Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K361000"
| Line 7: | Line 7: | ||
| − | [[Image: | + | [[Image:Mess_Recom.png]] |
Revision as of 21:49, 27 October 2010
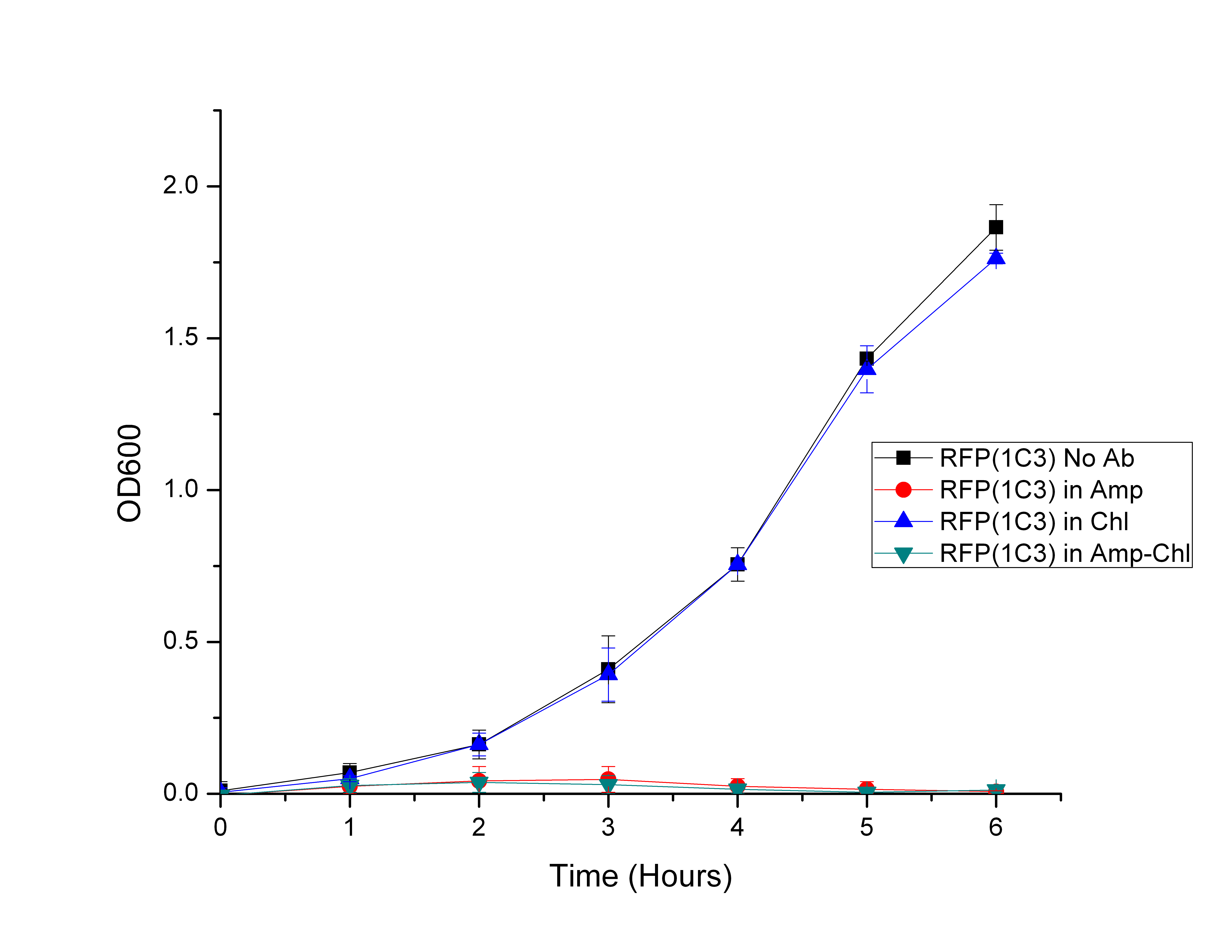
This part will prouce a 384-amino acid Rci site-specific recombinase used in shufflon system, which is a site-specific DNA recombination between two specific repeat sites as recognition.
After this recombinase is being expressed, it can alter the DNA sequence being inserted randomly with the specific repeat sites originally to become an unknown sequence.
This is a Wide type Rci recombinase.
- In the recombination activity study:
- Intramolecular inversion frequency = 0.062
- Intramolecular deletion frequency = 0 (recombinase inactive on this function)
- Intermolecular recombination = 0 (recombinase inactive on this function)
The inversion frequency is affected by the length of DNA sequence being flanked in vivo. Please refer to BBa_K361001
Usage and Biology
Usage:
- The Rci site-specific recombinase is used for the bacteria to adapt the change in environment by rearrange their gene pattern to create a new species of bacteria that has selective advantage in that changed environment for survival.
- The Rci site-specific recombinase is now exploited to randomly rearrange the DNA sequence carrying data. It allows data encryption to be possible.
Biology:
- In vitro study of conditions affecting recombination:
1. Additions of magnesium ion, EDTA, or ATP had little effect on recombination →Neither an energy source nor divalent cations are necessary. 2. The inversion was sensitive to KCl concentration →Maximal inversion activity at a KCl concentration of 80 mM. 3. The inversion reaction showed a broad pH optimum between 7.6 and 8.5. 4. The inversion reaction has a higher reaction activity at 42 oC as compared with that of 25 oC and 30 oC. 5. Negatively supercoiled DNA substrate was required for Rci protein. Little to zero recombination was observed in relaxed or linear DNA.
- In vitro study of recombination:
About 15-20 % inversion / recombination
- Reference:
Gyohda, A. & Komano, T. (2000). Purification and Characterization of the R64 Shufflon-Specific Recombinase. Journal of Bacteriology, 182 (10), 2787-2792.
Gyohda, A., Zhu, S., Furuya, N. & Komano, T. (2005). Asymmetry of Shufflon-specific Recombination Sites in Plasmid R65 Inhibits Recombination between Direct sfx Sequences. The Journal of Biological Chemistry, 281 (30), 20772-20779.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 362
Illegal NgoMIV site found at 857 - 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]