Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1554002"
(→Usage and Biology) |
(→Usage and Biology) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
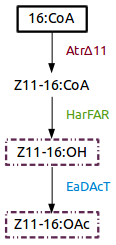
Figure 1. Insect sexual pheromone pathway for ''Nicotiana benthamiana''. | Figure 1. Insect sexual pheromone pathway for ''Nicotiana benthamiana''. | ||
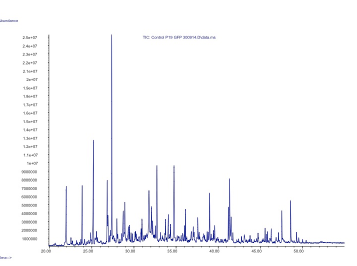
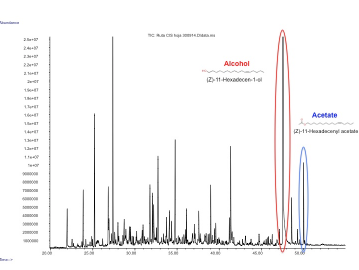
| − | In our project we made a device with these three pheromones and expressed them by transient expression it in our plant chasis, ''Nicotiana benthamiana''. In order to check if the insect sexual pheromones were present, we performed the analysis using HS-SPME coupled to GC-MS. We observed | + | In our project we made a device with these three pheromones and expressed them by transient expression it in our plant chasis, ''Nicotiana benthamiana''. In order to check if the insect sexual pheromones were present, we performed the analysis using HS-SPME coupled to GC-MS. We observed two additional peaks in the transformed plants that were not present in the control and had a similar mass spectrum and retention time as the standards, which confirmed that both molecules were the desired pheromones, (Z)-11-hexadecen-1-ol and (Z)-11-hexadecenyl acetate. |
[[File:UPV_rutas-biosintesis_feromonas.png]] | [[File:UPV_rutas-biosintesis_feromonas.png]] | ||
Revision as of 23:41, 15 October 2014
HarFAR
HarFAR-3 fatty acid reductase from Helicoverpa armigera with an ER retention signal (KKYR) attached to the C-terminal end. Codon optimization was perfomed for Nicotiana benthamiana.
Usage and Biology
The HarFAR protein is a fatty acid reductase coming from Helicoverpa armigera which transforms fatty acids into fatty alcohols.
Part:BBa_K1554001 (AtrΔ11), Part:BBa_K1554002 (HarFAR) and Part:BBa_K1554003 (EaDAcT) are enzymes of a biosynthesis pathway that lead to the production of insect sexual pheromones, Z11-16:OH and Z11-16:OAc, using palmitate as substrate.
Figure 1. Insect sexual pheromone pathway for Nicotiana benthamiana.
In our project we made a device with these three pheromones and expressed them by transient expression it in our plant chasis, Nicotiana benthamiana. In order to check if the insect sexual pheromones were present, we performed the analysis using HS-SPME coupled to GC-MS. We observed two additional peaks in the transformed plants that were not present in the control and had a similar mass spectrum and retention time as the standards, which confirmed that both molecules were the desired pheromones, (Z)-11-hexadecen-1-ol and (Z)-11-hexadecenyl acetate.
Figure 2. GC-MS analysis of the volatile organic compounds from a negative control of Nicotiana benthamiana.
Figure 3. GC-MS analysis of the volatile organic compounds from a genetically engineered Nicotiana benthamiana to produce insect pheromones.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 1104
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI site found at 929