Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K1399007"
m (→GFP (mut3b) with NYADAS-ssrA degradation tag) |
|||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | |||
<partinfo>BBa_K1399007 short</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K1399007 short</partinfo> | ||
GFP (mut3b) ([[Part:BBa_E0040]]) with added engineered NYADAS-ssrA degradation tag ([[Part:BBa_M0051]]). The tag increases GFP turn-over rate, thus providing better temporal resolution of green fluorescence. In the same time, maximal fluorescence amplitudes will be lower as newly formed protein is degraded as soon as it is formed. | GFP (mut3b) ([[Part:BBa_E0040]]) with added engineered NYADAS-ssrA degradation tag ([[Part:BBa_M0051]]). The tag increases GFP turn-over rate, thus providing better temporal resolution of green fluorescence. In the same time, maximal fluorescence amplitudes will be lower as newly formed protein is degraded as soon as it is formed. | ||
| − | SsrA tags encode peptide sequence that is recognized by ClpA and ClpX unfoldases and ClpX mediator SspB.[1] ClpA and ClpX then form a proteosome-like complex with ClpP protease and the protein is degraded.[1] The final three residues of the tag determines the strength of interaction with ClpX and thus the final protein degradation rate.[2] The NYADAS tag encodes peptide sequence AANDENYNYDAS is reported to have low affinity to ClpX thus its mediated degradation very much depends on the concentration of SspB (ClpX mediator).[1] The two additional residues ‘NY’ extends tag between SspB and ClpX binding sites, thus preventing clash when both proteins are bound to the tag.[3] However, be aware that exact protein degradation rate is influenced by multiple other factors: ClpXP and ClpAP protease concentrations, protein stability, Km of binding to the protease, temperature [4]. | + | SsrA tags encode peptide sequence that is recognized by ClpA and ClpX unfoldases and ClpX mediator SspB (Figure 1).[1] |
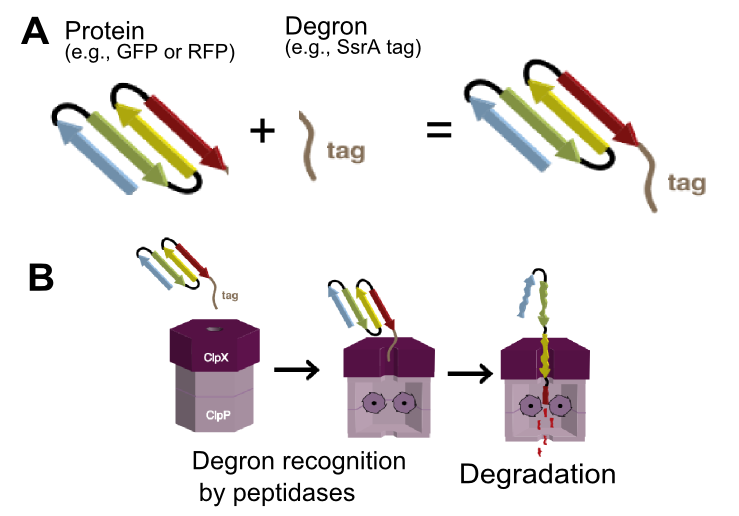
| + | [[File:EDiGEM14-SsrA degron mediated degradation.png|300px|thumb|right|'''Figure 1 SsrA degron mediated protein degradation.''' ('''A''') Any version of SsrA tags can be attached to any protein of interest (e.g. RFP or GFP). ('''B''') The tag is recognized by ClpX unfoldase forming a complex with ClpP protease and the tagged protein gets degraded.]] | ||
| + | ClpA and ClpX then form a proteosome-like complex with ClpP protease and the protein is degraded.[1] The final three residues of the tag determines the strength of interaction with ClpX and thus the final protein degradation rate.[2] The NYADAS tag encodes peptide sequence AANDENYNYDAS is reported to have low affinity to ClpX thus its mediated degradation very much depends on the concentration of SspB (ClpX mediator).[1] The two additional residues ‘NY’ extends tag between SspB and ClpX binding sites, thus preventing clash when both proteins are bound to the tag.[3] However, be aware that exact protein degradation rate is influenced by multiple other factors: ClpXP and ClpAP protease concentrations, protein stability, Km of binding to the protease, temperature [4]. | ||
===References=== | ===References=== | ||
[1] Flynn, J. M. et al. Overlapping recognition determinants within the ssrA degradation tag allow modulation of proteolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 10584–9 (2001). | [1] Flynn, J. M. et al. Overlapping recognition determinants within the ssrA degradation tag allow modulation of proteolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 10584–9 (2001). | ||
Revision as of 22:15, 15 October 2014
GFP (mut3b) with SsrA-DAS+2 degradation tag
GFP (mut3b) (Part:BBa_E0040) with added engineered NYADAS-ssrA degradation tag (Part:BBa_M0051). The tag increases GFP turn-over rate, thus providing better temporal resolution of green fluorescence. In the same time, maximal fluorescence amplitudes will be lower as newly formed protein is degraded as soon as it is formed.
SsrA tags encode peptide sequence that is recognized by ClpA and ClpX unfoldases and ClpX mediator SspB (Figure 1).[1]
ClpA and ClpX then form a proteosome-like complex with ClpP protease and the protein is degraded.[1] The final three residues of the tag determines the strength of interaction with ClpX and thus the final protein degradation rate.[2] The NYADAS tag encodes peptide sequence AANDENYNYDAS is reported to have low affinity to ClpX thus its mediated degradation very much depends on the concentration of SspB (ClpX mediator).[1] The two additional residues ‘NY’ extends tag between SspB and ClpX binding sites, thus preventing clash when both proteins are bound to the tag.[3] However, be aware that exact protein degradation rate is influenced by multiple other factors: ClpXP and ClpAP protease concentrations, protein stability, Km of binding to the protease, temperature [4].
References
[1] Flynn, J. M. et al. Overlapping recognition determinants within the ssrA degradation tag allow modulation of proteolysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 98, 10584–9 (2001). [2] Andersen, J. B. et al. New unstable variants of green fluorescent protein for studies of transient gene expression in bacteria. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 64, 2240–6 (1998). [3] McGinness, K. E., Baker, T. a & Sauer, R. T. Engineering controllable protein degradation. Mol. Cell 22, 701–7 (2006). [4] Purcell, O., Grierson, C. S., Bernardo, M. Di & Savery, N. J. Temperature dependence of ssrA-tag mediated protein degradation. J. Biol. Eng. 6, 10 (2012).
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 644