Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K823026"
| Line 13: | Line 13: | ||
The transformation into ''B. subtilis'' is explained [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/4/41/LMU-Munich_2012_Transformation_of_Bacillus_subtilis.pdf here]. | The transformation into ''B. subtilis'' is explained [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/4/41/LMU-Munich_2012_Transformation_of_Bacillus_subtilis.pdf here]. | ||
| − | CAUTION: THIS VECTOR DOES NOT WORK AS EXPECTED! THE PROMOTER IS STRONG CONSTITUTIVE INSTEAD OF IPTG-INDUCIBLE! | + | <b>CAUTION: THIS VECTOR DOES NOT WORK AS EXPECTED! THE PROMOTER IS STRONG CONSTITUTIVE INSTEAD OF IPTG-INDUCIBLE!</b> |
| − | + | ||
<p align="justify"> | <p align="justify"> | ||
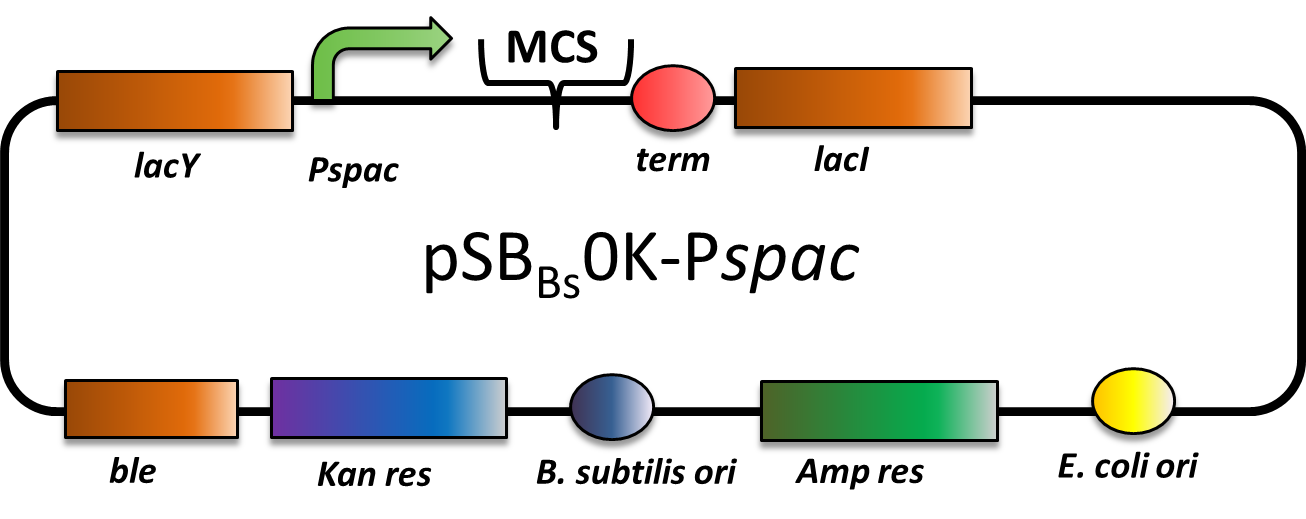
pSB<sub>''Bs''</sub>0K-P<sub><i>spac</i></sub> is a replicative expression vector with a kanamycin resistance. The IPTG (isopropylbeta-D-thiogalactopyranoside)-inducible Promoter P<sub>''spac''</sub> is followed by the multiple cloning site and a terminator. Also expressed are ''lac''Y, a transporter for IPTG (naturally allolactose), and ''lac'', the repressor. In presence of IPTG, LacI releases from the promoter and the gene of interest is expressed. | pSB<sub>''Bs''</sub>0K-P<sub><i>spac</i></sub> is a replicative expression vector with a kanamycin resistance. The IPTG (isopropylbeta-D-thiogalactopyranoside)-inducible Promoter P<sub>''spac''</sub> is followed by the multiple cloning site and a terminator. Also expressed are ''lac''Y, a transporter for IPTG (naturally allolactose), and ''lac'', the repressor. In presence of IPTG, LacI releases from the promoter and the gene of interest is expressed. | ||
Revision as of 08:48, 26 September 2012
pSBBs0K-Pspac (replicative Bacillus subtilis expression vector; IPTG inducible
This part is an expression vector for Bacillus subtilis. It is replicative both in E.coli and B.subtilis. It has an ampicillin resistance for cloning in E.coli and kanamycin resistance for selection in B. subtilis. The multiple cloning site is downstream of a Pspac promoter, that is inducible with IPTG (Isopropyl-β-D-thiogalactopyranosid).
This backbone is a BioBricked version of the B. subtilis overexpression vector pDG148. Reference: [http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/11728721 Joseph et al.]
For handling of B. subtilis vectors, please see here.
The transformation into B. subtilis is explained here.
CAUTION: THIS VECTOR DOES NOT WORK AS EXPECTED! THE PROMOTER IS STRONG CONSTITUTIVE INSTEAD OF IPTG-INDUCIBLE!
pSBBs0K-Pspac is a replicative expression vector with a kanamycin resistance. The IPTG (isopropylbeta-D-thiogalactopyranoside)-inducible Promoter Pspac is followed by the multiple cloning site and a terminator. Also expressed are lacY, a transporter for IPTG (naturally allolactose), and lac, the repressor. In presence of IPTG, LacI releases from the promoter and the gene of interest is expressed.
The ble gene encodes the bleomycin resisitance protein (BRP) which can be selected for by bleomycine or phleomycin in E. coli and B. subtilis. We did not use this resistance.
The presence of the vector can be checked for via colony PCR with the primers: CTACATCCAGAACAACCTCTGC and TTCGGAAGGAAATGATGACCTC. We did not perfom the colony PCR because we selected for functionality on plates with X-Gal and IPTG and we got blue colonies.
|
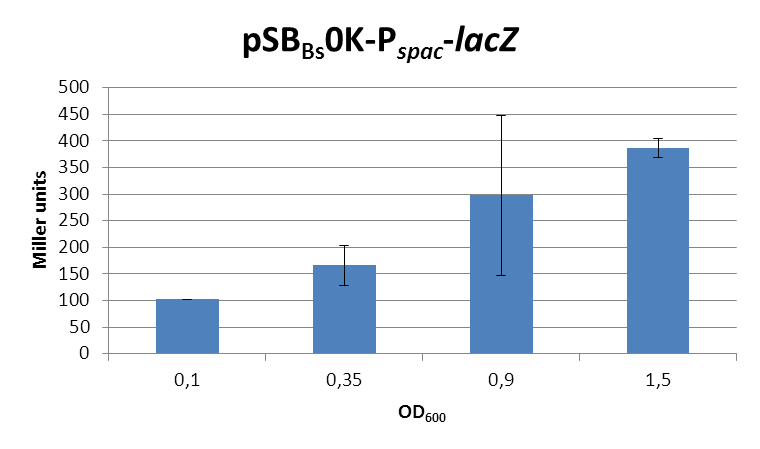
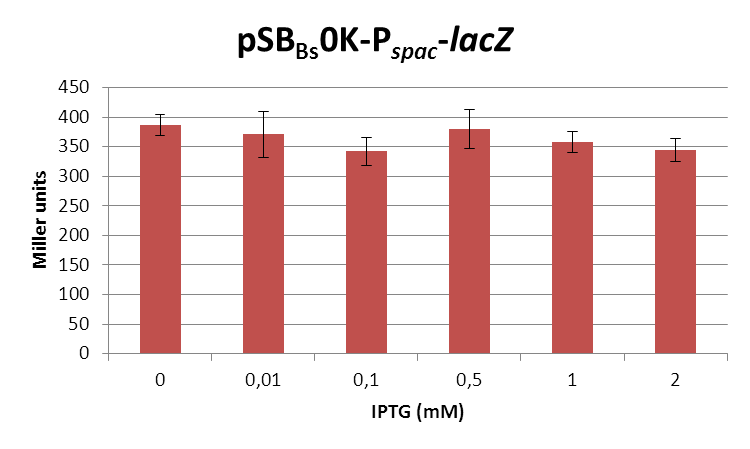
This expression vector was tested by insertion of lacZ into the multiple cloning site, transformation into W168 and ONPG assays. Overnight cultures were diluted 1:100 in LB-medium and incubated at 37°C, 230 rpm. Cells were harvested in 2 ml reaction tubes and frozen. For the induction assay, at an OD600 around 0.9 were split into 3 ml aliquots in test tubes with the given IPTG-concentrations and incubated for another hour. Data for splitting at OD600 around 0.3 is not shown, but similar.
|
In summary, the figures show that the expression is very strong, even without induction [in comparison to the native B. subtilis promoters] and does not change with IPTG addition. It does change depending on the growth phase, with a maximum strength in the stationary phase.
This vector was designed for overexpression of proteins, but is not inducible but constitutively active.
This BioBrick is part of the LMU 2012 igem project [http://2012.igem.org/Team:LMU-Munich/Bacillus_BioBricks BacillusBioBrickBox]
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 8268
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NotI site found at 9
Illegal NotI site found at 8274 - 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal EcoRI site found at 8268
Illegal BglII site found at 5862
Illegal BamHI site found at 1378 - 23INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]Illegal prefix found at 8268
Illegal suffix found at 2 - 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal prefix found at 8268
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal XbaI site found at 8283
Illegal SpeI site found at 2
Illegal PstI site found at 16
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 2925
Illegal AgeI site found at 5473
Illegal AgeI site found at 6435
Illegal AgeI site found at 7110 - 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Plasmid lacks a prefix.
Plasmid lacks a suffix.
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 2749
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 4188
Illegal BsaI.rc site found at 6704
Illegal SapI site found at 1666
Illegal SapI.rc site found at 5686