Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1321094"
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
Note that the start and stop codon, plus 6 bp either side of the sequence, are included the RFC25 prefix and suffix which is not shown. | Note that the start and stop codon, plus 6 bp either side of the sequence, are included the RFC25 prefix and suffix which is not shown. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
===Usage and Biology=== | ===Usage and Biology=== | ||
| + | |||
| + | For reference, the cellulose binding domain binding capability of CBDclos (N-terminally fused) to bacterial cellulose was measured relative to other cellulose binding domains when fused to sfGFP, the data for which can be seen ([https://parts.igem.org/Part:BBa_K1321346 here]) - K1321346. | ||
<!-- --> | <!-- --> | ||
Latest revision as of 06:06, 2 November 2014
CBDclos fused to Phytochelatin (PC) EC20
Synthetic phytochelatin EC20 (metal binding peptide) fused C-terminally to CBDclos (a cellulose-binding domain).
This construct is part of a library of fusions with cellulose binding domains which we designed to bind to cellulose and enable capture of heavy metals ([http://2014.igem.org/Team:Imperial/Functionalisation project page]). Other fusion parts with this metal binding protein can be seen in the table below: 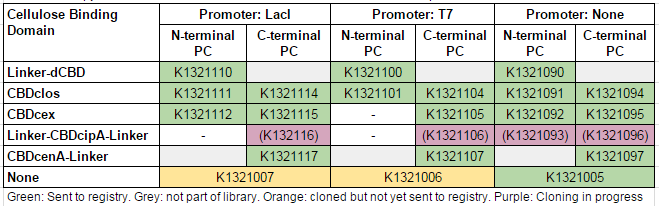
Note that the start and stop codon, plus 6 bp either side of the sequence, are included the RFC25 prefix and suffix which is not shown.
Usage and Biology
For reference, the cellulose binding domain binding capability of CBDclos (N-terminally fused) to bacterial cellulose was measured relative to other cellulose binding domains when fused to sfGFP, the data for which can be seen (here) - K1321346.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
