Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K4140008"
(→Usage) |
Ahmed Wael (Talk | contribs) (→Literature Characterization) |
||
| Line 11: | Line 11: | ||
alpha domain of ß-galactosidase (our reporter protein) which is produced in response to high levels of phenylalanine and generates a blue product when X-gal is cleaved which is a soluble colorless molecule that is a substrate of ß-galactosidase and generates a blue product when cleaved, is used to detect the alpha-complementation | alpha domain of ß-galactosidase (our reporter protein) which is produced in response to high levels of phenylalanine and generates a blue product when X-gal is cleaved which is a soluble colorless molecule that is a substrate of ß-galactosidase and generates a blue product when cleaved, is used to detect the alpha-complementation | ||
| − | == | + | ==Characterization of Mutational Landscape== |
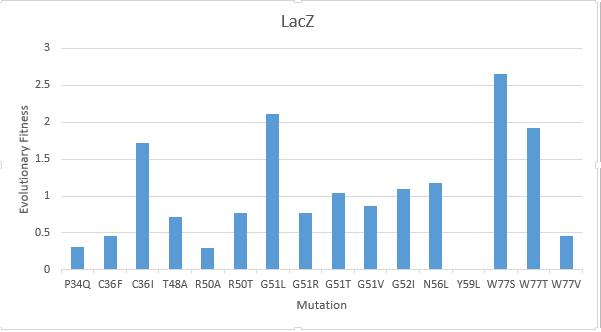
| − | + | After creating a multiple sequence alignment of the protein sequence and predicting mutational landscapes, the effect of these mutations on the evolutionary fitness of the protein is tested. The prediction of the mutational landscape by saturation mutagenesis of the LacZ protein. The (W77S ) mutation, as depicted in the chart, had the greatest score when compared to other mutations. On the other hand, it's clear that the (Y59L) had the least evolutionary fitness for LacZ protein. As displayed in Figure(1) | |
| − | + | ||
| + | [[File:Lacz.png|thumb|Right|Figure(1) shows the mutational landscape of the LacZ protein ]] | ||
| + | <br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br><br> | ||
==References== | ==References== | ||
Revision as of 07:58, 3 October 2022
lacZ alpha
Part Description
The LacZ-alpha fragment is encoded by this region and is derived from the pUC19 cloning vector. Because it is smaller than the LacZ-omega region, the LacZ-alpha fragment can be easily incorporated into a plasmid when the two non-functional LacZ gene fragments (alpha and omega) are co-expressed. X-gal (5-bromo-4-chloro-3-indoyl-d-galactopyranoside), a soluble colourless molecule that is a substrate of ß-galactosidase and generates a blue product when cleaved, is used to detect the alpha-complementation
Usage
alpha domain of ß-galactosidase (our reporter protein) which is produced in response to high levels of phenylalanine and generates a blue product when X-gal is cleaved which is a soluble colorless molecule that is a substrate of ß-galactosidase and generates a blue product when cleaved, is used to detect the alpha-complementation
Characterization of Mutational Landscape
After creating a multiple sequence alignment of the protein sequence and predicting mutational landscapes, the effect of these mutations on the evolutionary fitness of the protein is tested. The prediction of the mutational landscape by saturation mutagenesis of the LacZ protein. The (W77S ) mutation, as depicted in the chart, had the greatest score when compared to other mutations. On the other hand, it's clear that the (Y59L) had the least evolutionary fitness for LacZ protein. As displayed in Figure(1)
References
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]Illegal BamHI site found at 93
Illegal XhoI site found at 144 - 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]
- 1000COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]