Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa C0079"
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ====I. Characterisation of RhlR by Imperial College London iGEM 2016 ==== | ||
| + | |||
| + | Group: <b>Imperial College London 2016</b> | ||
| + | |||
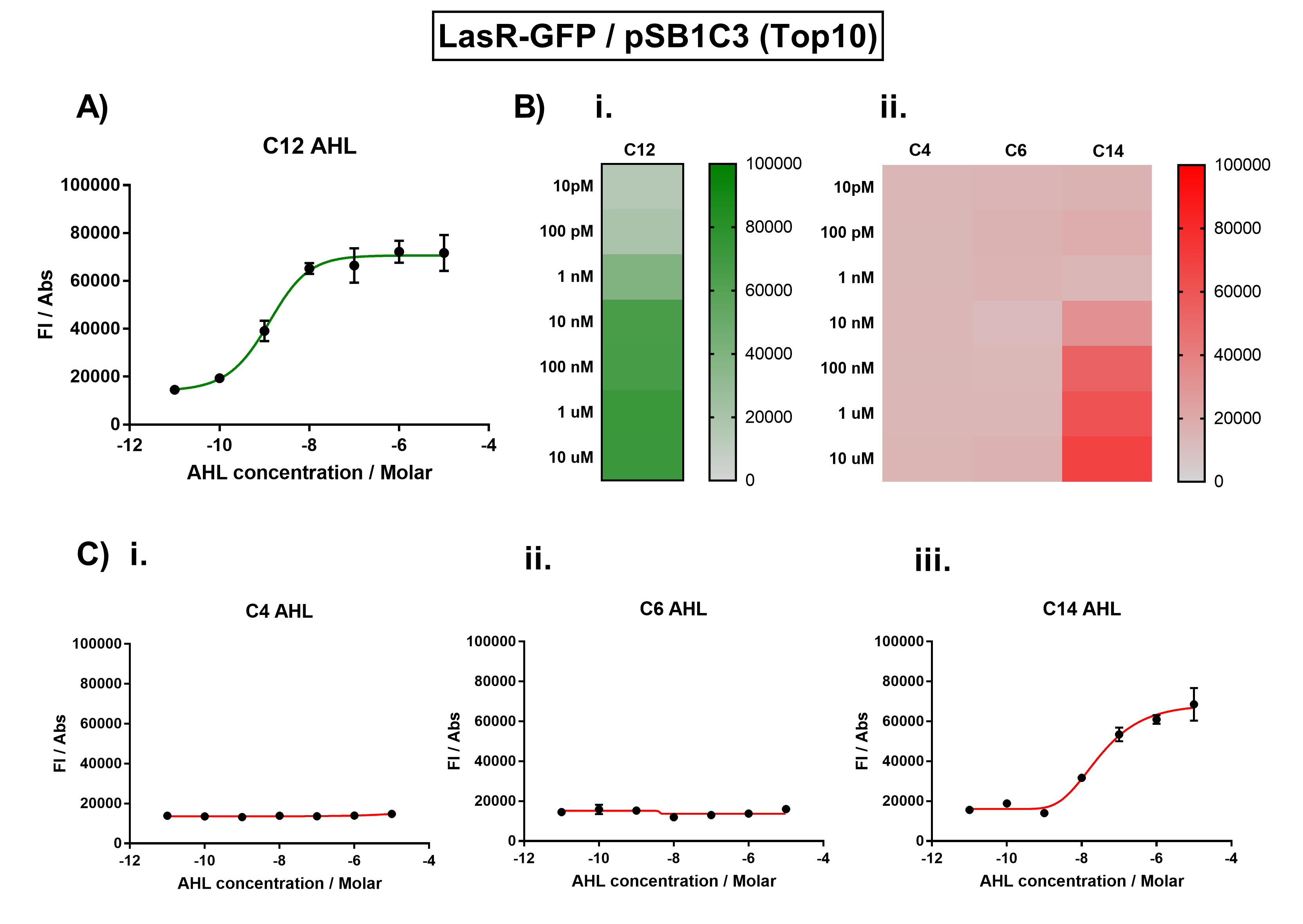
| + | We improved this part by characterising the crosstalk between LasR and non-cognate AHLs. We found the activation range of LasR when induced with C12-AHL. For the crosstalk experiments, we tested C4-AHL, C14-AHL, and C6-AHL. We placed the coding sequence downstream from the pLas promoter, and recorded the fluorescence for different concentrations of AHLs. | ||
| + | |||
| + | We found that there was no significant activation of LasR by the C4-AHL. | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:IC16_BBa_K1893001_characterisation.png|700px|center|]] | ||
| + | Figure 1. Characterisation of the Las response device (BBa_K1893001). (A) Transfer function curve of normalised fluorescence against cognate inducer C12-AHL (3O-C12 AHL) concentrations. (B) Heat map of normalised fluorescence of RhlR-GFP system over a range of AHL concentrations: (i) Binding of RhlR-GFP to its cognate AHL (C4 AHL). (ii) Binding of RhlR-GFP to 3 non-cognate AHLs (3O-C6 AHL, 3O-C12 AHL, 3OH-C14 AHL). (C) Transfer function curves of normalised fluorescence against non-cognate inducer AHL (3O-C12 AHL) concentrations to investigate inducer AHL crosstalk: (i) C4-AHL of the Rhl system (ii) C6-AHL (3O-C6 AHL) of the Lux system (iii) C14-AHL (3O-C14 AHL) of the Cin system. Experiments were performed in E. coli Top10 cell strain cultured at 37°C. Normalised fluorescence was calculated by dividing fluorescent signal by cell density (OD600). Fluorescence measurements were recorded at 180 minutes. Reported values represent the mean normalised fluorescence value from 3 technical repeats and error bars represent standard deviation of these. | ||
<span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | <span class='h3bb'>Sequence and Features</span> | ||
<partinfo>BBa_C0079 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_C0079 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
Revision as of 13:52, 23 October 2016
lasR activator from P. aeruginosa PAO1(+LVA)
coding region for lasR protein, which accepts chemical signal AI-1 (made by lasI protein)
I. Characterisation of RhlR by Imperial College London iGEM 2016
Group: Imperial College London 2016
We improved this part by characterising the crosstalk between LasR and non-cognate AHLs. We found the activation range of LasR when induced with C12-AHL. For the crosstalk experiments, we tested C4-AHL, C14-AHL, and C6-AHL. We placed the coding sequence downstream from the pLas promoter, and recorded the fluorescence for different concentrations of AHLs.
We found that there was no significant activation of LasR by the C4-AHL.
Figure 1. Characterisation of the Las response device (BBa_K1893001). (A) Transfer function curve of normalised fluorescence against cognate inducer C12-AHL (3O-C12 AHL) concentrations. (B) Heat map of normalised fluorescence of RhlR-GFP system over a range of AHL concentrations: (i) Binding of RhlR-GFP to its cognate AHL (C4 AHL). (ii) Binding of RhlR-GFP to 3 non-cognate AHLs (3O-C6 AHL, 3O-C12 AHL, 3OH-C14 AHL). (C) Transfer function curves of normalised fluorescence against non-cognate inducer AHL (3O-C12 AHL) concentrations to investigate inducer AHL crosstalk: (i) C4-AHL of the Rhl system (ii) C6-AHL (3O-C6 AHL) of the Lux system (iii) C14-AHL (3O-C14 AHL) of the Cin system. Experiments were performed in E. coli Top10 cell strain cultured at 37°C. Normalised fluorescence was calculated by dividing fluorescent signal by cell density (OD600). Fluorescence measurements were recorded at 180 minutes. Reported values represent the mean normalised fluorescence value from 3 technical repeats and error bars represent standard deviation of these. Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 322
Illegal AgeI site found at 519 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]