Difference between revisions of "Part:BBa K3809010"
FCASTANEDA (Talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 9: | Line 9: | ||
To verify that ESR1 would fold correctly and there would be no steric obstacle, we simulated the protein with its corresponding additions using the tool Robetta (https://robetta.bakerlab.org/). When we recieved the model, we made an structural alignment using the natural protein as reference with a PDB code 2IOG (Protein Data Bank, rcsb.org). Therefore, we concluded that the addition of the Linker, His Tag and Signal Peptide were not interfering with the correct folding of ESR1. Furthermore, we proved that the His Tag and the linker were exposed, so we could use them for the purposed we established previously. | To verify that ESR1 would fold correctly and there would be no steric obstacle, we simulated the protein with its corresponding additions using the tool Robetta (https://robetta.bakerlab.org/). When we recieved the model, we made an structural alignment using the natural protein as reference with a PDB code 2IOG (Protein Data Bank, rcsb.org). Therefore, we concluded that the addition of the Linker, His Tag and Signal Peptide were not interfering with the correct folding of ESR1. Furthermore, we proved that the His Tag and the linker were exposed, so we could use them for the purposed we established previously. | ||
| − | <div class=WordSection1> | + | <div class=WordSection1> |
<p class=MsoNormal><b><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height: | <p class=MsoNormal><b><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height: | ||
107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; | 107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; | ||
| − | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US' | + | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'></span></b></p> |
<p class=MsoNormal><b><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height: | <p class=MsoNormal><b><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height: | ||
107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; | 107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; | ||
| − | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'> | + | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'>Characterization of BBa_K3809012</span></b></p> |
| − | + | ||
<p class=MsoNormal><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%; | <p class=MsoNormal><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%; | ||
font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; | font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; | ||
| − | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'> | + | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'>For the characterization of the protein |
| − | + | BBa_K380912 we transformed the plasmid in <i>E. coli</i> BL21. We then examined | |
| − | + | the growth of different colonies and performed a Colony PCR to determine if | |
| − | + | they had the insert or not. The result can be seen in Figure 1. And 2. <span | |
| − | + | class=SpellE>and</span> illustrates that only 6 out of 30 colonies we chose had | |
| − | + | the insert. </span></p> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'>< | + | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><b style='mso-bidi-font-weight: |
| − | style='font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;color: | + | normal'><span style='font-size:15.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; |
| − | + | color:#1155CC;mso-no-proof:yes'><img width=624 height=351 | |
| − | src="https://2021.igem.org/wiki/images/ | + | src="https://2021.igem.org/wiki/images/2/27/T--TecCEM--PartsRegister2image002.jpg" |
| − | alt="Imagen que contiene | + | alt="Imagen que contiene Tabla Descripción generada automáticamente" |
| − | v:shapes=" | + | v:shapes="Imagen_x0020_3"></span></b><span lang=EN-US |
| − | 10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family: | + | style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; |
| − | "Times New Roman";color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US' | + | mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman";color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'></span></p> |
<p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><b><span lang=EN-US | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><b><span lang=EN-US | ||
| Line 50: | Line 42: | ||
1.</span></b><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%; | 1.</span></b><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%; | ||
font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; | font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; | ||
| − | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'> | + | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'> Gel electrophoresis of the colony PCR we |
| − | + | performed for the transformed bacteria BL21 from 1 to 19. We selected only | |
| − | + | those colonies (marked in blue, M8, M13 and M18) that showed the insert at the | |
| − | + | size we expected (1948 bp).</span></p> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | ( | + | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'>< | + | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><b style='mso-bidi-font-weight: |
| − | style='font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;color: | + | normal'><span style='font-size:15.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; |
| − | src="https://2021.igem.org/wiki/images/ | + | color:#1155CC;mso-no-proof:yes'><img width=624 height=351 |
| − | alt="Imagen que contiene | + | src="https://2021.igem.org/wiki/images/a/aa/T--TecCEM--PartsRegister2image004.jpg" |
| − | v:shapes=" | + | alt="Imagen que contiene Tabla Descripción generada automáticamente" |
| − | 10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family: | + | v:shapes="Imagen_x0020_4"></span></b><span lang=EN-US |
| − | "Times New Roman";color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US' | + | style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; |
| + | mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman";color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'></span></p> | ||
<p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><b><span lang=EN-US | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><b><span lang=EN-US | ||
style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; | style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; | ||
| − | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'>Figure 2</span | + | mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman";color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'>Figure |
| − | + | 2.</span></b><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%; | |
| − | line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;color:black;mso-ansi-language: | + | font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; |
| − | EN-US'> | + | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'> Gel electrophoresis of the colony PCR we |
| − | + | performed for the transformed bacteria BL21 from 20 to 30. We selected only | |
| − | and | + | those colonies (marked in blue, M21, M23 and M26) that showed the insert at the |
| − | + | size we expected (1948 bp).</span></p> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<p class=MsoNormal><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%; | <p class=MsoNormal><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%; | ||
| − | font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US' | + | font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; |
| − | + | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'></span></p> | |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | <p class=MsoNormal | + | <p class=MsoNormal><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%; |
| − | style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif | + | font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; |
| − | + | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'>After that, we propagated the selected | |
| − | + | colonies on liquid LB+CAM medium and took samples of all the cultures at 1.5, | |
| − | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'> | + | 3, 4.5 and 48 hours after their inoculation. We ran an SDS-PAGE electrophoresis |
| − | + | expecting to see a protein of around 69.5 <span class=SpellE>kDa</span> | |
| + | (corresponding to the size of the protein receptor ESR1) but discovered that | ||
| + | only the colonies M18 and M23 had produced a visible protein at the expected site. | ||
| + | The best result corresponded to M23, which we describe below. </span></p> | ||
<p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><span | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><span | ||
| − | style='mso-no-proof:yes'><img width= | + | style='font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;color:black;mso-no-proof:yes'><img width=545 height=268 |
| − | src="https://2021.igem.org/wiki/images/ | + | src="https://2021.igem.org/wiki/images/f/fa/T--TecCEM--PartsRegister2image006.jpg" v:shapes="Imagen_x0020_5"></span><span |
| − | + | ||
lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; | lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; | ||
| − | mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman";color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US' | + | mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman";color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'></span></p> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
<p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><b><span lang=EN-US | <p class=MsoNormal align=center style='text-align:center'><b><span lang=EN-US | ||
style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; | style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; | ||
| − | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'>Figure 3</span></b><span lang=EN-US | + | mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman";color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'>Figure |
| − | style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%;font-family:"Arial",sans-serif; | + | 3. </span></b><span lang=EN-US style='font-size:10.0pt;line-height:107%; |
| − | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'> | + | font-family:"Arial",sans-serif;mso-fareast-font-family:"Times New Roman"; |
| − | + | color:black;mso-ansi-language:EN-US'>SDS-PAGE electrophoresis showing the apparition | |
| + | of a protein of around 70 <span class=SpellE>kDa</span> which corresponds to | ||
| + | ESR1.</span></p> | ||
| − | <p class=MsoNormal | + | <p class=MsoNormal><span lang=EN-US style='mso-ansi-language:EN-US;mso-no-proof: |
| − | style=' | + | yes'></span></p> |
| − | + | ||
| − | <p class=MsoNormal><span lang=EN-US style=' | + | <p class=MsoNormal><span lang=EN-US style='mso-ansi-language:EN-US'></span></p> |
| − | + | ||
| − | + | ||
</div> | </div> | ||
Revision as of 16:24, 21 October 2021
ESR1 with Linker, His Tag and Signal Peptide
This sequence codes for the Human Estrogen Receptor Alpha. It was modified in order to express the ligand binding domain and the DNA binding domain. The sequence also includes a 6X Histidine Tag (for its purification), a linker sequence of 4 glycines, 1 serine and 1 cistein (for its immobilization) and a signal peptide sequence (NPS4). This protein is a natural ocurring receptor found in human cells that acts as an enhacer protein which activates after its binding with its ligand. ESR1's natural ligand is Estradiol and after the molecule binds in its domain, it will undergo structural changes that activate the receptor by the formation of a dimer. It has been established that the most important aminoacids for the correct binding of estradiol and ESR1 are Gly521, His524, Leu525 and Met528.
For the purification of ESR1, we added a 6X His Tag and for the immobilization of the protein in a piezoelectric sensor, we added a linker which includes a sequence of 4 glycines, 1 serine and 1 cistein. The addition of the cistein is very important since the immobilization method we chose is based on the formation of a disulfide bond. Furthermore, we chose to mantain the DNA binding domain because it has a region rich in cisteins. Finally, we added a signal peptide sequence NPS4 (which comes from BBa_K3606042), in order to guarantee the secretion of our protein and make it easier for us to purify.
To verify that ESR1 would fold correctly and there would be no steric obstacle, we simulated the protein with its corresponding additions using the tool Robetta (https://robetta.bakerlab.org/). When we recieved the model, we made an structural alignment using the natural protein as reference with a PDB code 2IOG (Protein Data Bank, rcsb.org). Therefore, we concluded that the addition of the Linker, His Tag and Signal Peptide were not interfering with the correct folding of ESR1. Furthermore, we proved that the His Tag and the linker were exposed, so we could use them for the purposed we established previously.
Characterization of BBa_K3809012
For the characterization of the protein BBa_K380912 we transformed the plasmid in E. coli BL21. We then examined the growth of different colonies and performed a Colony PCR to determine if they had the insert or not. The result can be seen in Figure 1. And 2. and illustrates that only 6 out of 30 colonies we chose had the insert.
<img width=624 height=351
src="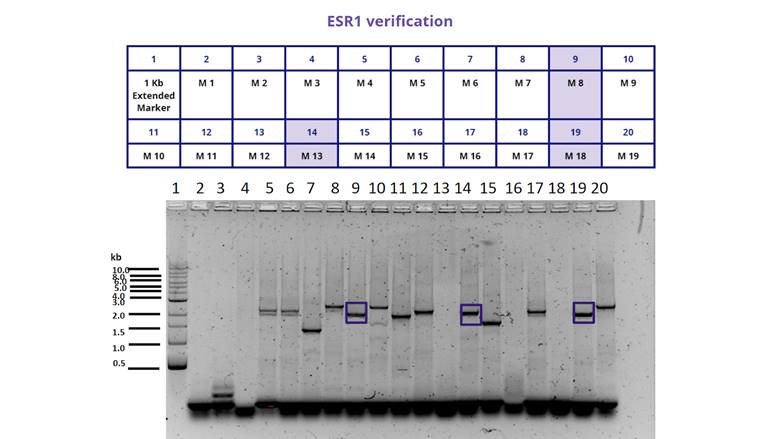 "
alt="Imagen que contiene Tabla
Descripción generada automáticamente"
v:shapes="Imagen_x0020_3">
"
alt="Imagen que contiene Tabla
Descripción generada automáticamente"
v:shapes="Imagen_x0020_3">
Figure 1. Gel electrophoresis of the colony PCR we performed for the transformed bacteria BL21 from 1 to 19. We selected only those colonies (marked in blue, M8, M13 and M18) that showed the insert at the size we expected (1948 bp).
<img width=624 height=351
src=" "
alt="Imagen que contiene Tabla
Descripción generada automáticamente"
v:shapes="Imagen_x0020_4">
"
alt="Imagen que contiene Tabla
Descripción generada automáticamente"
v:shapes="Imagen_x0020_4">
Figure 2. Gel electrophoresis of the colony PCR we performed for the transformed bacteria BL21 from 20 to 30. We selected only those colonies (marked in blue, M21, M23 and M26) that showed the insert at the size we expected (1948 bp).
After that, we propagated the selected colonies on liquid LB+CAM medium and took samples of all the cultures at 1.5, 3, 4.5 and 48 hours after their inoculation. We ran an SDS-PAGE electrophoresis expecting to see a protein of around 69.5 kDa (corresponding to the size of the protein receptor ESR1) but discovered that only the colonies M18 and M23 had produced a visible protein at the expected site. The best result corresponded to M23, which we describe below.
<img width=545 height=268
src=" " v:shapes="Imagen_x0020_5">
" v:shapes="Imagen_x0020_5">
Figure 3. SDS-PAGE electrophoresis showing the apparition of a protein of around 70 kDa which corresponds to ESR1.
Sequence and Features
- 10COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[10]
- 12COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[12]
- 21COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[21]
- 23COMPATIBLE WITH RFC[23]
- 25INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[25]Illegal NgoMIV site found at 48
- 1000INCOMPATIBLE WITH RFC[1000]Illegal BsaI site found at 1264
