Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K2796028"
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K2796028 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K2796028 short</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | <ul> | |
<li>Considering that <b>TIL cells</b> can't secret enough exosomes under normal condition, we fuse three genes to increase the number of exosomes (Alenquer, 2015), thus increasing the transfer efficiency of exosomes.</li> | <li>Considering that <b>TIL cells</b> can't secret enough exosomes under normal condition, we fuse three genes to increase the number of exosomes (Alenquer, 2015), thus increasing the transfer efficiency of exosomes.</li> | ||
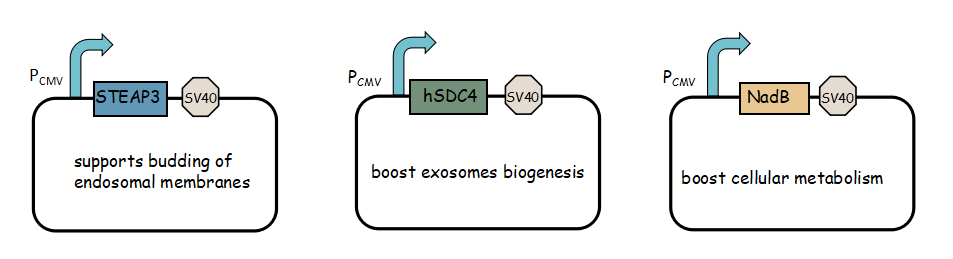
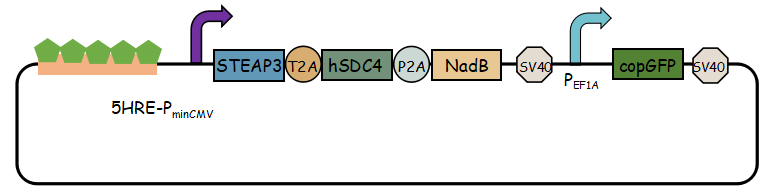
<li><b>Exosome booster</b> refers to hSDC4-T2A-STEAP3-P2A-NadB.We identified <b>STEAP3</b> (involved in exosomebiogenesis), syndecan-4(<b>SDC4</b>; supports budding of endosomal membranes to form multivesicular bodies), and a fragment of L-aspartate oxidase (<b>NadB</b>; possibly boosts cellular metabolism by tuning up the citric acid cycle) as potential synthetic exosome production boosters. Combined expression of these genes significantly increased exosome production.(Ryosuke Kojima et al. 2008)</li> | <li><b>Exosome booster</b> refers to hSDC4-T2A-STEAP3-P2A-NadB.We identified <b>STEAP3</b> (involved in exosomebiogenesis), syndecan-4(<b>SDC4</b>; supports budding of endosomal membranes to form multivesicular bodies), and a fragment of L-aspartate oxidase (<b>NadB</b>; possibly boosts cellular metabolism by tuning up the citric acid cycle) as potential synthetic exosome production boosters. Combined expression of these genes significantly increased exosome production.(Ryosuke Kojima et al. 2008)</li> | ||
| − | + | </ul> | |
[[File:T--LZU-CHINA--design1.png|600px|thumb|center|]] | [[File:T--LZU-CHINA--design1.png|600px|thumb|center|]] | ||
Revision as of 02:25, 16 October 2018
Exosome booster
- Considering that TIL cells can't secret enough exosomes under normal condition, we fuse three genes to increase the number of exosomes (Alenquer, 2015), thus increasing the transfer efficiency of exosomes.
- Exosome booster refers to hSDC4-T2A-STEAP3-P2A-NadB.We identified STEAP3 (involved in exosomebiogenesis), syndecan-4(SDC4; supports budding of endosomal membranes to form multivesicular bodies), and a fragment of L-aspartate oxidase (NadB; possibly boosts cellular metabolism by tuning up the citric acid cycle) as potential synthetic exosome production boosters. Combined expression of these genes significantly increased exosome production.(Ryosuke Kojima et al. 2008)
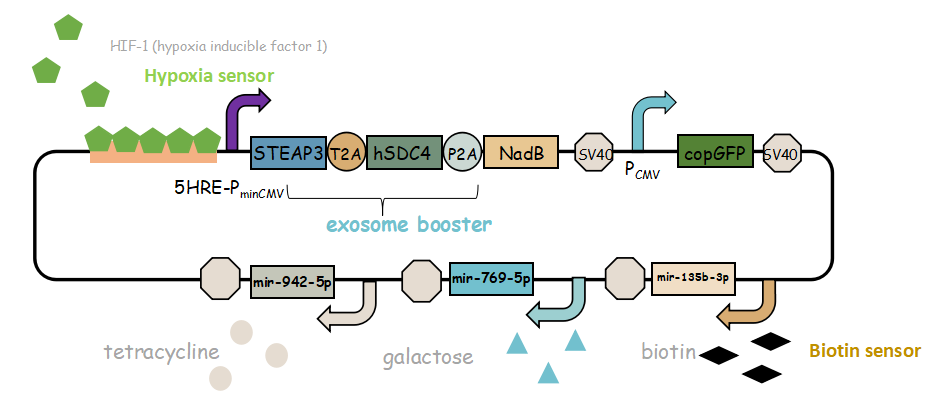
They combine with each other to boost exosomal transfer efficiency:
In previous article, it use IRES (internal ribosome entry site,IRES) to connect three genes, we change it into linkers T2A and P2A to ensure proper expression of three genes. Then we use use reporter gene copGFP to manifest the expression of exosome booster with the promoter of 5-HRE-PminCMV. Here is the final device that we designed for this project.
It combines with exosome booster and miR attacker under control of induced promoter.More details and description you can obtain in our wiki!
Sequence and Features
Assembly Compatibility:
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 192
Illegal BglII site found at 1777 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 2657
Illegal AgeI site found at 3277 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI site found at 1367