Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1991003"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
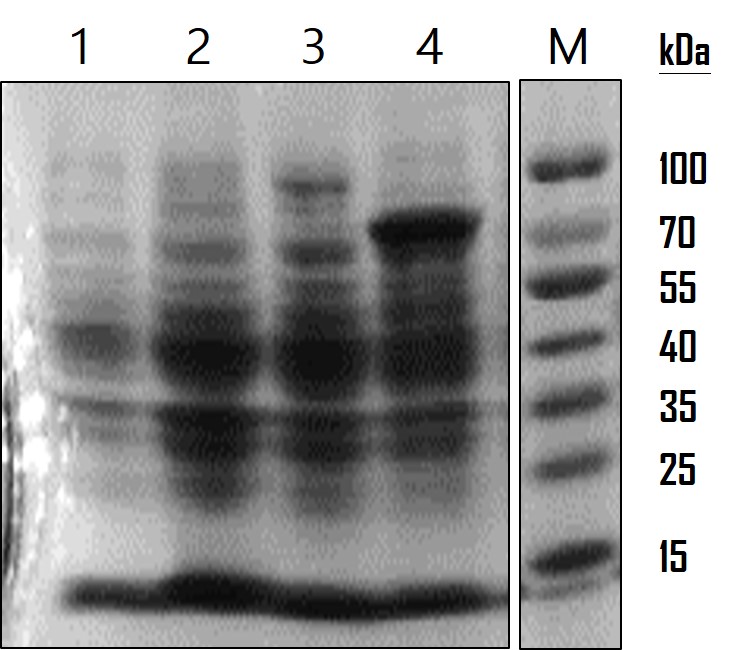
<p>To analyze the AOX gene expression, we run on a SDS-PAGE gel and observed by Coomassie Blue staining. The overnight-cultured E. coli were centrifuged and lysed with Lysis Buffer (12.5 mM Tris pH 6.8, 4% SDS). The resulting lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE with a 10% polyacrylamide gel. The gel was stained with 0.25% Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 for 2 hours and destained until the protein bands were clear. As the data showed in Figure 2, LO protein was expressed at around the estimated molecular weight of 17 kDa, LO-AOX fusion protein at 91 kDa and AOX protein at 79 kDa. The protein expression level was consistent with the data of GFP in Figure 1, demonstrating the low gene expression level of a LO fusion protein. However, so far we cannot confirm whether LO fusion protein is able to direct AOX or GFP proteins displayed on the cell surface of E. coli. We’re planning to do a subcellular fractionation to separate the outer membrane proteins for analysis in the future.</p> | <p>To analyze the AOX gene expression, we run on a SDS-PAGE gel and observed by Coomassie Blue staining. The overnight-cultured E. coli were centrifuged and lysed with Lysis Buffer (12.5 mM Tris pH 6.8, 4% SDS). The resulting lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE with a 10% polyacrylamide gel. The gel was stained with 0.25% Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 for 2 hours and destained until the protein bands were clear. As the data showed in Figure 2, LO protein was expressed at around the estimated molecular weight of 17 kDa, LO-AOX fusion protein at 91 kDa and AOX protein at 79 kDa. The protein expression level was consistent with the data of GFP in Figure 1, demonstrating the low gene expression level of a LO fusion protein. However, so far we cannot confirm whether LO fusion protein is able to direct AOX or GFP proteins displayed on the cell surface of E. coli. We’re planning to do a subcellular fractionation to separate the outer membrane proteins for analysis in the future.</p> | ||
<div class="propic5"> | <div class="propic5"> | ||
| − | [[File:2016Mingdao_Proof2.jpg| | + | [[File:2016Mingdao_Proof2.jpg|300px|thumb|left]] |
<p>[https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/5/55/T--Mingdao--Proof2.jpg Figure]: AOX protein analysis. SDS-PAG and Coomassie Blue staining were used to observe protein expression level. Lane 1: wild-type E. coli as a mock control; Lane 2: LO outer membrane protein ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1991007 BBa_K1991007]) (17 kDa) expression in E. coli; Lane 3: LO-AOX fusion protein ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1991009 BBa_K1991009]) (91 kDa) expression in E. coli.; Lane 4: AOX protein ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1991003 BBa_K1991003]) (79 kDa) expression in E. coli.</p> | <p>[https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2016/5/55/T--Mingdao--Proof2.jpg Figure]: AOX protein analysis. SDS-PAG and Coomassie Blue staining were used to observe protein expression level. Lane 1: wild-type E. coli as a mock control; Lane 2: LO outer membrane protein ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1991007 BBa_K1991007]) (17 kDa) expression in E. coli; Lane 3: LO-AOX fusion protein ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1991009 BBa_K1991009]) (91 kDa) expression in E. coli.; Lane 4: AOX protein ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1991003 BBa_K1991003]) (79 kDa) expression in E. coli.</p> | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 06:50, 20 October 2016
Pcons-RBS-AOX2
Alcohol oxidase (AOX) is an oxido-reductase that catalyzes the oxidation of alcohol and produce aldehyde and hydrogen peroxide (C2H5OH + O2 → CH3CHO + H2O2). There are two Alcohol Oxidase (AOX) genes, AOX1 (CAY72092.1) and AOX2 (CAY71377.1), on chromosome 4 in [http://bioinformatics.psb.ugent.be/genomes/view/Pichia-pastoris Pichia pastoris]. AOX was utilized to provide carbon source and energy for the methylotrophic yeast by metabolizing primary alcohol including methanol and some short-chain alcohols such as ethanol.
To analyze the AOX gene expression, we run on a SDS-PAGE gel and observed by Coomassie Blue staining. The overnight-cultured E. coli were centrifuged and lysed with Lysis Buffer (12.5 mM Tris pH 6.8, 4% SDS). The resulting lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE with a 10% polyacrylamide gel. The gel was stained with 0.25% Coomassie Brilliant Blue R250 for 2 hours and destained until the protein bands were clear. As the data showed in Figure 2, LO protein was expressed at around the estimated molecular weight of 17 kDa, LO-AOX fusion protein at 91 kDa and AOX protein at 79 kDa. The protein expression level was consistent with the data of GFP in Figure 1, demonstrating the low gene expression level of a LO fusion protein. However, so far we cannot confirm whether LO fusion protein is able to direct AOX or GFP proteins displayed on the cell surface of E. coli. We’re planning to do a subcellular fractionation to separate the outer membrane proteins for analysis in the future.
Figure: AOX protein analysis. SDS-PAG and Coomassie Blue staining were used to observe protein expression level. Lane 1: wild-type E. coli as a mock control; Lane 2: LO outer membrane protein (BBa_K1991007) (17 kDa) expression in E. coli; Lane 3: LO-AOX fusion protein (BBa_K1991009) (91 kDa) expression in E. coli.; Lane 4: AOX protein (BBa_K1991003) (79 kDa) expression in E. coli.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]