is a metabolic fuel.
A key process in amino acid degradation is transamination, in which the amino group of an amino acid is transferred to an α-ketoacid, typically catalyzed. So during a osmotic high environment, with the induced in the certain condition, it will increase the rate of the metabolism.
Primer of this part AOX-FP: ATGATTTCTGGAATTCGCGGCCGCTTCTAGAGATCTAACATCCAAAGACGAAAGGT Glt-B-RP: TGACACCTTGCCCTTTTTTGCCGGACTGCAGTTAAACAAATGGTGCAGCATCATGC
ShanghaiFLS_China 2019 characterization
The AOX1 (alcohol oxidase, PAS_chr4_0821) promoter used in this plasmid, homogenous to Pichia pastoris, is a very strong promoter that is tightly regulated by the carbon source present in the media: it is strongly inhibited by glucose and glycerol, but significantly induced when methanol is present as the only carbon source. This characteristic allows P. pastoris to be a very preferable strain for regulated bioreactor production. We wanted to quantify the regulation of the AOX1 promoter in wild type P. pastoris under different carbon sources and found various published papers detailing such regulation. We decided, therefore, that simply repeating the experiments might not be as valuable as providing published and validated experimental data and the relevant literature for later teams to refer to.
The activity of the AOX1 promoter is characterized by GFP fluorescence and is compared to that of the GAP promoter, a strong constitutive promoter in P. pastoris. Specifically, GFP is expressed by either of the promoters and these constructed strains of P. pastoris are incubated for 12 hours in YNB medium (0.67% yeast nitrogenous base without amino acids) and 50 mg/mL histidine supplemented with 1% glucose (YND), 1% glycerol (YNG), or 0.5% methanol(YNM). The geometric mean of the fluorescence of the GFP expressed is then measured by an enzyme-labeled instrument (Synergy 2 by BioTek Instruments) and normalized to unit cell concentrations (in terms of arbitrary units as represented by OD600 measured by the enzyme-labeled instrument).
As illustrated by figure 1, the activity of the GAP promoter remains largely unchanged relative to the carbon source in the media. The activity of the AOX1 promoter, however, is minimal in glycerol and glucose media, yet very significant in methanol media.
In wild type P. pastoris, alcohol oxidase allows the methylotrophic yeast to metabolize methanol. The regulation of the AOX1 promoter indicates high specificity in the expression of alcohol oxidase and therefore makes P. pastoris a very attractive candidate for regulated fermentation on an industrial scale, especially if the production of a certain chemical needs to be precisely controlled: the protein expressed by the AOX1 promoter can be relatively simply controlled by shifting the carbon source present in the media.
This experiment is published in Wang et al.,2016. Complete AOX1 promoter sequence: GATCTAACATCCAAAGACGAAAGGTTGAATGAAACCTTTTTGCCATCCGACATCCACAGGTCCATTCTCACACATAAGTG CCAAACGCAACAGGAGGGGATACACTAGCAGCAGACCGTTGCAAACGCAGGACCTCCACTCCTCTTCTCCTCAACACC CACTTTTGCCATCGAAAAACCAGCCCAGTTATTGGGCTTGATTGGAGCTCGCTCATTCCAATTCCTTCTATTAGGCTACTA ACACCATGACTTTATTAGCCTGTCTATCCTGGCCCCCCTGGCGAGGTTCATGTTTGTTTATTTCCGAATGCAACAAGCTCC GCATTACACCCGAACATCACTCCAGATGAGGGCTTTCTGAGTGTGGGGTCAAATAGTTTCATGTTCCCCAAATGGCCCAAA ACTGACAGTTTAAACGCTGTCTTGGAACCTAATATGACAAAAGCGTGATCTCATCCAAGATGAACTAAGTTTGGTTCGTTGA AATGCTAACGGCCAGTTGGTCAAAAAGAAACTTCCAAAAGTCGGCATACCGTTTGTCTTGTTTGGTATTGATTGACGAATGC TCAAAAATAATCTCATTAATGCTTAGCGCAGTCTCTCTATCGCTTCTGAACCCCGGTGCACCTGTGCCGAAACGCAAATGGG GAAACACCCGCTTTTTGGATGATTATGCATTGTCTCCACATTGTATGCTTCCAAGATTCTGGTGGGAATACTGCTGATAGCCT AACGTTCATGATCAAAATTTAACTGTTCTAACCCCTACTTGACAGCAATATATAAACAGAAGGAAGCTGCCCTGTCTTAAACC TTTTTTTTTATCATCATTATTAGCTTACTTTCATAATTGCGACTGGTTCCAATTGACAAGCTTTTGATTTTAACGACTTTTAACG ACAACTTGAGAAGATCAAAAAACAACTAATTATTCGAAACG
Reference
Wang, X., Wang, Q., Wang, J., Zhou, M., Shi, L., Zhou, X., … Shen, W. (2016). Mit1 Transcription Factor Mediates Methanol Signaling and Regulates the Alcohol Oxidase 1 ( AOX1 ) Promoter in Pichia pastoris. Journal of Biological Chemistry, 291(12), 6245–6261. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m115.692053
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1
Illegal BamHI site found at 938 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 1480