Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K801072"
Nadine1990 (Talk | contribs) (→References) |
Nadine1990 (Talk | contribs) (→References) |
||
| Line 54: | Line 54: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K801072 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K801072 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
| − | + | =References= | |
| + | ---- | ||
*[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18068204 Ashihara et al., 2008]] Ashihara, H., Sano, H., and Crozier, A. (2008). Caffeine and related purine alkaloids: biosynthesis, catabolism, function and genetic engineering. ''Phytochemistry'', 69(4):841–56. | *[[http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18068204 Ashihara et al., 2008]] Ashihara, H., Sano, H., and Crozier, A. (2008). Caffeine and related purine alkaloids: biosynthesis, catabolism, function and genetic engineering. ''Phytochemistry'', 69(4):841–56. | ||
Revision as of 12:46, 16 October 2012
3,7-dimethylxanthine N-methyltransferase CaDXMT1-strep
This part encodes for 3,7-dimethylxanthine N-methyltransferase CaDXMT1 from Coffea arabica followed by a strep-tag for purification and/or detection via western blot.
This part is based upon the mRNA sequences having been isolated out of coffea arabica by [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12746542/ Uefuji et al.], 2003, and registered at [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/nuccore/AB084125 NCBI]. The sequence was modified in several ways, to make it iGEM compatible and improve the usage in general, respectively.
This part is characterized in Saccharomyces cerevisiae by cloning it into a yeast shuttle vector (pTUM104) and 'the expression was proved successfully by SDS-PAGE and western blot analysis '.
Background and principle
Usage and Biology
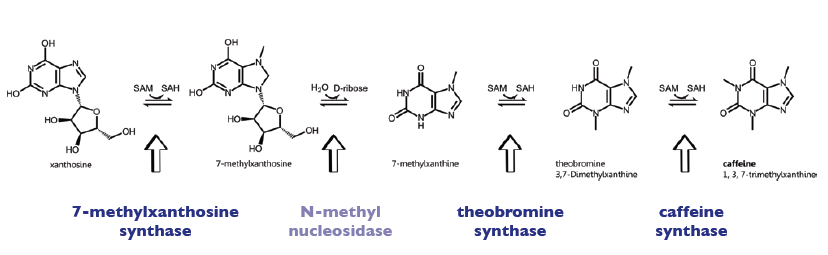
The enzyme CaDXMT1 (3,7-dimethylxanthine N-methyltransferase of coffea arabica) catalyses the fourth reaction step of the caffeine biosynthesis, leading to caffeine. Furthermore it exists as homodimer, being also able to form heterodimers with the other enzymes of the caffeine pathway (see [http://www.brenda-enzymes.info Brenda]).
Modifications
- the 5' UTR and 3' UTR of the original sequences were removed
- the yeast consensus sequence for improved ribosome binding (TACACA) was added 5' of the start codon ATG
- according to N- end rule and the yeast consensus sequence for improved ribosome binding, the first triplet after ATG (GAG) was exchanged with TCT (serine), to optimize both, protein stability and mRNA translation. This decision was made after proofing the 3D- structure of the enzyme CaDXMT1. Due to the fact, that the first two residues of the amino acid sequence are not shown in the crystalized structure (probably because of high flexibility), we chose to exchange this amino acid, because it is probably not necessary for the uptake of the ligands ([http://www.uniprot.org/uniprot/Q8H0D2 uniprot] entry further shows, that it is not immediately involved in ligand binding). Because of the high similarity of the enzyme sequences, we also exchanged this amino acid.
- we added a c- terminal strep-tag for purification and detection
- the remaining coding sequence was extended with the standard RFC10 prefix and suffix, respectively
- at last we made an optimization of the coding sequences with respect to the codon usage and mRNA structures
- remove of all critical restriction sites (RFC10 and RFC25)
Note: Because of the yeast consensus sequence, this coding part does not start with ATG!
Biosynthesis Pathway
Characterization
Cloning into pSB1C3
The cloning into pSB1C3 was proved by performing an analytical digest with XbaI and PstI.
Westernblot
Western blot of the crude extract of Saccharomyces cerevisiae INVSc1 transformed with pTUM104CaDXMT1 cultivated in selective expression Sc minimal medium lacking Uracil with 2% galactose as inducer. (from left to right: prestained protein ladder; CaDXMT1 (uninduced); CaDXMT1 (20h); unstained protein ladder (previously stained with ponceau's reagent))
Note: Because of probable posttranslational modifications in yeast, the apparent weight of the protein differs from the theoretical weight!
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BglII site found at 994
Illegal BglII site found at 1090 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]
References
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18068204 Ashihara et al., 2008 Ashihara, H., Sano, H., and Crozier, A. (2008). Caffeine and related purine alkaloids: biosynthesis, catabolism, function and genetic engineering. Phytochemistry, 69(4):841–56.
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/22849837 Franco et al., 2012 Franco, L., Sánchez, C., Bravo, R., Rodriguez, A., Barriga, C., and Juánez, J. C. (2012). The sedative effects of hops (humulus lupulus), a component of beer, on the activity/rest rhythm. Acta Physiol Hung, 99(2):133–9.
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/18036626 Kim and Sano, 2008 Kim, Y.-S. and Sano, H. (2008). Pathogen resistance of transgenic tobacco plants producing caffeine. Phytochemistry, 69(4):882–8.
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16925551 Kuranda et al., 2006 Kuranda, K., Leberre, V., Sokol, S., Palamarczyk, G., and François, J. (2006). Investigating the caffeine effects in the yeast Saccharomyces cerevisiae brings new insights into the connection between TOR, PKC and Ras/cAMP signalling pathways. Mol Microbiol, 61(5):1147–66.
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/12746542 Uefuji et al., 2003 Uefuji, H., Ogita, S., Yamaguchi, Y., Koizumi, N., and Sano, H. (2003). Molecular cloning and functional characterization of three distinct n-methyltransferases involved in the caffeine biosynthetic pathway in coffee plants. Plant Physiol, 132(1):372–80.
- http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/16247553 Uefuji et al., 2005 Uefuji, H., Tatsumi, Y., Morimoto, M., Kaothien-Nakayama, P., Ogita, S., and Sano, H. (2005). Caffeine production in tobacco plants by simultaneous expression of three coffee n-methyltrasferases and its potential as a pest repellant. Plant Mol Biol, 59(2):221–7.