Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1856000"
Jinchentian (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1856000 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1856000 short</partinfo> | ||
| Line 17: | Line 16: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1856000 parameters</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1856000 parameters</partinfo> | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Description== | ||
| + | Members of the Anderson promoter collection are suitable for general protein expression in ''E. coli'' and likely other prokaryotes. The collection is known to cover a range of activities so by testing a few promoters it should be possible to find a promoter activity that suits your application. The promoters were recovered from a library screen by [https://andersonlab.qb3.berkeley.edu/ Chris Anderson]. | ||
| + | |||
| + | Parts J23100 through J23119 are a family of constitutive promoter parts isolated from a small combinatorial library. J23119 is the "consensus" promoter sequence and the strongest member of the family. The NheI and AvrII restriction sites present within these promoter parts make them a scaffold for further modification. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Characterization== | ||
| + | [[Image:BerkiGEM2006-PromotersEppendorfs.jpg|300px|right]] | ||
| + | ===Measured strengths=== | ||
| + | Reported activities of the promoters are given as the relative fluorescence of these plasmids in strain TG1 grown in LB media to saturation. See part [https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_J61002 J61002] for details on their use. | ||
| + | |||
| + | ==Obtaining the Anderson promoter collection== | ||
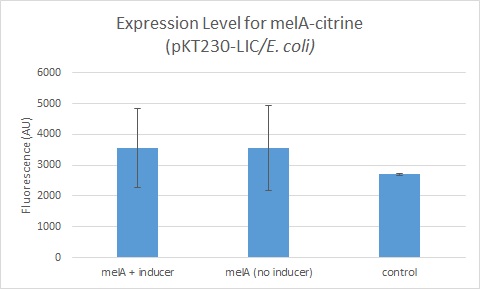
| + | [[Image:Expression_Level_for_melA-citrine_%28pKT230-Lic%29.jpg|right|150px|right]] | ||
| + | The sequences of the Anderson promoters can be found via the table below. To obtain the physical DNA, we recommend two approaches - <br> | ||
| + | '''Via ''de novo'' synthesis''': Since the promoters are short sequences, they can be easily and cheaply ordered as two single-stranded complementary oligo's and annealed. See [[Help:Promoters/Construction|here]] for a tutorial on how to construct short parts via oligo annealing. | ||
| + | |||
| + | '''Via the Registry distribution''': The promoters are included in the Registry distribution. All parts except <partinfo>J23119</partinfo> are present in plasmid <partinfo>J61002</partinfo>. This places the RFP downstream of the promoter. Part <partinfo>J23119</partinfo> is present in <partinfo>pSB1A2</partinfo>. | ||
| + | <br style="clear:both" /> | ||
Revision as of 21:18, 20 September 2015
bacA-citrine-T7 terminator
bacA promoter fused to citrine
Sequence and Features
- 10INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
Illegal NotI site found at 945 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
Illegal BamHI site found at 914
Illegal XhoI site found at 954 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal EcoRI site found at 920
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
Description
Members of the Anderson promoter collection are suitable for general protein expression in E. coli and likely other prokaryotes. The collection is known to cover a range of activities so by testing a few promoters it should be possible to find a promoter activity that suits your application. The promoters were recovered from a library screen by Chris Anderson.
Parts J23100 through J23119 are a family of constitutive promoter parts isolated from a small combinatorial library. J23119 is the "consensus" promoter sequence and the strongest member of the family. The NheI and AvrII restriction sites present within these promoter parts make them a scaffold for further modification.
Characterization
Measured strengths
Reported activities of the promoters are given as the relative fluorescence of these plasmids in strain TG1 grown in LB media to saturation. See part J61002 for details on their use.
Obtaining the Anderson promoter collection
The sequences of the Anderson promoters can be found via the table below. To obtain the physical DNA, we recommend two approaches -
Via de novo synthesis: Since the promoters are short sequences, they can be easily and cheaply ordered as two single-stranded complementary oligo's and annealed. See here for a tutorial on how to construct short parts via oligo annealing.
Via the Registry distribution: The promoters are included in the Registry distribution. All parts except BBa_J23119 are present in plasmid BBa_J61002. This places the RFP downstream of the promoter. Part BBa_J23119 is present in pSB1A2.