Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K777001"
(→Usage and Biology) |
(→Usage and Biology) |
||
| Line 16: | Line 16: | ||
* Here is the complete sequence of this part as an [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/f/fc/Tar_receptor_under_the_control_of_constitutive_promoter.zip ApE file]. | * Here is the complete sequence of this part as an [https://static.igem.org/mediawiki/2012/f/fc/Tar_receptor_under_the_control_of_constitutive_promoter.zip ApE file]. | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | [[Image:Tar Bindingsite01labled.png|thumb| | + | [[Image:Tar Bindingsite01labled.png|thumb|500px|left|'''Fig. 2:''' PYMOL images of Tar with aspartate in its binding pocket (PDB ID: 1WAT). The mutated amino acid residues involved in ligand binding are labeled.]] |
Here, we mutated this part at in total 5 amino acid sites which are important for ligand binding. The mutated sites are the nucleotides for the amino acids at position 69, 73, 149, 150 and 154. | Here, we mutated this part at in total 5 amino acid sites which are important for ligand binding. The mutated sites are the nucleotides for the amino acids at position 69, 73, 149, 150 and 154. | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | [[Image:Sequencing2.png|thumb|500px|left|'''Fig. 3:''' Sequencing chromatogram excerpt of the generated mutated chemoreceptor Tar_QC library in comparison to the original sequence Tar_QC. On the left, the sequencing chromatogram excerpt represents the original sequence, the right side shows the mutated sequence chromatogram. Sequencing results (top) with mutations for the amino acidsat position 149, 150 and 154 and (bottom) with mutations at 69 and 73. Inserted mutations are indicated by the triplets consisting of N and K, whereby K stands for guanine or thymine, N for any possible base. Only in the mutated regions no distinct peaks are present.G: guanine, C: cytosine, A: adenine, T: thymine.]] | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
The sequencing chromatogram of the generated chemoreceptor Tar_QC library revealed a functional mutagenesis. Randomly picked clones indicated a diversity of 2x 10<sup>5</sup> clones. | The sequencing chromatogram of the generated chemoreceptor Tar_QC library revealed a functional mutagenesis. Randomly picked clones indicated a diversity of 2x 10<sup>5</sup> clones. | ||
| − | + | <br> | |
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | <br> | ||
The constructed library was tested in a library selection experiment in which seven new chemical attractants were tested for chemotaxis of the novel generated receptors. | The constructed library was tested in a library selection experiment in which seven new chemical attractants were tested for chemotaxis of the novel generated receptors. | ||
As similar chemoreceptors were found to recognize the same respective chemicals, this is evidence for a functional part. | As similar chemoreceptors were found to recognize the same respective chemicals, this is evidence for a functional part. | ||
| Line 33: | Line 66: | ||
<partinfo>BBa_K777001 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | <partinfo>BBa_K777001 SequenceAndFeatures</partinfo> | ||
<br> | <br> | ||
| − | [[Image:K777001_in_pSB1C3.png|thumb|240px|frame|left|'''Fig. | + | [[Image:K777001_in_pSB1C3.png|thumb|240px|frame|left|'''Fig. 4:''' Plasmid map of K777001 in pSB1C3]] |
<!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | <!-- Uncomment this to enable Functional Parameter display | ||
Revision as of 20:42, 25 September 2012
Tar receptor under the control of constitutive promoter J23100
The transmembrane chemoreceptor Tar of E. coli mediates chemotaxis towards aspartate and exists as a functional homodimer.
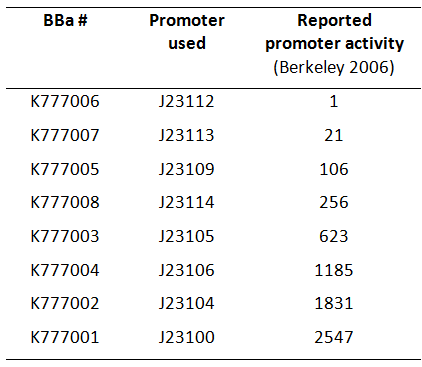
Here we used a set of 8 constitutive Anderson promoters from the 2006 Berkeley group to test how different levels of constitutive Tar expression affect the chemotaxis of E. coli.
Usage and Biology
This part can be used for chemotaxis assays.
- Here is the complete sequence of this part as an ApE file.
Here, we mutated this part at in total 5 amino acid sites which are important for ligand binding. The mutated sites are the nucleotides for the amino acids at position 69, 73, 149, 150 and 154.

The sequencing chromatogram of the generated chemoreceptor Tar_QC library revealed a functional mutagenesis. Randomly picked clones indicated a diversity of 2x 105 clones.
The constructed library was tested in a library selection experiment in which seven new chemical attractants were tested for chemotaxis of the novel generated receptors.
As similar chemoreceptors were found to recognize the same respective chemicals, this is evidence for a functional part.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]Illegal NheI site found at 7
Illegal NheI site found at 30 - 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal AgeI site found at 1323
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal SapI.rc site found at 152