Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1688004"
Flindeberg (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
__NOTOC__ | __NOTOC__ | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1688004 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1688004 short</partinfo> | ||
| + | |||
| + | Composite part consisting of the RBS, BBa_B0034, and the red fluorescent protein, dTomato (BBa_K1688019). dTomato has not been bricked previously. | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K1688004 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1688004 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
Revision as of 17:56, 18 September 2015
dTomato (inc RBS)
Composite part consisting of the RBS, BBa_B0034, and the red fluorescent protein, dTomato (BBa_K1688019). dTomato has not been bricked previously.
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
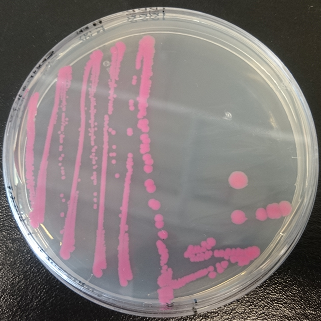
Figure 1. dTomato expressed in E. coli DH5-alpha with an inducible promoter.
Usage and Biology
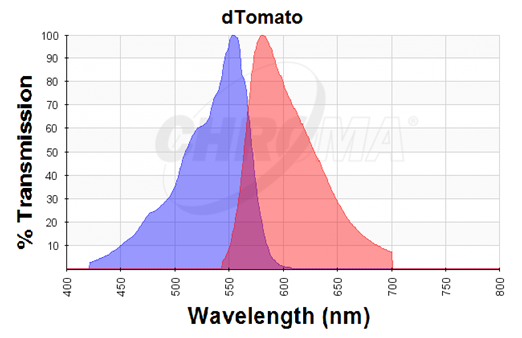
The dTomato protein is a fluorescent protein dimer, created by direct evolution of the wild-type DsRed, from Discosoma sp. (Shaner et al, - Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein, 2004). The dTomato protein is a fluorescent dimer protein that emits orange-red light when it is excited by green-yellow light. It is preferable to use – especially in self-made fluorometry tests – because the excitation wavelengths and the emission wavelengths don't overlap as much as in other fluorescent proteins. The dTomato excitation peak is at 554 nm and 50% of it is at 510 nm. Also, its emission peak is at 581 nm and its 50% emission at 629 nm (Figure 2).
Figure 2. Excitation (blue curve) and emission (red curve) spectra for the dTomato fluorescent protein (the graph is designed with the following tool: https://www.chroma.com/spectra-viewer)
References
Nathan C Shaner, Robert E Campbell, Paul A Steinbach, Ben N G Giepmans, Amy E Palmer & Roger Y Tsien. “Improved monomeric red, orange and yellow fluorescent proteins derived from Discosoma sp. red fluorescent protein”, 2004